Low Damage Highly Inhibitive Water Based Drilling Fluid for Drilling Shale Oil Reservoir
-
摘要: 长73页岩储层发育微纳米级孔缝,地层岩石强度低,钻井液滤液易侵入储层造成井壁失稳和储层伤害。厘清了长73页岩井壁失稳机理及钻井液技术难点,借鉴“1/3和2/3架桥封堵规则”,引入刚性和可变形封堵材料,构建了广谱型多级粒径分布区间。以瞬时滤失量为评价指标,通过曲面响应建模优化出最佳配比,室内优选了防塌抑制剂组合,在此基础上研发出一套低伤害强防塌水基钻井液体系,评价实验结果表明,所构建的钻井液能够有效平衡地层坍塌应力,老化后静置72 h流变性依旧良好,抑制性强,页岩线性膨胀率较清水环境和现场钻井液分别降低了16.74%和13.61%;封堵性显著,瞬时滤失量仅为1 mL,对岩心的封堵率高达93.5%,储层保护性好,泥饼清除后岩心板中无孔喉堵塞现象,渗透率恢复值高达95.2%;润滑性能适中,钻井液老化前后摩阻系数均保持在0.08左右,现场试验水平段平均井径扩大率仅为4.27%,平均机械钻速可达18.4 m/h,钻进期间水平段无井下复杂事故,各项性能能够满足长73页岩油水平井钻井的需要。Abstract: Chang 73 reservoirs have the characteristics of micron-nano crack development and low strength of formation rocks. It can lead to the intrusion of drilling fluid filtrate into the reservoir causing borehole collapse and reservoir damage. We clarified the destabilization mechanism of Chang 73 shale and the technical difficulties of drilling fluids. Then the multi-stage particle size distribution intervals with broad spectrum was constructed by introducing rigid and deformable plugging materials, which was based on the "1/3 and 2/3 bridging rule". Next, using the instantaneous water loss as the evaluation index, the optimal ratio was optimized by surface response modeling, and the combination of anti-collapse inhibitor was preferred in the room. Based on which a low damage and anti-collapse water-based drilling fluid was developed. The results of the evaluation indicated that the drilling fluid can effectively balance the formation collapse stress, and the rheological properties remain satisfactory after aging for 72 h. It also reduced shale linear swell by 16.74% and 13.61% compared to clear water environments and in the field drilling fluids respectively. Due to its remarkable plugging properties, the instantaneous filtration loss of the drilling fluid was only 1mL and the plugging rate of the core was as high as 93.5%. Based on the reservoir protection capability of the drilling fluid, there was no pore throat plugging in the core slab after mud cake removal and the permeability recovery value of the core was as high as 95.2%. It was important that the lubricity of the drilling fluid was moderate and the friction coefficient remain around 0.08 before and after the drilling fluid ages. The average diameter expansion rate of the horizontal section in the field test was only 4.27%, and the average mechanical drilling speed could reach 18.4m/h. There were no complicated downhole accidents in the horizontal section during the drilling period, and all the performances could meet the needs of horizontal wells in the Chang 73 reservoirs.
-
表 1 长73页岩全岩矿物衍射分析
% 石英 斜长石 钾长石 正长石 黄铁矿 碳酸盐 TCCM 46.42 8.28 13.56 2.95 5.35 0.68 22.76 表 2 长73地层岩石力学参数分析
地层
岩性取心深度/
m泊松比 弹性模量/
MPa内摩擦角/
(°)地层坍塌压力
当量密度/(g·cm−3)地层破裂压力
当量密度/(g·cm−3)最大剪应力/
MPa抗剪强度/
MPa页岩 2420.00 0.26 20.30 27.53 1.22 2.18 20.30 18.30 表 3 多级封堵材料粒径分布区间
代号 级别 封堵材料种类 D50/
μm备注 X1 一级(刚性) 8000目碳酸钙
(现场)1.6 2 μm的2/3~1/1 X2 二级(刚性) 10 000目碳酸钙 1.3 2 μm的1/3~2/3 X3 三级(可变形) G325(现场) 0.76 <2 μm的1/3 表 4 模型方程各参数及误差分析
方程
系数数值 标准
误差Reduced
Chi-Sqr残差平
方和R2 调整R2 a 32.186 28 0.959 06 0.327 77 3.605 47 0.968 57 0.952 14 b −0.746 32 0.065 61 c −0.719 44 0.040 18 d 0.007 34 8.054 76×
10−4e 0.004 61 3.723 16×
10−4f 0.007 29 7.915 67×
10−4表 5 不同密度下钻井液流变性能评价
ρ/(g·cm−3) 测试条件 AV/mPa·s PV/mPa·s YP/Pa Gel/(Pa/Pa) YP/PV/(Pa/mPa ·s) FLAPI/mL pH 1.20 老化前 24.5 15.0 9.5 4.5/8.0 0.63 2.2 8.0 老化后 25.5 17.0 8.5 3.0/6.0 0.50 2.6 8.0 1.30 老化前 29.5 16.0 13.5 5.0/9.0 0.84 3.6 8.0 老化后 31.5 19.0 12.5 4.0/8.0 0.66 3.6 8.0 1.40 老化前 32.0 19.0 13.0 5.0/9.0 0.68 4.5 8.0 老化后 31.5 19.0 12.5 4.0/8.0 0.66 4.5 8.0 注:钻井液体系加重材料选用重晶石,老化条件:120 ℃×16 h,静置72 h。 表 6 岩样滚动回收率评价
层位 实验方案 初始质量/
g回收质量/
g岩样回收率/
%长73 清水 50.0 43.6 87.2 现场钻井液 50.0 46.2 92.4 强封堵防塌钻井液 50.0 48.8 97.6 注:老化条件:120 ℃×16 h。 表 7 储层保护性能评价
岩心
编号驱替
介质T/
℃t/
hK/mD 封堵率/
%渗透率恢复/
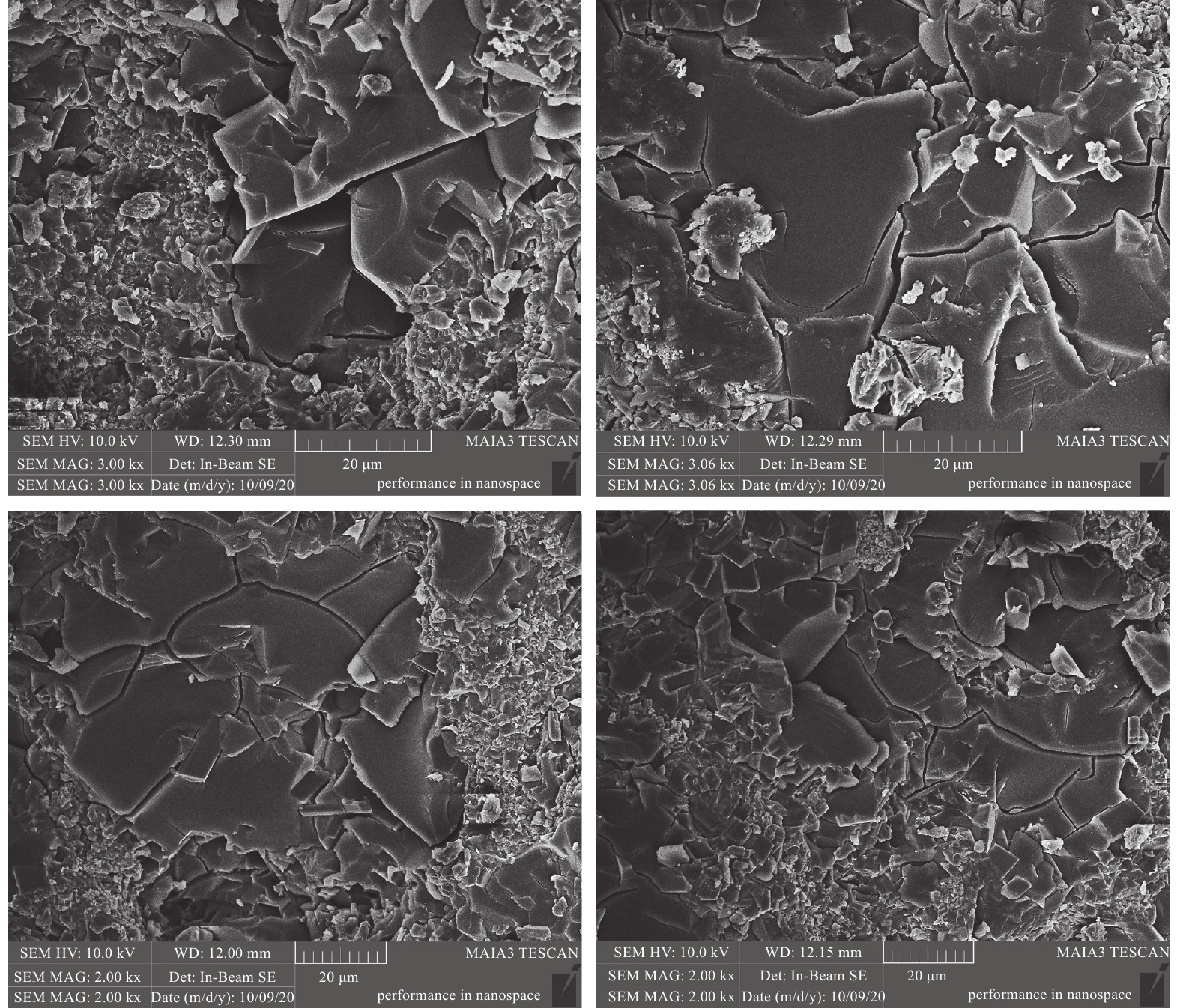
%伤害前正向 伤害后正向 伤害后反向 1# 煤油 65.0 2.0 14.98 4.56 10.88 69.6 72.6 2# 2.0 15.60 1.01 14.85 93.5 95.2 注:1#为现场钻井液;2#为低伤害强防塌水基钻井液。 -
[1] 姚兰兰. 页岩油储层微观孔隙结构特征评价及渗流机理研究[D]. 廊坊:中国科学院大学(中国科学院渗流流体力学研究所),2021:6-9.YAO Lanlan. Evaluation of microscopic pore structure characteristics and flow mechanism of shale oil reservoirs[D]. Langfang: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Porous Flow and Fluid Mechanics), 2021 :6-9. [2] 国家市场监督管理总局,国家标准化管理委员.GB/T 38718-2020.页岩油地质评价方法[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2020.State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 38718-2020. Geological evaluating methods for shale oil[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. [3] 肖玲, 陈曦, 雷宁, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区三叠系长7段页岩油储层特征及主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏,2023,35(2):80-93.XIAO Ling, CHEN Xi, LEI Ning, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of shale oil reservoirs of Triassic Chang 7 member in Heshui area,Ordos basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(2): 80-93. [4] 周小航,陈冬霞,夏宇轩,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7段页岩油储层自发渗吸特征及影响因素[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(8):3045-3055. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.8.dqkx202208027ZHOU Xiaohang, CHEN Dongxia, XIA Yuxuan, et al. Spontaneous imbibition characteristics and influencing factors of Chang 7 shale oil reservoirs in Longdong area, Ordos basin[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(8):3045-3055. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.8.dqkx202208027 [5] 杜晓宇, 金之钧, 曾联波, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7页岩油储层天然裂缝发育特征与控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2589-2600.DU Xiaoyu, JIN Zhijun, ZENG Lianbo, et al. Development characteristics and controlling factors of natural fractures in Chang 7 shale oil reservoir, Longdong area, Ordos basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2589-2600. [6] 肖玲,胡榕,韩永林,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地新安边地区长7页岩油储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,49(3):284-293.XIAO Ling, HU Rong, HAN Yonglin, et al. Characteristics of pore throat structure of Chang 7 shale oil sandstone reservoir in the western Xin'anbian area, Ordos basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition) , 2022, 49(3):284-293. [7] DEVILLE J P, FRITZ B, JARRETT M. Development of water-based drilling fluids customized for shale reservoirs[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2011, 26(4):484-491. [8] BLAND R G, WAUGHMAN R R, TOMKINS P G, et al. Water-based alternatives to oil-based muds: do they actually exist?[C]//IADC/SPE Drilling Conference. Dallas, Texas: SPE, 2002: SPE-74542-MS. [9] 徐志勇. 高性能水基钻井液技术研究进展[J]. 西部探矿工程,2022,34(5):76-77, 79.XU Zhiyong. Research progress of high performance water-based drilling fluid technology[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2022, 34(5): 76-77, 79. [10] 赵小平,孙强. 环境友好型水基钻井液技术研究新进展[J]. 山东化工,2018,47(20):52-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2018.20.020ZHAO Xiaoping, SUN Qiang. New progress in the research of environment-friendly water-based drilling fluid technology[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(20):52-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2018.20.020 [11] ABRAMS, A. Mud design to minimize rock impairment due to particle invasion.[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1977, 29(5):586-592. doi: 10.2118/5713-PA [12] DA ROCHA H O, DA COSTA J L S, CARRASQUILLA A A G, et al. Petrophysical characterization using well log resistivity and rock grain specific surface area in a fractured carbonate pre-salt reservoir in the Santos basin, Brazil[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 183:106372. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106372 [13] 刘大伟,康毅力,雷鸣,等. 保护碳酸盐岩储层屏蔽暂堵技术研究进展[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2008,25(5):57-61. doi: 10.2118/1652-G-PALIU Dawei, KANG Yili, LEI Ming, et al. Research progresses in temporary plugging technology for carbonate reservoir protection[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2008, 25(5):57-61. doi: 10.2118/1652-G-PA [14] HANDS N, KOWBEL K, MAIKRANZ S, et al. Drill-in fluid reduces formation damage, increases production rates[J]. Oil & Gas Journal, 1998, 96(28):65-69. [15] 蒋官澄,毛蕴才,周宝义,等. 暂堵型保护油气层钻井液技术研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2018,35(2):1-16.JIANG Guancheng, MAO Yuncai, ZHOU Baoyi, et al. Progress made and trend of development in studying on temporarily type plugging reservoir protection drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2018, 35(2):1-16. [16] 徐同台,陈永浩,冯京海,等. 广谱型屏蔽暂堵保护油气层技术的探讨[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2003,20(2):39-41.XU Tongtai, CHEN Yonghao, FENG Jinghai, et al. The general-purpose temporary shield plugging technology in protecting hydrocarbon reservoir[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2003, 20(2):39-41. [17] 马毅超. 封堵型防塌水基钻井液技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学石油工程学院, 2016: 1–10.MA Yichao. Research on the technology of plugging type anti-collapse water-based drilling fluid[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2016. [18] 马成云,宋碧涛,徐同台,等. 钻井液用纳米封堵剂研究进展[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2017,34(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.001MA Chengyun, SONG Bitao, XU Tongtai, et al. Research progress of nano plugging agents for drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2017, 34(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2017.01.001 [19] JI L J, GUO Q X, FRIEDHEIM J, et al. Laboratory evaluation and analysis of physical shale inhibition of an innovative water-based drilling fluid with nanoparticles for drilling unconventional shales[C]//SPE Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition. Perth, Australia: SPE, 2012: SPE-158895-MS. [20] LI Z Y, ZHOU Y, QU L, et al. A new method for designing the bridging particle size distribution for fractured carbonate reservoirs[J]. SPE Journal, 2022, 27(5):2552-2562. doi: 10.2118/209617-PA [21] 马腾飞,周宇,李志勇,等. 新型低伤害高性能微泡沫钻井液性能评价与现场应用[J]. 油田化学,2021,38(4):571-579. doi: 10.19346/j.cnki.1000-4092.2021.04.001MA Tengfei, ZHOU Yu, LI Zhiyong, et al. Evaluation and field application of new microfoam drilling fluid with low-damage and high-performance[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2021, 38(4):571-579. doi: 10.19346/j.cnki.1000-4092.2021.04.001 [22] 王建华,李建男,闫丽丽,等. 油基钻井液用纳米聚合物封堵剂的研制[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2013,30(6):5-8,91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.06.002WANG Jianhua, LI Jiannan, YAN Lili, et al. The development and performance evaluation of plugging agent for oil-base drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2013, 30(6):5-8,91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.06.002 [23] SAVARI S, KUMAR A, WHITFILL D L, et al. Improved lost circulation treatment design and testing techniques minimize formation damage[C]//SPE European Formation Damage Conference. Noordwijk, The Netherlands: SPE, 2011: SPE-143603-MS. [24] KULKARNI S, SAVARI S, KUMAR A, et al. Novel rheological Tool to determine lost circulation materials (LCM) plugging performance[C]//North Africa Technical Conference and Exhibition. Cairo, Egypt: SPE, 2012: SPE-150726-MS. -





 下载:
下载: