Microscopic Behavior Analysis of Core Components of Water-based Drilling Fluid at High Temperature
-
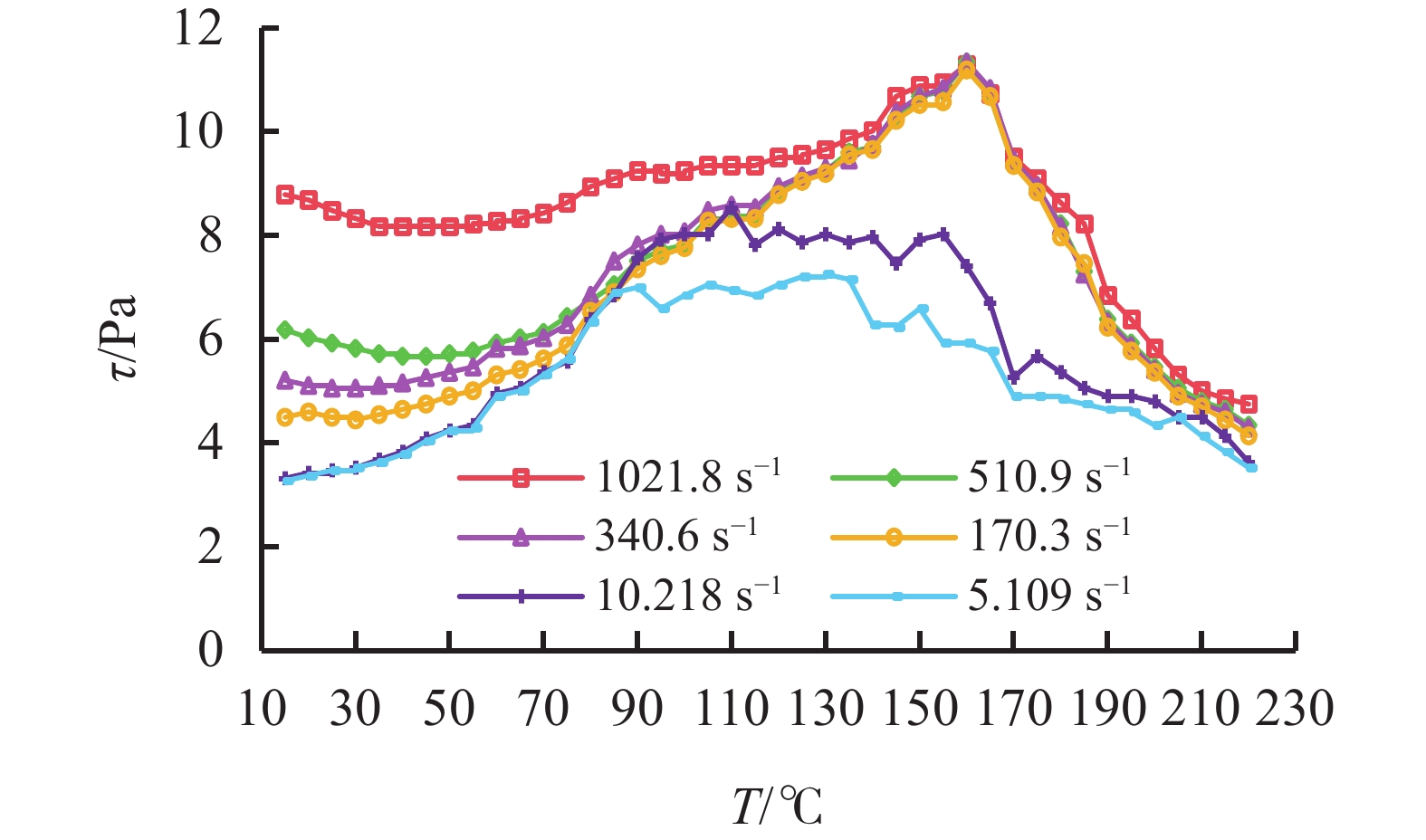
摘要: 水基钻井液在高温下性能调控难度大,主要与核心胶体粒子的分散状态有关,而水基钻井液成分复杂,单一组分与多组分间受高温作用性能变化规律不同,对胶体粒子的分散状态均有影响。针对水基钻井液核心组分,通过高温高压流变性测试获得了膨润土胶体剪切应力-温度曲线,并测试了不同温度下胶体颗粒粒度分布,分析了黏土矿物胶体粒子在室温~220 ℃范围内的分散、絮凝与聚结状态及形成机制,同时利用SEM测试和黏土矿物晶层结构分析,从微观角度揭示了富含镁多孔纤维状黏土矿物胶体的高温稳定机理,此外,基于对高温热滚前后流变性和滤失量等性能变化的分析,从黏土矿物结构特征和聚合物断链、吸附特性等角度揭示膨润土/复配黏土矿物与聚合物类处理剂在高温下的互相作用机理,结合实验结果,明确了低浓度膨润土与海泡石复配胶体具有明显的高温稳定优势,为超高温水基钻井液的构建提供了理论支撑。Abstract: The key to the stable performance of water-based drilling fluid at high temperature is related to the dispersion state of core colloidal particles, but the influence of the dispersion state of colloidal particles is very complicated. For the core components of water-based drilling fluid, the shear stress-strain temperature curve of bentonite colloid was obtained through high-temperature and high-pressure rheological testing, and the particle size distribution of colloidal particles was tested after different temperature effects. The dispersion, flocculation, and aggregation states and formation mechanisms of clay mineral colloidal particles were analyzed within the temperature range of room temperature to 220 ℃. In addition, the high temperature stability mechanism of porous fibrous clay mineral colloid rich in magnesium was revealed from a microscopic perspective by means of SEM test and clay mineral layer structure analysis. At the same time, based on a comprehensive analysis of the changes in rheological properties and filtration loss before and after high-temperature hot rolling, the interaction mechanism between bentonite/composite clay minerals and polymer based treatment agents at high temperatures is revealed from the perspectives of clay mineral structure characteristics, polymer chain breakage, adsorption characteristics, etc. Combined with experimental results, it is clear that low concentration bentonite/sepiolite composite colloids have significant high-temperature stability advantages, which provides theoretical support for the construction of ultra-high temperature water-based drilling fluid.
-
Key words:
- High temperature /
- Water-based drilling fluid /
- Micro-analysis /
- Clay colloid /
- Dispersed state
-
表 1 膨润土、海泡石和凹凸棒土晶体结构特征
造浆土 分子式 晶层结构 沸石状孔道 膨润土 Nax(H2O)4(OH)2
(AI2-xMg0.83)Si4O102∶1层硅铝酸盐 无 海泡石 (OH2)4[OH]4
Mg8[Si12030]·8H202∶1层状硅酸盐 3.8Å×9.8Å~
5.6Å×11.0Å凹凸棒土 (OH2)4(OH)2
Mg5Si8O20·4H2O2∶1层状硅酸盐 3.7Å×6.4Å -
[1] 苏义脑,路保平,刘岩生,等. 中国陆上深井超深井钻完井技术现状及攻关建议[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):527-542.SU Yinao, LU Baoping, LIU Yansheng, et al. Status and research suggestions on the drilling and completion technologies for onshore deep and ultra deep wells in China[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5):527-542. [2] 汪海阁,葛云华,石林. 深井超深井钻完井技术现状、挑战和“十三五”发展方向[J]. 天然气工业,2017,37(4):1-8. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.04.001WANG Haige, GE Yunhua, SHI Lin. Technologies in deep and ultra-deep well drilling: Present status, challenges and future trend in the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-2020)[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(4):1-8. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2017.04.001 [3] 张高波,李培海,乔汉,等. 控制水基钻井液高温高压滤失量的方法及途径[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(4):406-414,422. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.04.002ZHANG Gaobo, LI Peihai, QIAO Han, et al. Methods of controlling low HTHP filtration rate of water based drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(4):406-414,422. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.04.002 [4] 许洁,乌效鸣,王稳石,等. 松科2井抗超高温钻井液技术[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2018,35(2):29-34,39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.02.004XU Jie, WU Xiaoming, WANG Wenshi, et al. Ultra-high temperature drilling fluid technology of well Songke-2[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2018, 35(2):29-34,39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.02.004 [5] 李科,赵怀珍,李秀灵,等. 抗高温高性能水基钻井液及其在顺北801X井的应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(3):279-284. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.03.003LI Ke, ZHAO Huaizhen, LI Xiuling, et al. The development and application of high-temperature and high-performance water base drilling fluid on the well Shunbei 801x[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(3):279-284. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.03.003 [6] 鄢捷年. 钻井液工艺学[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社, 2001.YAN Jienian. Drilling fluid technology[M]. Dongying: Petroleum University Press, 2001. [7] 孟雪芬,冯辉霞,张斌,等. 海泡石的改性方法及其应用研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2020,49(9):2319-2323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.039MENG Xuefen, FENG Huixia, ZHANG Bin, et al. Progress in modification method and application of sepiolite[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(9):2319-2323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.039 [8] 张俊,王冰莹,曹建新. 改性凹凸棒土处理垃圾渗滤液中氨氮的实验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2012,31(4):861-864,875.ZHANG Jun, WANG Bingying, CAO Jianxin. Research on treatment of ammonia-nitrogen of landfill leachate by alter-attapuligite[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2012, 31(4):861-864,875. [9] AL-MALKI Needaa,POURAFSHARY Peyman,AL-HADRAMI Hamoud,等. 采用海泡石纳米颗粒控制膨润土基钻井液性能[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(4):656-661.AL-MALKI N, POURAFSHARY P, AL-HADRAMI H, et al. Controlling bentonite-based drilling mud properties using sepiolite nanoparticles[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4):656-661. -





 下载:
下载: