A Preliminary Method for Identifying Xanthan Gum and Welan Gum
-
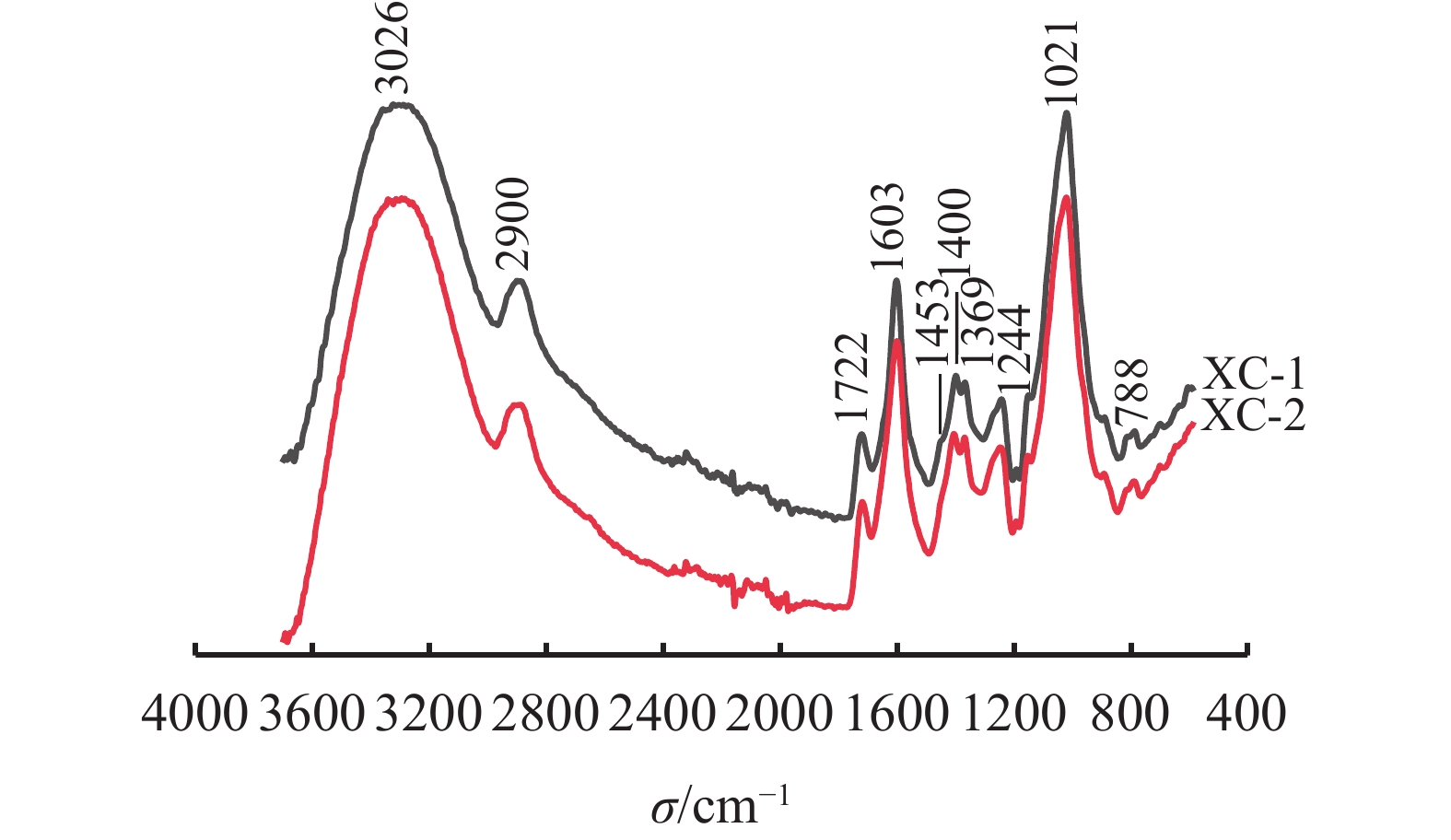
摘要: 温伦胶和黄原胶均属于阴离子生物多糖,具有假塑性流体特性和相似的外观。温伦胶性能优于黄原胶,但价格远高于黄原胶,规范市场应用和鉴别2种生物多糖就显得必要和重要。从红外光谱、黏温性及在固井水泥浆中应用3方面对2种生物胶进行对比。结果表明,2种生物胶的红外光谱极为相似,温伦胶分子结构所特有的鼠李糖环上甲基在(2978±2)cm−1附近产生特有吸收峰;在剪切速率为0.5 s−1、温度扫描为25 ~180 ℃、质量浓度均为0.4 %时,2种生物多糖的黏温曲线呈现截然相反的走势,黄原胶呈向下走势,温伦胶呈向上走势;在65 ℃下,水灰比为1.0的水泥浆中,0.4%同等掺量时,温伦胶可以获得稳定的水泥浆体而黄原胶则难获得。综合利用上述3方面差别,可对黄原胶与温伦胶进行初步鉴别。Abstract: Welan gum and xanthan gum are all anionic bio-saccharide, their water solutions all have pseudo-plastic fluid characteristics and similar appearance. Welan gum has properties that are superior to those of xanthan gum, and its price is much higher than that of xanthan gum, which render necessity and importance to regulate market application and identification of the two bio-saccharides. The characteristics of the two saccharides were compared by IR spectroscopy, viscosity change with temperature and their performance in cement slurries. The results of the experiments show that the two bio gums have generally similar IR spectra, a methyl group on the unique rhamnose ring of the welan gum molecular structure has a unique absorption peak around 2,978 ± 2 cm−1. At shear rate of 0.5 s−1, temperature between 25 ℃ and 180 ℃, and mass concentration of 0.4%, the viscosity – temperature curves of the two gums run against each other; the viscosity of xanthan gum decreases with temperature while the viscosity of welan gum increases with temperature. At 65 ℃, a cement slurry with water/cement ratio of 1.0 treated with 0.4% welan gum has stable properties, while the same cement slurry treated with 0.4% xanthan gum does not. Using these three differences shown by xanthan gum and welan gum together, preliminary identification of xanthan gum and welan gum can be made.
-
Key words:
- Infrared spectrum /
- Viscosity-temperature curve /
- Cement slurry /
- Xanthan gum /
- Welan gum /
- Identification
-
表 1 水泥浆体旋转黏度及静胶凝值
名称 冷浆(25 ℃) 热浆(65 ℃) φ300/φ3 Gel/(Pa/Pa) φ300/φ3 Gel/(Pa/Pa) XC-1 63/22 40/26 43/3 12/3 XC-2 68/23 42/29 48/7 12/4 WG-1 126/14 31/17 135/25 40/25 WG-2 145/24 39/26 143/30 48/31 表 2 水泥浆体稳定性及其稠化实验状况
名称 浆体稳定性 稠化实验状况 自由基
液BP实验密度/
(g·cm−3)(上/中/下)XC-1 有 1.44/1.48/1.53 曲线不正常,有“包芯” XC-2 有 1.41/1.45/1.55 曲线不正常,有“包芯” WG-1 无 1.49/1.50/1.51 正常 WG-2 无 1.50/1.50/1.50 正常 -
[1] 吉武科,赵双枝,严希海,等. 韦兰胶与黄原胶流变性比较研究[J]. 化学与生物工程,2011,28(10):50-56.JI Wuke, ZHAO Shuangzhi, YAN Xihai, et al. Comparative study on rheology of welan gum and xanthan gum[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2011, 28(10):50-56. [2] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会.GB 13886—2007.食品添加剂 黄原胶[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB 13886—2007. Food additive-xanthan gum[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007. [3] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部.QB/T 5545—2020.工业用温轮胶[S].北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2020.Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China. QB/T 5545—2020. Welan gum for industry[S]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2020. [4] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会.GB/T 5005—2010.钻井液材料规范[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 5005—2010. Specifications of drilling fluid materials[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2010. [5] 黄海东, 李晓雁, 潘奕臣, 等.一种用于鉴别三赞胶、结冷胶和温轮胶的分子标记的引物及分子标记和应用: CN201811206214.9[P].2019-01-11.HUANG Haidong, LI Xiaoyan, PAN Yichen, et al. A primer and molecular marker for identification of sanzan gum, gelan gum and welan gum: CN201811206214.9[P]. 2019-01-11. [6] XU L, XU G, LIU T, et al. The comparison of rheological properties of aqueous welan gum and xanthan gum solutions[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 92(1):516-522. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.082 [7] XU L, DONG M, GONG H, et al. Effects of inorganic cations on the rheology of aqueous welan, xanthan, gellan solutions and their mixtures[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 121:147-154. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.12.030 [8] 刘如林. 黄单胞胶中的丙酮酸与溶液性质[J]. 微生物学通报,1991,18(4):241-249.LIU Rulin. Pyruvic acid in xanthan gum and its solution properties[J]. Microbiology China, 1991, 18(4):241-249. [9] 李琪雯,周嫄,柯成竹,等. 微生物生产威兰胶的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,1991,40(4):337-342, 348.LI Qiwen, ZHOU Yuan, KE Chengzhu, et al. Reseach progress in microbial production of welan gum[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 1991, 40(4):337-342, 348. [10] NAVARRETE R C, SHAH S N. New biopolymer for coiled tubing applications[C]//SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing Roundtable. Houston, Texas: SPE, 2001: SPE-68487-MS. [11] NAVARRETE R C, SEHEULT J M, COFFEY M D. New biopolymers for drilling, drill-in, completions, spacer, and coil-tubing fluids, part II[C]//SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry. Houston, Texas: SPE, 2001: SPE-64982-MS. [12] NAVARRETE R C, SEHEULT J M, COFFEY M D. New bio-polymers for drilling, drill-in, completions, spacer fluids and coiled tubing applications[C]//IADC/SPE Asia Pacific Drilling Technology. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: SPE, 2000: SPE-62790-MS. [13] 石磊,韩龙,刘超. 多糖的构象研究方法综述[J]. 曲阜师范大学学报(自然科学版),2012,38(3):78-84,112.SHI Lei, HAN Long, LIU Chao. Methodogy of study on conformation of polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Qufu Normal University, 2012, 38(3):78-84,112. [14] HOWARD S, KAMINSKI L, DOWNS J. Xanthan stability in formate brines-formulating non-damaging fluids for high temperature applications[C]//SPE European Formation Damage Conference and Exhibition. Budapest, Hungary: SPE, 2015: SPE-174228-MS. [15] SARKAR A, & PéREZ, S. PolySac3DB: an annotated data base of 3 dimensional structures of polysaccharides[J]. BMC bioinformatics, 2012, 13(1):302. -





 下载:
下载: