Research for low shear rheological properties of low return velocity cementing drilling fluid in Kuqa Piedmont
-
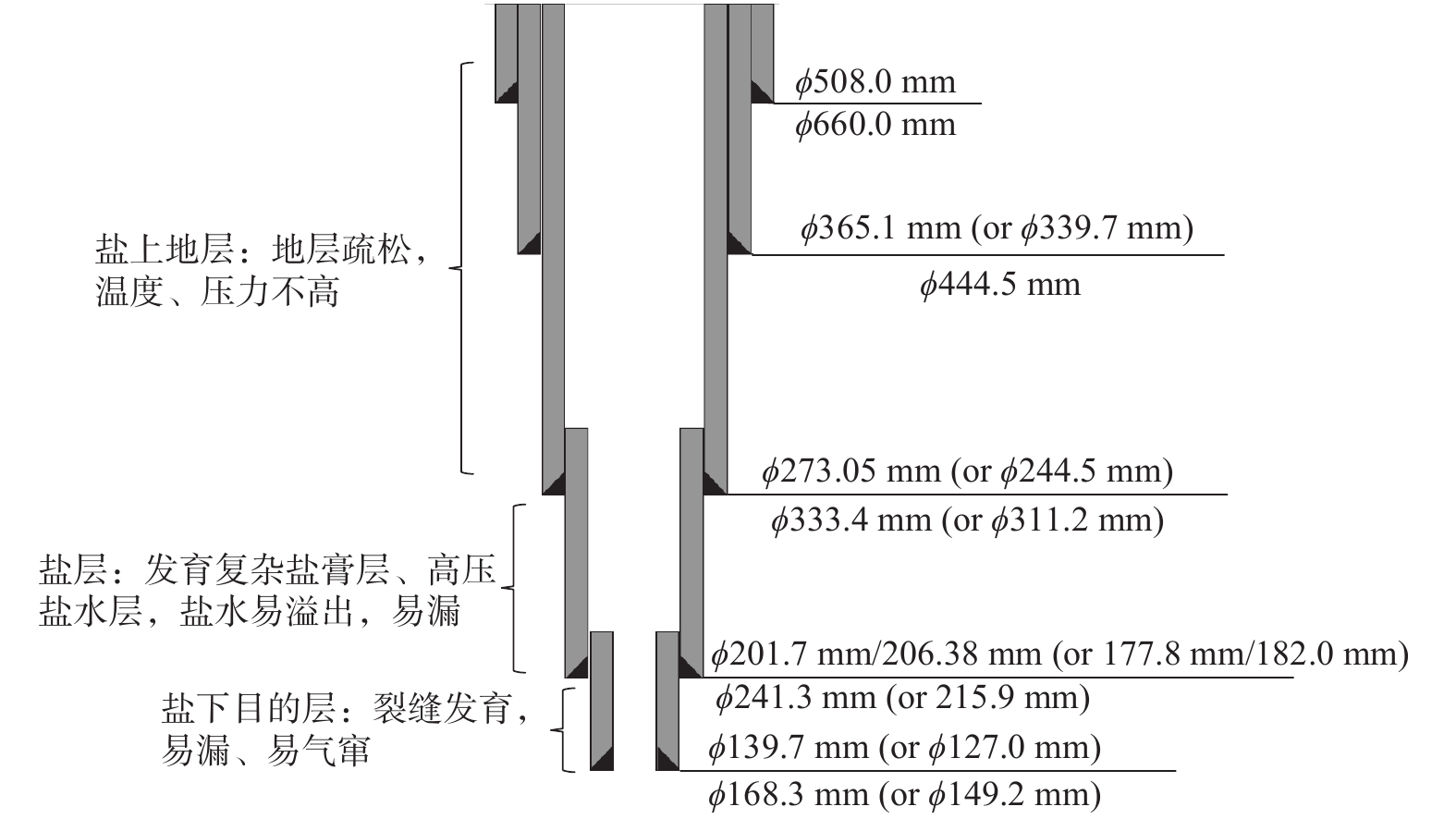
摘要: 针对塔里木库车山前超高压气井四开低返速固井过程中钻井液实际处于低剪切流动状态和现场采用全剪切速率流变测试数据拟合其流变模式和流变参数的不足,研究了库车山前钻井液在低返速固井过程中的低剪切速率范围、对应的流变模式和流变参数及其对注水泥环空流动摩阻系数的影响。研究结果表明,在低返速固井过程中,钻井液的剪切速率明显小于1022 s−1(600 r/min),且对应的流变模式及流变参数与全剪切速率范围内的差异巨大,导致基于二者的注水泥环空摩阻系数也存在较大的差异,从而影响对注水泥环空压力计算的精确控制。为此,对低返速固井,应根据其低剪切速率范围内的流变模式和流变参数计算环空流动压耗,控制固井排量,提高低返速防漏固井的成功率。Abstract: In view of the fact that the drilling fluid is in the low shear flow state during the fourth spud in ultra-high pressure gas well in Kuqa mountain front of Tarim Basin, the rheological model and rheological parameters of the drilling fluid were fitted by the rheological test data of the full shear rate. The low shear rate range, corresponding rheological mode and rheological parameters of the drilling fluid and its effect on the cementing annulus were studied The influence of flow friction coefficient. The results show that the shear rate of drilling fluid is obviously less than 1022 s−1 (600 r/min) in the process of cementing with low return velocity, and the corresponding rheological mode and rheological parameters are greatly different from the range of full shear rate, which leads to a certain or even large difference in the friction coefficient of cement injection annulus, which affects the accurate control of the calculation of cementing annulus pressure, For low return velocity cementing, the annular flow pressure loss should be calculated according to the rheological mode and rheological parameters within the low shear rate range, the cementing displacement should be controlled, and the success rate of low return velocity and leak proof cementing should be improved.
-
Key words:
- Low return rate cementing /
- Drilling fluid /
- Low shear rate range /
- Rheology
-
表 1 低返速固井排量数据
井号 ρ钻井液/
g·cm−3ρ隔离液/
g·cm−3ρ水泥浆/
g·cm−3排量/
L·s−1KS905 2.50 2.52 2.58 6 KS907 2.50 2.53 2.51 6 KS603 1.90 1.95 2 2 KS605 1.91 1.91 2.06 5 表 2 钻井液流变性基础数据
转速/
r/min剪切速
率/s−1剪切应力/Pa 30 ℃、
10 MPa60 ℃、
30 MPa90 ℃、
50 MPa120 ℃、
50 MPa150 ℃、
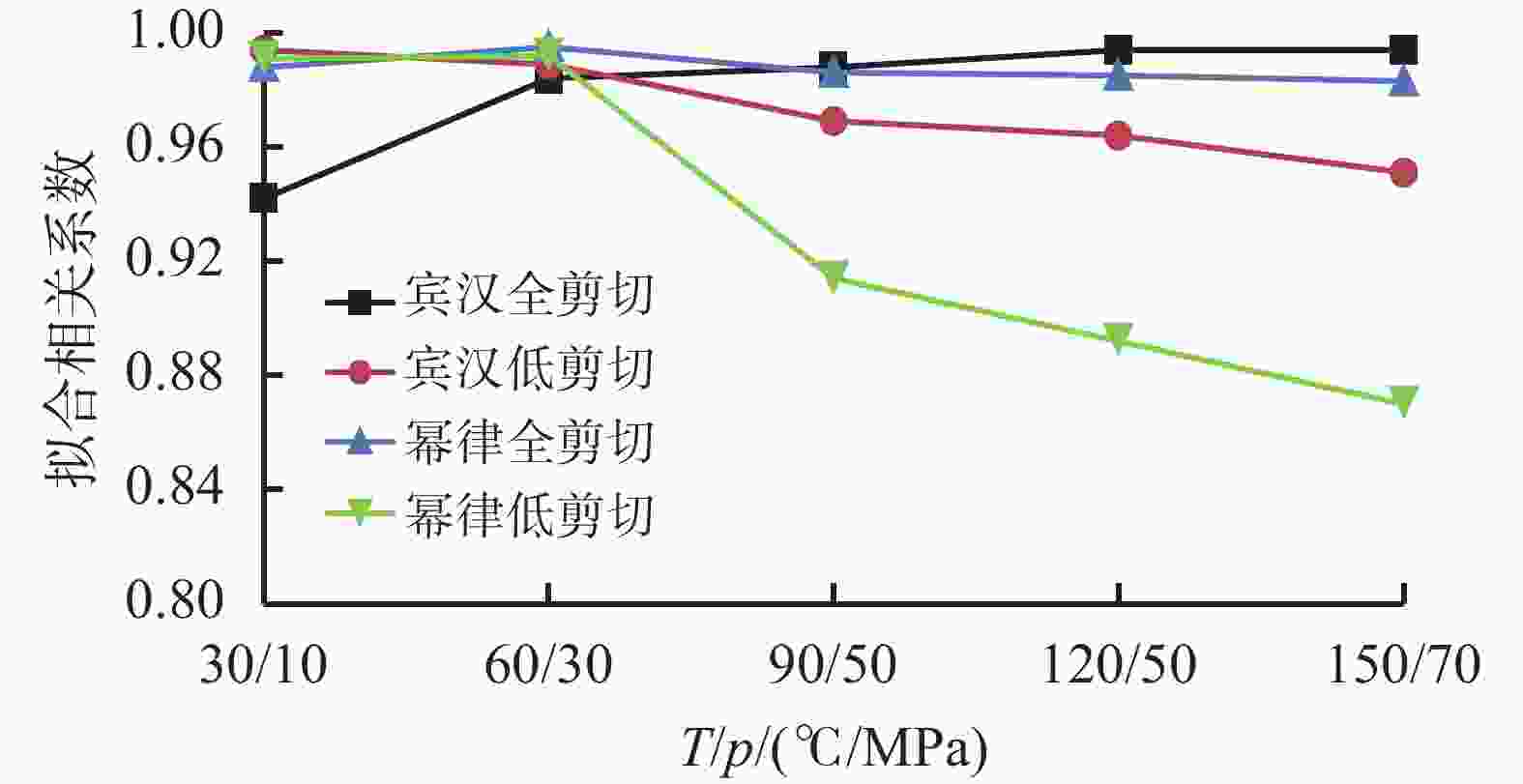
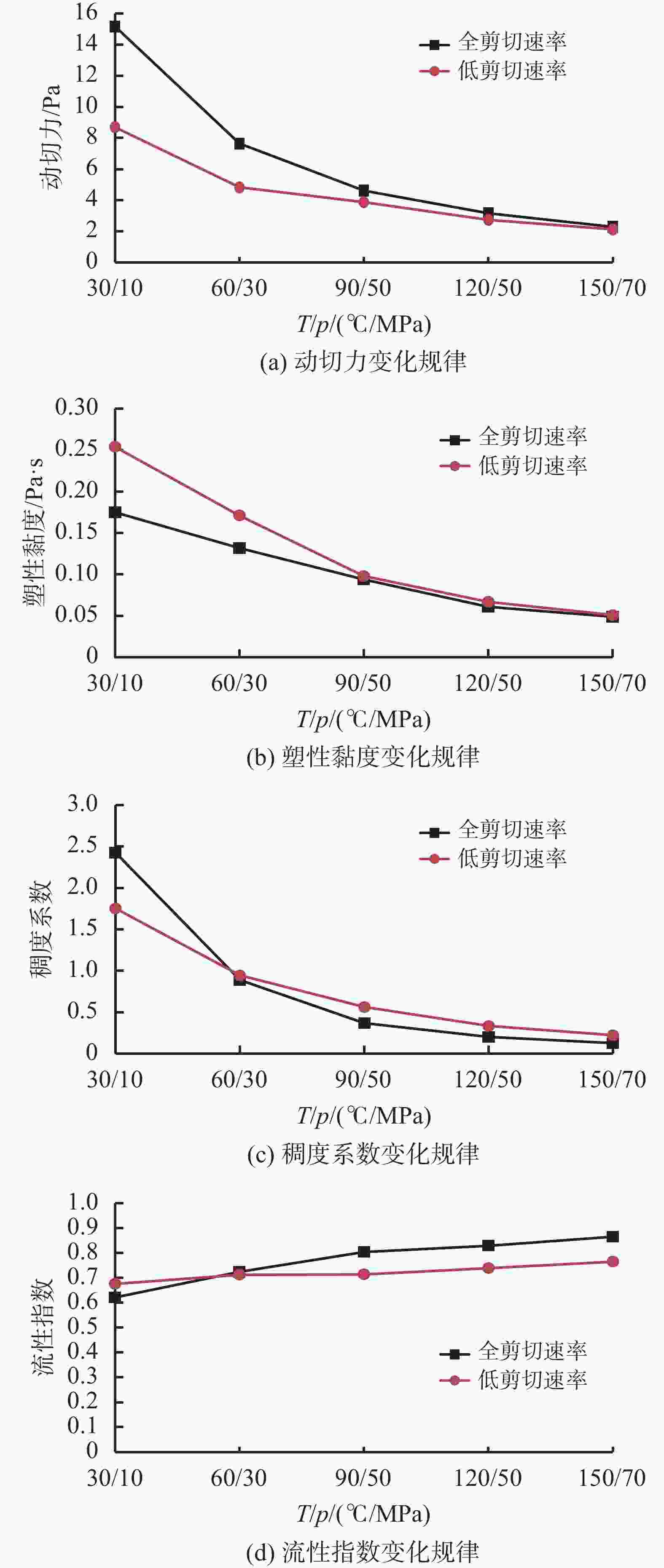
70 MPa600 1021.40 172.10 135.00 96.12 64.71 51.76 300 510.69 131.99 81.31 60.21 34.49 26.89 200 340.50 92.85 60.42 39.76 27.54 21.35 100 170.20 53.91 38.41 16.34 11.21 8.24 60 102.10 37.97 23.49 12.31 8.24 5.64 30 51.07 24.17 14.13 10.12 6.04 4.94 20 34.05 19.06 11.68 9.15 5.24 4.21 12 20.43 13.39 7.61 6.44 4.78 3.54 6 10.21 10.94 6.13 5.57 4.55 3.45 3 5.11 8.38 4.70 4.29 4.32 2.89 2 3.40 7.61 4.29 4.09 3.12 2.84 1 1.70 6.54 3.88 3.68 2.21 2.12 表 3 库车山前钻井液在全剪切速率范围下不同流变模式的流变参数
T/
℃p/
MPa流变
模式YP/
PaPV/
Pa·sR2 流变
模式K/
Pa·snn R2 30 10 宾汉 15.18 0.175 0.942 幂律 2.428 0.621 0.988 60 30 宾汉 7.642 0.1318 0.984 幂律 0.724 0.674 0.995 90 50 宾汉 4.618 0.094 0.988 幂律 0.370 0.804 0.986 120 50 宾汉 3.154 0.061 0.994 幂律 0.204 0.829 0.985 150 70 宾汉 2.285 0.049 0.994 幂律 0.128 0.865 0.983 表 4 钻井液在不同排量、温压和流变模式下的剪切速率
排量/
L·s−1井眼直
径/m套管直
径/m环空返速/
m·s−1宾汉模式 幂律模式 30 ℃/10 MPa下
钻井液的剪切
速率/s−1120 ℃/50 MPa下
钻井液的剪切
速率/s−130 ℃/10 MPa下
钻井液的剪切
速率/s−1120 ℃/50 MPa下
钻井液的剪切
速率/s−115 0.24 0.21 1.22 449.29 445.89 505.49 448.92 12 0.24 0.21 0.98 365.28 361.88 404.39 359.13 10 0.24 0.21 0.81 309.27 305.88 336.99 299.28 8 0.24 0.21 0.65 253.27 249.87 269.59 239.42 6 0.24 0.21 0.49 197.26 193.87 202.19 179.57 4 0.24 0.21 0.33 141.26 137.86 134.80 119.71 2 0.24 0.21 0.16 85.25 81.86 67.40 59.86 表 5 井深5321.55 m漏失地层承压能力计算结果
环空系列 环空尺寸/
mm段长/
mT/
℃PV/
Pa·sYP/
Pa排量/
L·s−1环空压耗/
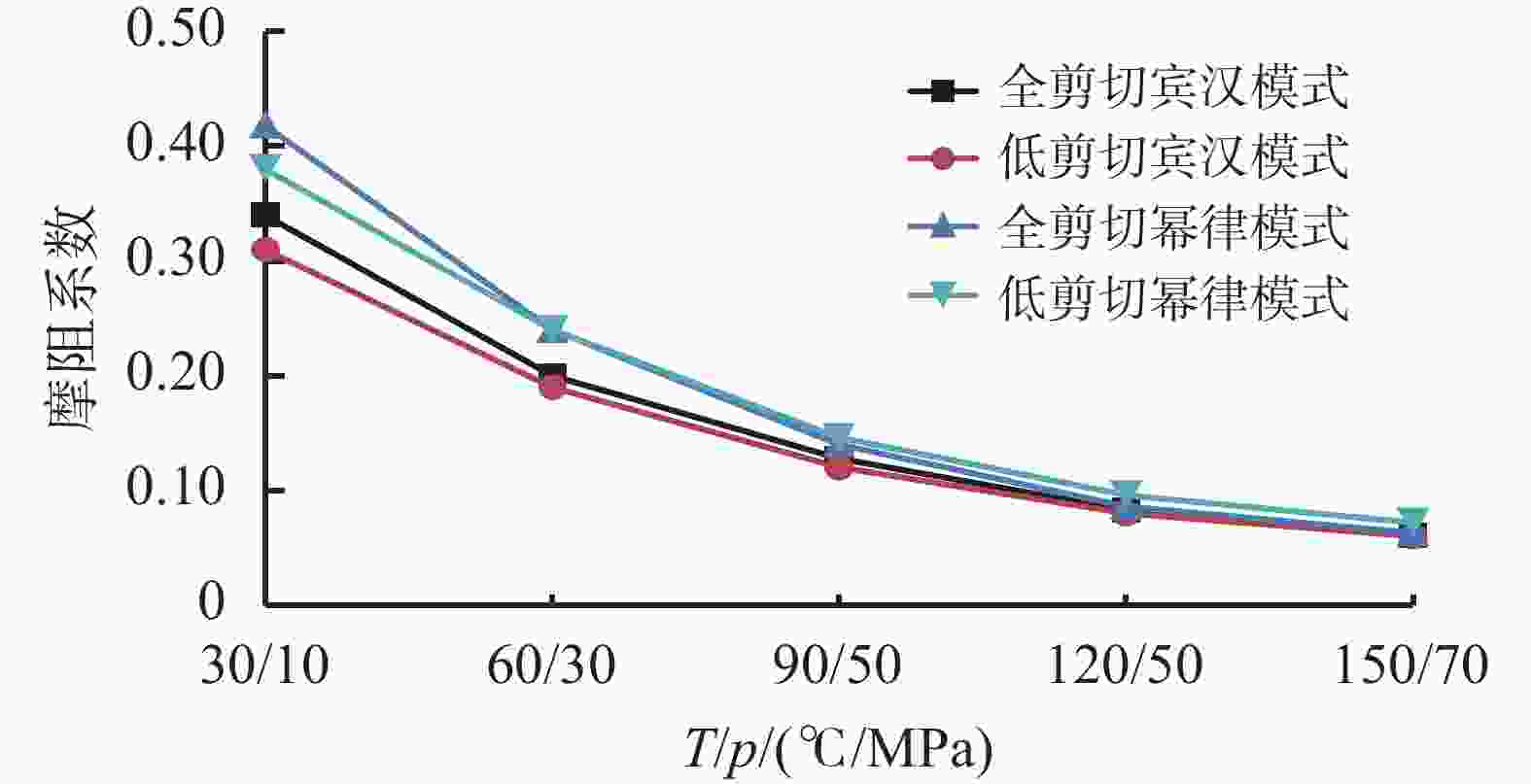
MPa钻-套 52.835 960.50 30 0.0621 1.139 00 26 0.266 钻-套 52.835 960.50 60 0.0419 0.879 98 26 0.233 钻-套 52.835 960.50 60 0.0419 0.879 98 26 0.233 钻-套 53.525 786.55 90 0.0280 0.632 07 26 0.157 钻-裸 53.525 786.70 90 0.0280 0.632 07 26 0.157 钻-裸 50.800 676.80 120 0.0210 0.548 06 26 0.145 钻-裸 31.750 190 120 0.0210 0.548 06 26 0.143 静液柱压力 99.609 MPa 合计 1.334 漏层压力 100.943 MPa ECD 1.9356 表 6 固井注替排量计算表
全剪切/低剪切速率下固井ECD计算 环空系列 流体类型 T/
℃PV/
Pa·sYP/
Pa环空尺寸/
mm段长/
m排量/
L·s−1环空压耗/
MPa钻-套 钻井液 30 0.062/0.051 1.14/1.12 52.835 708 5 0.049/0.037 钻-套 钻井液 60 0.042/0.037 0.88/0.76 52.835 708 5 0.028/0.016 钻-套 钻井液 60 0.042/0.037 0.88/0.76 52.835 708 5 0.028/0.016 钻-套 钻井液 90 0.028/0.027 0.63/0.58 52.835 708 5 0.011/0.004 钻-套 钻井液 90 0.028/0.027 0.63/0.58 53.525 711 5 0.011/0.007 环空系列 流体类型 T/
℃n K /
Pa·s n环空尺寸/
mm段长/
m排量/
L·s−1环空压耗/
MPa钻-套 隔离液 90 0.97/0.77 0.04/0.11 53.525 461 5 0.01/0.018 钻-套 水泥领浆 120 0.91/0.7 0.06/0.18 53.525 200 5 0.006/0.011 套-套 水泥领浆 120 0.91/0.7 0.06/0.18 24.95 221 5 0.051/0.068 套-裸 水泥尾浆 120 0.97/0.84 0.03/0.06 17.485 1178 5 0.55/0.585 静液柱压力 105.496 MPa 合计 0.744/0.762 注替压力 106.240 MPa ECD 1.9348/1.9351 -
[1] 李晓春,李坤,刘锐,等. 塔里木盆地超深天然气井全过程塞流防漏注水泥技术[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(10):102-109. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.013LI Xiaochun, LI Kun, LIU Rui, et al. Whole process plugging and leakage prevention cement injection technology for ultra deep gas wells in Tarim basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(10):102-109. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.013 [2] 滕学清,崔龙连,李宁,等. 库车山前超深井储层钻井提速技术研究与应用[J]. 石油机械,2017,45(12):1-6.TENG Xueqing, CUI Longlian, LI Ning, et al. Research and application of drilling speed increase technology for ultra deep reservoir in Kuqa mountain front[J]. Petroleum Machinery, 2017, 45(12):1-6. [3] 袁中涛,杨谋,艾正青,等. 库车山前固井质量风险评价研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2017,34(6):89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.06.017YUAN Zhongtao, YANG Mou, AI Zhengqing, et al. Study on risk assessment of cementing quality in Piedmont of Kuche[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2017, 34(6):89-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.06.017 [4] TENG X, YANG P, LI N, et al. Successful HPHT drilling through innovative practices: Sharing the subsalt HPHT well drilling case in Tarim basin[C]//SPE Middle East Oil & Gas Show and Conference, 2015. [5] Yan, Ye An, WenHua Wang, et al. Drilling fluid challenge during the ultra-deep HT/HP/HS drilling in the mountainous area, Tarim Basin[C]// Society of Petroleum Engineers-International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition in China 2010, IOGCEC, 2010, Vol. 3: 2057-2064. [6] 朱仁发, 喻可彬, 熊明勇. 库车山前钻井技术难点及技术对策——以大北208井为例[C]//2017年全国天然气学术年会, 2017.ZHU Renfa, YU Kebin, XIONG Mingyong. Technical difficulties and countermeasures of Kuqa piedmont drilling—Taking well Dabei 208 as an example [C]// 2017 national natural gas annual meeting, 2017. [7] 周健,贾红军,刘永旺,等. 库车山前超深超高压盐水层安全钻井技术探索[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2017,34(1):54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.010ZHOU Jian, JIA Hongjun, LIU Yongwang, et al. Safety drilling technology exploration of ultra deep and ultra-high pressure salt water layer in front of Kuqa mountain[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2017, 34(1):54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.010 [8] 周健,刘永旺,贾红军,等. 库车山前巨厚盐膏层提速技术探索与应用[J]. 钻采工艺,2017,40(1):21-24. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2017.01.06ZHOU Jian, LIU Yongwang, JIA Hongjun, et al. Exploration and application of speed increasing technology for thick salt gypsum layer in front of Kuqa mountain[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2017, 40(1):21-24. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2017.01.06 [9] 刘崇建, 黄柏宗, 徐同台, 等. 油气井注水泥理论与应用[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 526.LIU Chongjian, HUANG Baizong, XU Tongtai, et al. Theory and application of cementing in oil and gas wells [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 526 [10] 李邦和. 低返速固井技术及固井质量检测[J]. 中国海上油气(工程),1992,4(1):35-42.LI Banghe. Cementing technology and cementing quality inspection with low return velocity[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Engineering) , 1992, 4(1):35-42. [11] 丁士东. 塔河油田紊流、塞流复合顶替固井技术[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2002,24(1):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2002.01.007DING Shidong. Combined displacement cementing technology of turbulent flow and plug flow in Tahe Oil field[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2002, 24(1):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2002.01.007 [12] 李早元,杨绪华,郭小阳,等. 固井前钻井液地面调整及前置液紊流低返速顶替固井技术[J]. 天然气工业,2005,25(1):93-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.01.026LI Zaoyuan, YANG Xuhua, GUO Xiaoyang, et al. Surface adjustment of drilling fluid before cementing and low return velocity displacement cementing technology with pre fluid turbulent flow[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(1):93-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2005.01.026 [13] 张明深. 高温高压固井新概念和新技术在南海西部的应用[J]. 中国海上油气(工程),1999,11(6):31-37.ZHANG Mingshen. Application of new concept and new technique in cementing high temperature/ high pressure wells[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Engineering) , 1999, 11(6):31-37. [14] 管志川. 温度和压力对深水钻井油基钻井液液柱压力的影响[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),2003,27(4):48-52.GUAN Zhichuan. Effects of temperature and pressure on the pressure of oil-based drilling fluid in deep water drilling[J]. Journal of Petroleum University(Edition of Natural Science) , 2003, 27(4):48-52. [15] 李健,李早元,辜涛,等. 塔里木山前构造高密度油基钻井液固井技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2014,31(2):51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2014.02.014LI Jian, LI Zaoyuan, GU Tao, et al. Cementing technology of high density oil-based drilling fluid in Tarim Piedmont structure[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2014, 31(2):51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2014.02.014 [16] 张峰,刘子帅,李宁,等. 塔里木库车山前深井窄间隙小尾管固井技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(4):473-479.ZHANG Feng, LIU Zishuai, LI Ning, et al. Cementing small liner strings with narrow clearance in deep wells in the Kuche piedmont structure in Tarim basin[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(4):473-479. [17] 宋洵成,王根成,管志川,等. 小井眼环空循环压耗预测系统方法[J]. 石油钻探技术,2004,32(6):11-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2004.06.004SONG Xuncheng, WANG Gencheng, GUAN Zhichuan, et al. Prediction system method of annular circulation pressure loss in slim hole[J]. Petroleum Drilling Technology, 2004, 32(6):11-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2004.06.004 -




 下载:
下载: