Experimental Study on Mud Intrusion in Tarim Tightly Fractured Reservoirs
-
摘要: 近年来致密砂岩储层伤害与保护问题引起学者们的关注。由于存在天然裂缝通道沟通,在裂缝性致密储层的开发过程中,工作液很容易沿裂缝进入储层,对储层造成严重的伤害。为了探究钻井液对裂缝性储层的伤害程度和机理,以塔里木库车山前区块裂缝性致密砂岩储层为研究对象,进行了钻井液侵入伤害实验。实验结果表明,钻井液侵入过程按照泥饼的形成过程可分为4个阶段,分别是无泥饼阶段、泥饼快速生成阶段、泥饼动态平衡阶段和形成封堵阶段;钻井液侵入速率受储层渗透率、泥饼渗透率、流体性质以及密度的影响,当储层渗透率高于临界渗透率时,侵入速率主要由滤饼渗透率决定;通过扫描电镜结果可得,钻井液固相颗粒在岩心孔喉中的堵塞状态分为堵塞状、黏附状和填充状3种,不同堵塞状态对储层渗透率伤害程度不同。得到的钻井液动态伤害分析与固相颗粒侵入研究有助于复杂油藏模拟器的改进,对现场施工作业以及钻井液优化具有一定的指导意义。Abstract: In recent years, the problem of tight sandstone reservoir damage and protection has attracted the attention of scholars. Due to the existence of natural fracture channel communication, the fluids can easily enter the reservoir along the fractures during the development of fractured tight reservoirs and cause serious damage to the reservoir. In order to investigate the degree and mechanism of mud damage to fractured reservoirs, this paper conducts mud intrusion damage experiments with fractured tight sandstone reservoirs in Tarim Kucha Piedmont block as the research object. The experimental results show that the mud intrusion process can be divided into four stages according to the formation process of mud cake, namely, no mud cake stage, mud cake rapid generation stage, mud cake dynamic equilibrium stage and formation of sealing stage; the mud intrusion rate is affected by the reservoir permeability, mud cake permeability, fluid properties and specific gravity, and when the reservoir permeability is higher than the critical permeability, the intrusion rate is mainly determined by the filter cake permeability; by Scanning electron microscope results show that the blockage state of mud solid phase particles in core pore throat is divided into three kinds: blockage, adhesion and filling, and different blockage states have different degrees of damage to reservoir permeability. The mud dynamic damage analysis and solid-phase particle intrusion study obtained in this paper can help improve the complex reservoir simulator, which has certain guiding significance for the field construction operation and mud optimization.
-
Key words:
- Drilling fluid /
- Tight fracture reservoir /
- Mud intrusion /
- Solid particle /
- Reservoir protection
-
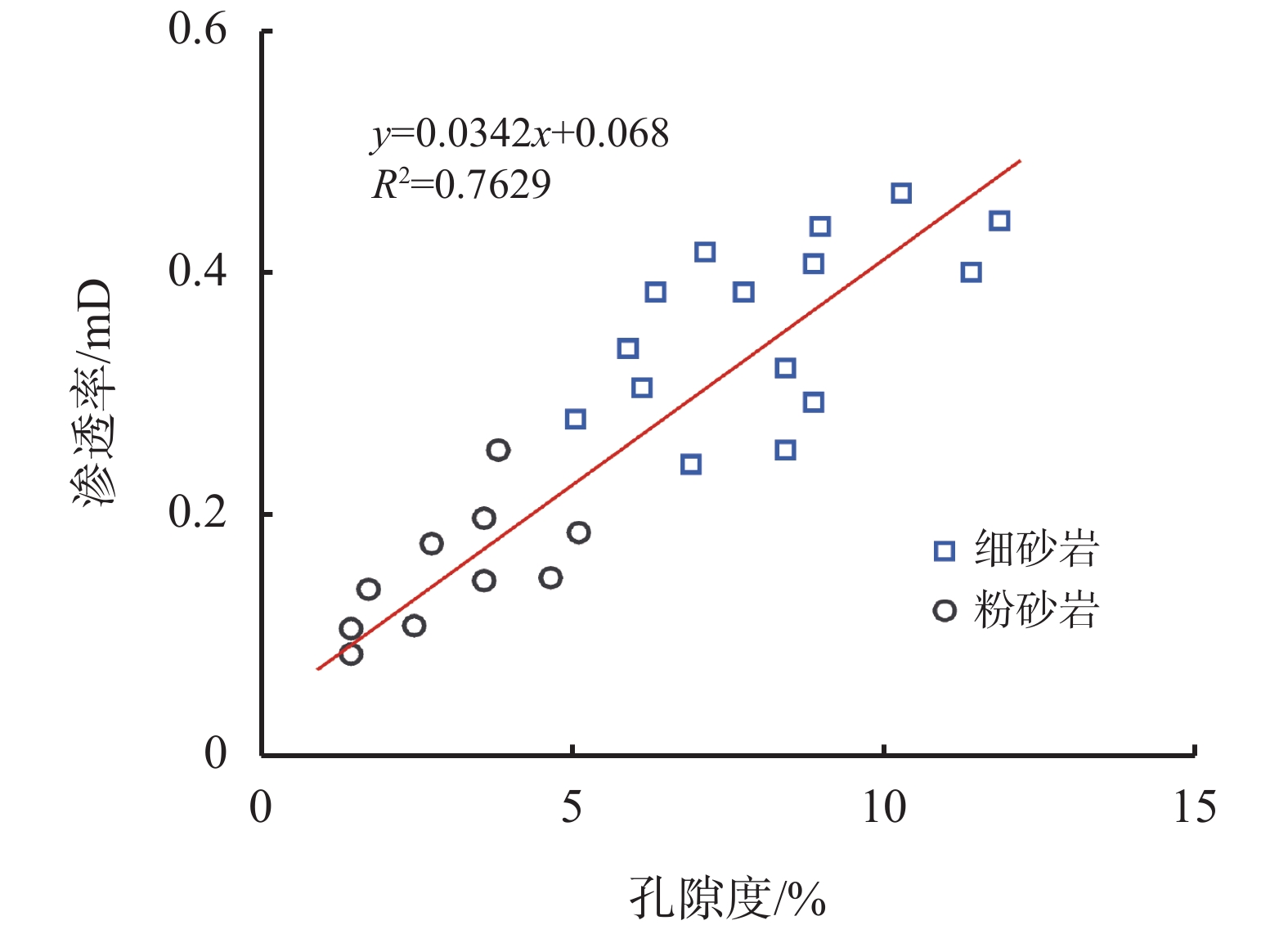
表 1 塔里木库车山前岩石的全岩矿物分析
岩心 矿物含量/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 硬石膏 TCCM 细砂岩 46.1 12.6 17.3 8.5 15.5 粉砂岩 44.3 15.2 15.0 1.5 20.1 3.9 表 2 塔里木库车山前岩石的黏土分析
岩心 黏土矿物含量/% 混层比/% 伊利石 伊/蒙混层 蒙脱石 高岭石 绿泥石 伊/蒙混层 细砂岩 45.1 45.9 3.7 2.0 3.4 10 粉砂岩 47.0 44.2 3.2 3.1 2.5 10 表 3 高黏度和低黏度现场钻井液的性能
钻井液 FL瞬时/
mLFLAPI/
mLAV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
Pa低黏 0.7 3.05 26 21 5.1 高黏 0.2 2.15 45 35 10.2 表 4 不同钻井液在不同储层流体下侵入岩心的实验参数
岩心
编号孔隙度/
%渗透率/
mD储层流体
类型钻井液
类型1# 4.6 0.63 水层 低黏度 2# 6.1 0.98 水层 低黏度 3# 4.5 0.15 水层 低黏度 4# 6.2 1.41 水层 低黏度 5# 5.8 0.74 水层 低黏度 6# 5.2 0.56 水层 低黏度 7# 6.0 0.33 气层 低黏度 8# 6.1 0.92 水层 低黏度 9# 6.3 1.54 水层 高黏度 表 5 钻井液侵入过程中不同泥饼形成阶段的渗透率数据
泥饼形成
阶段t/
min泥饼渗透率/
μD无泥饼阶段 0~10 $ \mathrm{\infty } $ 泥饼快速形成阶段 10~40 >2.00 动态平衡阶段 40~100 0.01~0.50 封堵阶段 >100 <0.01 -
[1] ELKEWIDY T I. Integrated evaluation of formation damage/remediation potential of low permeability reservoirs[C]//SPE Kuwait International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro, 2012(15): 45-48. [2] 黎明,周福建,王庆,等. 致密砂岩储层应力敏感模型建立与验证[J]. 天然气与石油,2021,39(6):75-81.LI Ming, ZHOU Fujian, WANG Qqing, et al. Establishment and validation of stress-sensitive model for dense sandstone reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2021, 39(6):75-81. [3] 鄢捷年,宗习武,李秀兰,等. 泥浆滤液侵入对油藏岩石水驱油动态的影响[J]. 石油学报,1995,16(4):84-92.YAN Jienian, ZONG Xiwu, LI Xilan, et al. Influence of mud filtrate intrusion on reservoir rock water drive dynamics[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 1995, 16(4):84-92. [4] 黎明,周福建,王庆,等. 考虑温度变化的砂岩油藏应力敏感模型[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(34):14542-14547.LI Ming, ZHOU Fujian, WANG Qing, et al. Stress sensitivity model of sandstone reservoir considering temperature change[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(34):14542-14547. [5] 汪津,邹磊落,米兴夺,等. 油气储层中盐水泥浆侵入规律研究[J]. 石油化工应用,2018,37(11):25-28.WANG Jin, ZOU Leiluo, MI Xingduo, et al. Study on the invasion law of salt-water slurry in oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Petrochemical Application, 2018, 37(11):25-28. [6] 刘向君,陈福煊. 泥浆滤液径向侵入特征研究[J]. 西南石油学院学报,1995(1):83-88.LIU Xiangjun, CHEN Fuxuan. Study on the radial intrusion characteristics of mud filtrate[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 1995(1):83-88. [7] 范翔宇,夏宏泉,陈平,等. 测井计算钻井泥浆侵入深度的新方法研究[J]. 天然气工业,2004(5):68-70.FAN Xiangyu, XIA Hongquan, CHEN Ping, et al. Research on a new method of logging to calculate drilling mud invasion depth[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004(5):68-70. [8] GREEN J, PATEY I, WRIGHT L, et al. The nature of drilling fluid invasion, clean-up, and retention during reservoir formation drilling and completion[C]//SPE Bergen One Day Seminar. OnePetro, 2017, (6): 98-102. [9] ROMAIN L,CHASSAGNE AND PAUL ,HAMMOND S. Simulation of drilling fluid filtrate invasion near an observation well[J]. SPE journal, 2012, 17(4):1047-1055. doi: 10.2118/154014-PA [10] MAKAROV A, ELTSOV I. Invasion modeling assists in the formation permeability evaluation from resistivity profiles and mudcake thickness[C]//SPE Russian Oil and Gas Exploration and Production Technical Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro, 2012, 18(1): 120-128. [11] 范宜仁,胡云云,李虎,等. 泥饼动态生长与泥浆侵入模拟研究[J]. 测井技术,2013,37(5):466-471.FAN Yiren, HU Yunyun, LI HU, et al. Research on dynamic growth of mud cake and simulation of mud invasion[J]. Logging Technology, 2013, 37(5):466-471. [12] 范宜仁,王小龙,巫振观,等. 考虑地层伤害影响的钻井液侵入模拟研究[J]. 测井技术,2018,42(4):383-389.FAN Yiren, WANG Xiaolong, WU Zhenguan, et al. Research on drilling fluid invasion simulation considering the effect of formation damage[J]. Logging Technology, 2018, 42(4):383-389. [13] 张振华,鄢捷年,王书琪. 保护裂缝性碳酸盐岩油气藏的钻井完井液[J]. 钻采工艺,2000(1):63-66.ZHANG Zhenhua, YAN Jienian, WANG Shuqi. Drilling and completion fluids for protecting fractured carbonate reservoirs[J]. Drilling and Production Technology, 2000(1):63-66. [14] 李春月,李沁,李德明,等. 顺北碳酸盐岩储层长期酸蚀裂缝导流能力预测方法[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(5):646-653.LI Chunyue, LI Qin, LI Deming, et al. Method of predicting flow conductivity of long-term acid-etched fractures in carbonate reservoirs in shunbei oilfield[J]. Drilling Fluid and Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(5):646-653. [15] BAILEY L, BOEK E S, JACQUES S D M, et al. Particulate invasion from drilling fluids[J]. SPE Journal, 2000, 5(4):412-419. doi: 10.2118/67853-PA [16] 张福祥,汪周华,郭平,等. 应用CT技术研究钻井液污染三维空间分布特征[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2015,37(3):48-52. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2015.03.012ZHANG Fuxiang, WANG Zhouhua, GUO Ping, et al. Studying the 3D spatial distribution characteristics of drilling fluid pollution using ct technology[J]. Petroleum Drilling and Production Technology, 2015, 37(3):48-52. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2015.03.012 [17] 张松扬,陈玉魁. 钻井液侵入机理特征及影响因素研究[J]. 勘探地球物理展,2002(6):28-31.ZHANG Songyang, CHEN Yukui. Study on the mechanism characteristics and influencing factors of drilling fluid invasion[J]. Exploration Geophysics Exhibition, 2002(6):28-31. [18] 张建华,胡启,刘振华. 钻井泥浆滤液侵入储集层的理论计算模型[J]. 石油学报,1994(4):73-78.ZHANG Jianhua, HU Qi, LIU Zhenhua. Theoretical calculation model of drilling mud filtrate invasion into reservoir[J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 1994(4):73-78. [19] 杨震,李智强,邓少贵,等. 大斜度井钻井液侵入数值模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2008(3):55-59.YANG Zhen, LI Zhiqiang, DENG Shaogui, et al. Numerical simulation of drilling fluid invasion in highly deviated wells[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science Edition) , 2008(3):55-59. -





 下载:
下载: