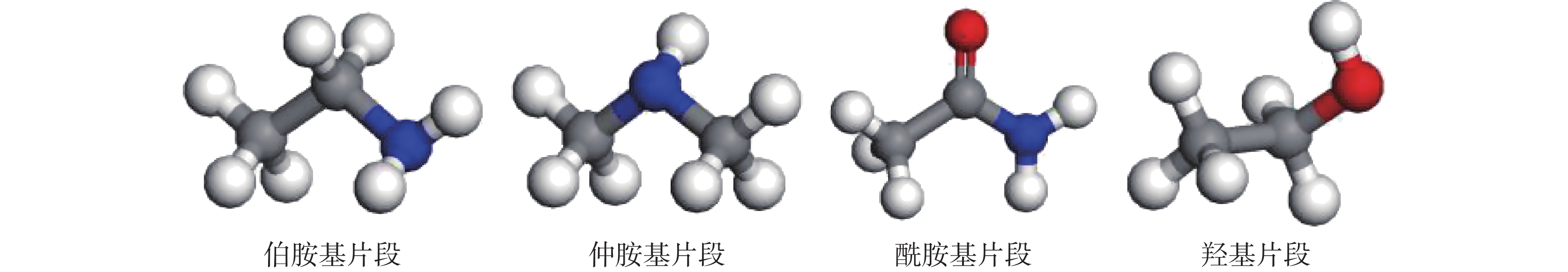
Adsorption of Polar Fragments of Amide Lubricants on Iron Surface
-
摘要: 针对深井、超深井、大位移井和水平井等复杂境况带来的高温、高摩阻环境,利用DFT模拟方法,分析了油酸酰胺亲水链段中伯胺基、仲胺基、酰胺基和羟基等极性片段在铁(001)表面的吸附作用力,进一步探究油酸酰胺类润滑剂在铁表面的吸附润滑机理。结果表明,酰胺基、伯胺基、羟基在Fe(001)面上的桥位产生稳定吸附,仲胺基在Fe(001)面上顶位产生最稳定吸附,吸附能从大到小依次为伯胺基、仲胺基、羟基、酰胺基。布居数分析结果表明,4种极性基团在吸附过程中轨道布居数均发生变化,从Fe(001)面得到电子,其中仲胺基得到0.16e电子,伯胺基和酰胺基得到0.09e电子,羟基得到电子数最少,为0.08e。态密度分析结果表明,仲胺基和伯胺基中N原子的2p轨道与铁原子的3p、4s轨道间有态密度重叠,存在化学成键作用。在极压润滑测试和四球摩擦实验中,油酸二乙烯三胺的润滑系数降低率为83.6%,高于油酸二乙醇酰胺的78.2%;摩斑半径为287.184 μm,小于油酸二乙醇酰胺的摩斑半径,表明含有胺基与酰胺基的润滑材料润滑性能优于含有羟基的表面活性剂。Abstract: DFT simulation was used to investigate the bonding effects of different polar segments on iron (001) surface. These polar segments were intercepted from the hydrophilic chain segments of oleic acid amide lubricants, include primary amine, secondary amine, amide, and hydroxyl. Results indicated that amide group, primary amine group, and hydroxyl group generated the most stable adsorption at the bridge site of Fe (001) surface, and secondary amino group generated the most stable adsorption on the top site of Fe (001) surface. The adsorption energy in descending order were primary amine group, secondary amino group, hydroxyl group, and amide group. Results of population analysis indicated that the orbital population of four polar groups changed during the process and obtained electrons from Fe (001) surface. Among them, secondary amino group obtained 0.16e electrons, primary amino and amide group obtained 0.09e electrons, and hydroxyl group obtained the lowest number of electrons at 0.08e. Results of DOS analysis showed that there exist DOS overlap between 2p orbitals of N and 3p、4s orbitals of iron, with chemical bonding effect. In the extreme pressure lubrication test and four ball friction test results, the lubrication coefficient reduction rate of oleic acid Diethylenetriamine is 83.6%, higher than 78.2% of oleic acid diethanolamide, and the wear scar radius is 287.184 μ m. The wear radius is lower than that of oleic acid diethanolamide. The experimental results indicate that surfactants containing amine and amide groups have better lubrication performance than surfactants containing hydroxyl groups.
-
Key words:
- Drilling fluid /
- Amide type lubricant /
- Adsorption energy /
- Electron cloud overlap /
- Chemical bonding
-
表 1 极性片段在Fe (001)面吸附前后电荷数 (e)
极性片段 吸附前总电荷数 吸附后总电荷数 电荷转移数 伯胺基片段 0.01 −0.08 0.09 仲胺基片段 −0.01 −0.17 0.16 酰胺基片段 −0.01 −0.1 0.09 羟基片段 0.01 −0.07 0.08 表 2 润滑材料在基浆中性能测试
润滑
材料ρ基浆/
g·cm−3AV/
mPa·s润滑系数降低率/
%基浆 1.03 14 油酸酰胺 1.02 15 80.9 油酸二乙烯三胺 1.02 15 83.6 油酸二乙醇酰胺 0.89 20 78.2 -
[1] 宋海,龙武,邓雄伟. 页岩气水基钻井液用抗高温环保润滑剂的研制及应用[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(6):761-764.SONG Hai, LONG Wu, DENG Xiongwei. Development and application of high temperature resistant and environmental protection lubricant for shale gas water-based drilling fluid[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(6):761-764. [2] 张永耀,侯树岭. 页岩油定向井水平井摩阻分析探讨[J]. 石化技术,2020,27(11):140-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.11.059ZHANG Yongyao, HOU Shuling. Analysis and discussion on frictional resistance of horizontal well in shale oil directional well[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(11):140-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.11.059 [3] 武金平. 分析定向井水平井摩阻控制与优化处理[J]. 石化技术,2020,27(1):350-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.01.222WU Jinping. Analysis of horizontal well friction control and optimization of directional wells[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(1):350-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.01.222 [4] 魏佳怡,李月红,于文婧,等. 环保型水基钻井液润滑剂的研究进展[J]. 化工技术与开发,2021,50(6):36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9905.2021.06.010WEI Jiayi, LI Yuehong, YU Wenjing, et al. Research progress of environmental friendly water based drilling fluid lubricant[J]. Technology & Development of Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(6):36-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9905.2021.06.010 [5] 李公让,王承俊. 极性吸附钻井液润滑剂的研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):541-549.LI Gongrang, WANG Chengjun. Research progress made and development trend of drilling fluid lubricants with polar adsorption ability[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5):541-549. [6] 管申,何淼,曹峰,等. 环保强吸附水基润滑剂BM-1的研制与评价[J]. 精细石油化工,2021,38(4):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2021.04.002GUAN Shen, HE Miao, CAO Feng, et al. Development and evaluation of environment-friendly strong adsorption lubricant BM-1[J]. Speciality Petrochemicals, 2021, 38(4):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9384.2021.04.002 [7] 王承俊. 植物油改性钻井液润滑剂的合成与性能研究[J]. 山东化工,2022,51(11):7-9.WANG Chengjun. Preparation of vegetable modified lubricant for drilling fluid and research on its lubricating performance[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(11):7-9. [8] 孙丙向,李文博. 氨解改性大豆卵磷脂钻井液润滑剂[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(2):164-170.SUN Bingxiang, LI Wenbo. Ammonolysis modified soybean lecithin as a drilling fluid lubricant[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(2):164-170. [9] 张顺从,戴尧,徐浩,等. 油酸酰胺型润滑剂在铁表面减摩作用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(5):596-600. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.05.010ZHANG Shuncong, DAI Yao, XU Hao, et al. Friction reduction of oleamide lubricants on iron surface[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(5):596-600. doi: 10.12358/j.issn.1001-5620.2022.05.010 [10] 张冬,程延海,冯世哲,等. 溶氧水在Fe(001)表面吸附的第一性原理研究[J]. 河北科技大学学报,2018,39(1):24-34. doi: 10.7535/hbkd.2018yx01004ZHANG Dong, CHENG Yanhai, FENG Shizhe, et al. First principles study of dissolved oxygen water adsorption on Fe (001) surfaces[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2018, 39(1):24-34. doi: 10.7535/hbkd.2018yx01004 [11] CLARK S J, SEGALL M D, PICKARD C J, et al. First principles methods using CASTEP[J]. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie-Crystalline Materials, 2005, 220(5/6):567-570. [12] 李震宇,贺伟,杨金龙. 密度泛函理论及其数值方法新进展[J]. 化学进展,2005,17(2):192-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-281X.2005.02.003LI Zhenyu, HE Wei, YANG Jinlong. Recent progress in density functional theory and its numerical methods[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2005, 17(2):192-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-281X.2005.02.003 [13] 伊丁,武镇,杨柳,等. 有机分子在铁磁界面处的自旋极化研究[J]. 物理学报,2015,64(18):203-208. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.187305YI Ding, WU Zhen, YANG Liu, et al. Spin-polarization of organic molecules at the ferromagnetic surface[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(18):203-208. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.187305 [14] FLETCHER R. A new approach to variable metric algorithms[J]. The Computer Journal, 1970, 13(3):317-322. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/13.3.317 [15] VANDERBILT D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism[J]. Physical Review B, 1990, 41(11):7892-7895. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.7892 [16] 王宗轮,孙金声,刘敬平,等. 耐高温高盐钻井液润滑剂的研制与性能评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(5):538-544.WANG Zonglun, SUN Jinsheng, LIU Jingping, et al. Development and performance evaluation of high temperature salt resistant drilling lubricant[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(5):538-544. [17] 张立权,侯珊珊,吴宇,等. 钻井液用环保润滑剂研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 油田化学,2022,39(1):163-169.ZHANG Liquan, HOU Shanshan, WU Yu, et al. Research progress and development trend of environmentally friendly lubricants for drilling fluids[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2022, 39(1):163-169. [18] 杨川,孟祥娟,赛亚尔·库西马克,等. 钻井液用润滑剂与螺杆橡胶的配伍性[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2023,40(1):60-66.YANG Chuan, MENG Xiangjuan, KOXMAK Sayyara, et al. Study on compatibility of drilling fluid lubricants and screw rubbers[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2023, 40(1):60-66. [19] YAN J J, BOCKSTALLER M R, MATYJASZEWSKI K. Brush-modified materials: control of molecular architecture, assembly behavior, properties and applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2020, 100:101180. [20] WANG Y J, JIA D, PAN J G, et al. Multiple-phase tectonic superposition and reworking in the Junggar basin of northwestern China-implications for deep-seated petroleum exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(8):1489-1521. [21] 陶怀志,明显森,马光长,等. 水基钻井液强吸附多元醇酯键合润滑剂及作用机理[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2022,39(5):579-586.TAO Huaizhi, MING Xiansen, MA Guangchang, et al. Study on mechanisms of a highly adsorptive polyol ester bonded lubricant for water based drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2022, 39(5):579-586. -





 下载:
下载: