Using RSM to Determine Electric Gel Breaking Conditions for Waste High Density Water Based Drilling Fluids
-
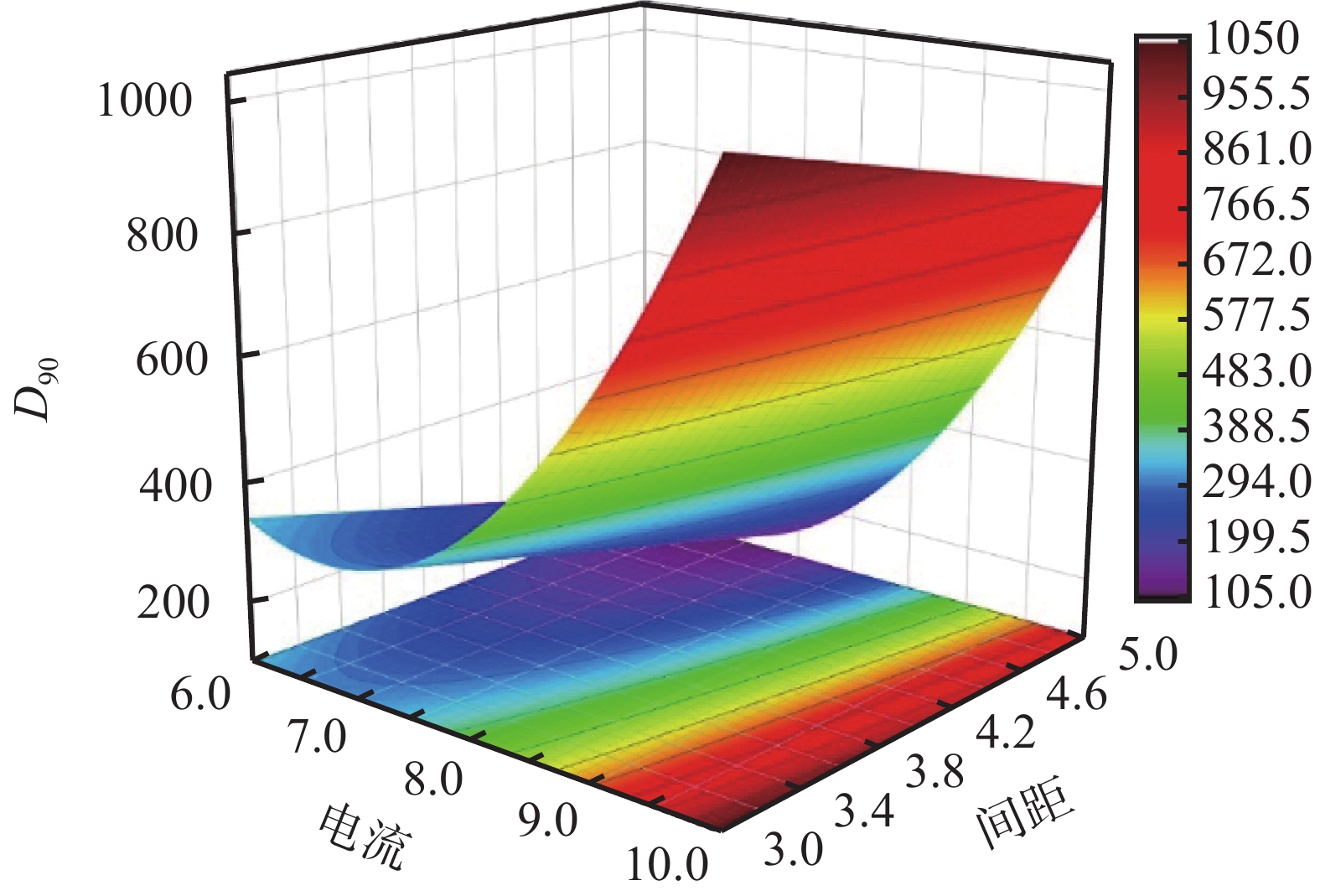
摘要: 随着深层、超深层油气资源开发力度的不断加大,地层压力逐渐升高,高密度废弃钻井液处理量也不断增长。传统的化学絮凝剂存在成本高、普适性差及潜在的二次污染等问题,利用外加电场是高密度废弃钻井液绿色处理的新手段。在单因素实验的基础上,运用响应曲面法(RSM)研究了电流强度、破胶时间、极板间距3个因素及其交互作用对钻井液体系的Zeta电位和粒径分布的影响。结果表明,在电流强度为8 A、极板间距为3 cm、破胶时间为10 min的条件下,废弃钻井液破胶效果达到最优。破胶后的钻井液体系的Zeta电位上升率为38.29 %,达到了−26.2 mV,其体系的粒径分布D90达到了562.5 μm。废弃钻井液体系的胶体稳定性得以破坏,为后续体系中有用组分的回收及废弃组分的处理工作提供有力支撑。Abstract: As oil and gas wells are drilled deeper and deeper, higher formation pressures need to be balanced with high density drilling fluids, and this leads to another problems: the treatment of more and more high density waste muds. Waste muds are generally treated with chemical flocculants and problems such as high treatment cost, poor universality and potential secondary pollution are the norm. In a study an electric field was applied to treat a high density waste mud. Based on the results of a single-factor experiment, the effects of three factors, i.e., current intensity, time of gel breaking and the distance between two electrodes, as well as the interaction of the three factors on the Zeta potential and particle size distribution of the drilling fluid were studied using response surface methodology (RSM). It was found that an optimum gel breaking can be obtained when the electric current intensity = 8 A, the time of gel breaking = 10 min, and the distance between two electrodes = 3 cm. After gel breaking, the Zeta potential of the drilling fluid was increased by 38.29%, reaching −26.2 mV, and the particle size distribution factor D90 reached 562.5 μm, indicating that the gel stability of the waste drilling fluid was broken, and this provided a powerful support to the subsequent recovery of the useful mud components as well as the treatment of the waste portion of the waste drilling fluid.
-
表 1 CCD设计方案及响应值
实验编号 电流强度/A t破胶/min 极板间距/cm D90/μm ζ/mV 1 6 5.0 3 220.0 −33.75 2 10 5.0 3 910.0 −28.94 3 6 10.0 3 140.0 −34.30 4 10 10.0 3 811.6 −30.12 5 6 5.0 5 660.0 −28.53 6 10 5.0 5 1138.0 −26.57 7 6 10.0 5 217.3 −30.80 8 10 10.0 5 1065.0 −27.33 9 6 7.5 4 180.0 −35.33 10 10 7.5 4 1024.0 −29.46 11 8 5.0 4 506.4 −27.92 12 8 10.0 4 208.2 −31.33 13 8 7.5 3 198.4 −32.45 14 8 7.5 5 562.5 −26.18 15 8 7.5 4 250.6 −30.94 16 8 7.5 4 290.0 −30.56 17 8 7.5 4 250.0 −30.33 18 8 7.5 4 270.0 −29.88 19 8 7.5 4 260.8 −31.04 20 8 7.5 4 310.8 −28.66 表 2 响应曲面的方差分析结果
项 效应 系数 标准误差 T值 P值 显著性 粒径分布 X1 706.300 353.100 23.400 15.09 0 显著 X2 −198.500 −99.200 23.400 −4.24 0.002 显著 X3 272.600 136.300 23.400 5.82 0 显著 X12 532.300 266.200 44.600 5.96 0 显著 X22 42.900 21.400 44.600 0.48 0.641 不显著 X32 89.200 44.600 44.600 1.00 0.341 不显著 X1X2 87.800 43.900 26.200 1.68 0.124 不显著 X1X3 −9 .000 −4.500 26.200 −0.17 0.867 不显著 X2X3 −84.300 −42.200 26.200 −1.61 0.138 不显著 Zeta电位 X1 4.059 2.029 0.345 5.88 0 显著 X2 −1.633 −0.816 0.345 −2.37 0.040 显著 X3 4.031 2.016 0.345 5.84 0 显著 X12 −3.724 −1.862 0.658 −2.83 0.018 不显著 X22 1.819 0.910 0.658 1.38 0.197 不显著 X32 2.439 1.220 0.658 1.85 0.093 不显著 X1X2 0.218 0.109 0.386 0.28 0.783 不显著 X1X3 −0.892 −0.446 0.386 −1.16 0.275 不显著 X2X3 −0.325 −0.162 0.386 −0.42 0.682 不显著 -
[1] 田野. 废弃钻井液处理技术探讨[J]. 西部探矿工程,2021,33(3):30-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.03.009TIAN Ye. Discussion on treatment technology of waste drilling fluid[J]. West-china Exploration Engineering, 2021, 33(3):30-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.03.009 [2] 李月龙. 油田废弃钻井液无害化处理技术的研究[J]. 西部探矿工程,2022,34(1):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2022.01.015LI Yuelong. Research on harmless treatment technology of waste drilling fluid in oilfield[J]. West-china Exploration Engineering, 2022, 34(1):48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2022.01.015 [3] 刘利明. 钻井工程废弃钻井液处理技术分析[J]. 西部探矿工程,2019,31(5):91-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2019.05.031LIU Liming. Analysis on treatment technology of waste drilling fluid in drilling engineering[J]. West-china Exploration Engineering, 2019, 31(5):91-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2019.05.031 [4] 何长明,李俊华,王佳. 废弃钻井液无害化处理技术的研究[J]. 应用化工,2016,45(9):1792-1794. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2016.09.004HE Changming, LI Junhua, WANG Jia. Research of waste drilling fluid disposal technology[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(9):1792-1794. doi: 10.16581/j.cnki.issn1671-3206.2016.09.004 [5] 苏勤,何青水,张辉,等. 国外陆上钻井废弃物处理技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2010,38(5):106-110.SU Qin, HE Qingshui, ZHANG Hui, et al. Foreign onshore drilling waste treatment technology[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2010, 38(5):106-110. [6] 王眉山,郑毅. 中国废弃钻井液处理技术发展趋势[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2009,26(6):77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2009.06.023WANG Meishan, ZHENG Yi. The prospect of waste drilling fluid treatment technology in China[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2009, 26(6):77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2009.06.023 [7] 蔡利山,阮光明,王全周,等. 加重剂回收利用技术探讨与可行性分析[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2012,29(1):34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.01.010CAI Lishan, RUAN Guangming, WANG Quanzhou, et al. Research and feasibility analysis on recycling technology of weighting materials[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2012, 29(1):34-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.01.010 [8] 刘培坤,徐金广,张悦刊,等. 钻井液加重剂回收试验研究[J]. 过滤与分离,2017,27(2):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8265.2017.02.001LIU Peikun, XU Jinguang, ZHANG Yuekan, et al. Experimental research on recovery of drilling fluid weighting compound[J]. Journal of Filtration & Separation, 2017, 27(2):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8265.2017.02.001 [9] 周礼. 废弃水基钻井液无害化处理技术研究及应用[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2014.ZHOU Li. Research and application of harmless treatment technology of waste water-based drilling fluid. [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2014. [10] LARSON T R. Methods for recovery and reuse of lcm. US: 12001490[P]. 2009-6-11. [11] 蔡利山,杨健,彭琳. 离心机分离固相测定分析方法及其应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2018,35(6):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.06.006CAI Lishan, YANG Jian, PENG Lin. Method of solids composition determination of centrifuge and the application thereof[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2018, 35(6):31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.06.006 [12] 张爱顺,黄达全,曹孜英,等. 废弃聚合物钻井液无害化处理技术实验研究[J]. 油气田环境保护,2014,24(3):17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3158.2014.03.007ZHANG Aishun, HUANG Quanda, CAO Ziying, et al. Experimental research into harmless treatment technology of waste polymer drilling liquid[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields, 2014, 24(3):17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3158.2014.03.007 [13] 王学川,胡艳鑫,郑书杰,等. 国内外废弃钻井液处理技术研究现状[J]. 陕西科技大学学报(自然科学版),2010,28(6):169-174.WANG Xuechuan, HU Yanxin, ZHENG Shujie, et al. Application status of waste drilling fluid treatment technology at home and abroad[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2010, 28(6):169-174. [14] VLYSSIDES A G, KARLIS P K, ZORPAS A A. Eletrochemical oxidation of noncyanide strippers wastes[J]. Environment International, 1999, 25:663-670. doi: 10.1016/S0160-4120(99)00028-8 [15] 陆香玉,俞海祥,陈亚,等. 化学絮凝与电絮凝调理污泥脱水性能影响作用的对比研究[J]. 环境科学学报,2022,42(3):257-267. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0441LU Xiangyu, YU Haiyang, CHEN Ya, et al. Comparison of the effects of chemical flocculation and electric flocculation conditioning on sludge dewatering performance[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2022, 42(3):257-267. doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2021.0441 [16] 谢水祥,任雯,李兴春,等. 电吸附再生废弃水基钻井液作用机理[J]. 天然气工业,2019,39(12):139-145. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.12.018XIE Shuixiang, REN Wen, LI Xingchun, et al. Mechanism of electrosorption recycled waste water-based drilling fluid[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(12):139-145. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.12.018 [17] SHER F, HANIF K, IQBAL S Z, et al. Implications of advanced wastewater treatment: Electrocoagulation and electroflocculation of effluent discharged from a wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 33(C):101101-101101. [18] TURAN N B, ERKAN H S, ENGIN G O. The investigation of shale gas wastewater treatment by electro-Fenton process: Statistical optimization of operational parameters[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 109:203-213. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.04.002 [19] 袁青松,冯辉,张栋,等. 强封堵钻井液体系在河南页岩气钻井中的研究和应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(1):29-35.YAN Qingsong, FENG Hui, ZHANG Dong, et al. Study of a strong plugging drilling fluid used in shale gas drilling in He’nan province[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(1):29-35. [20] 陈彬,张伟国,姚磊,等. 基于井壁稳定及储层保护的钻井液技术[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2021,43(2):184-188.CHEN Bin, ZHANG Weiguo, YAO Lei, et al. Drilling fluid technology based on well stability and reservoir protection[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 43(2):184-188. [21] 夏海英,兰林,杨丽,等. 强抑制钻井液体系研究及现场应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(4):427-430.XIA Haiying, LAN Lin, YANG Li, et al. Study and field application of a highly inhibited drilling fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(4):427-430. [22] 周启成,梁应红,单海霞,等. 抗高温高密度生物质钻井液体系研究及应用[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(6):78-84.ZHOU Qicheng, LIANG Yinghong, SHAN Haixia, et al. Research and application of a high-temperature resistant and high-density biomass drilling fluid system[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(6):78-84. [23] 王景. 临兴-神府井区废弃钻井液处理技术[J]. 石油钻探技术,2022,50(1):60-64.WANG Jing. Treatment technology of waste drilling fluids in the Linxing-Shenfu Well Area[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2022, 50(1):60-64. [24] 周姗姗,钟成兵,刘杰,等. 超低摩阻水基钻井液在页岩气水平井的应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(3):313-318.ZHOU Shanshan, ZHONG Chengbing, LIU Jie, et al. Application of ultra-low friction wwater-based ddrilling ffluid in shale gas horizontal wells[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(3):313-318. -





 下载:
下载: