ECD Sensitivity Analyses and Prediction Based on Interpretable Machine Learning
-
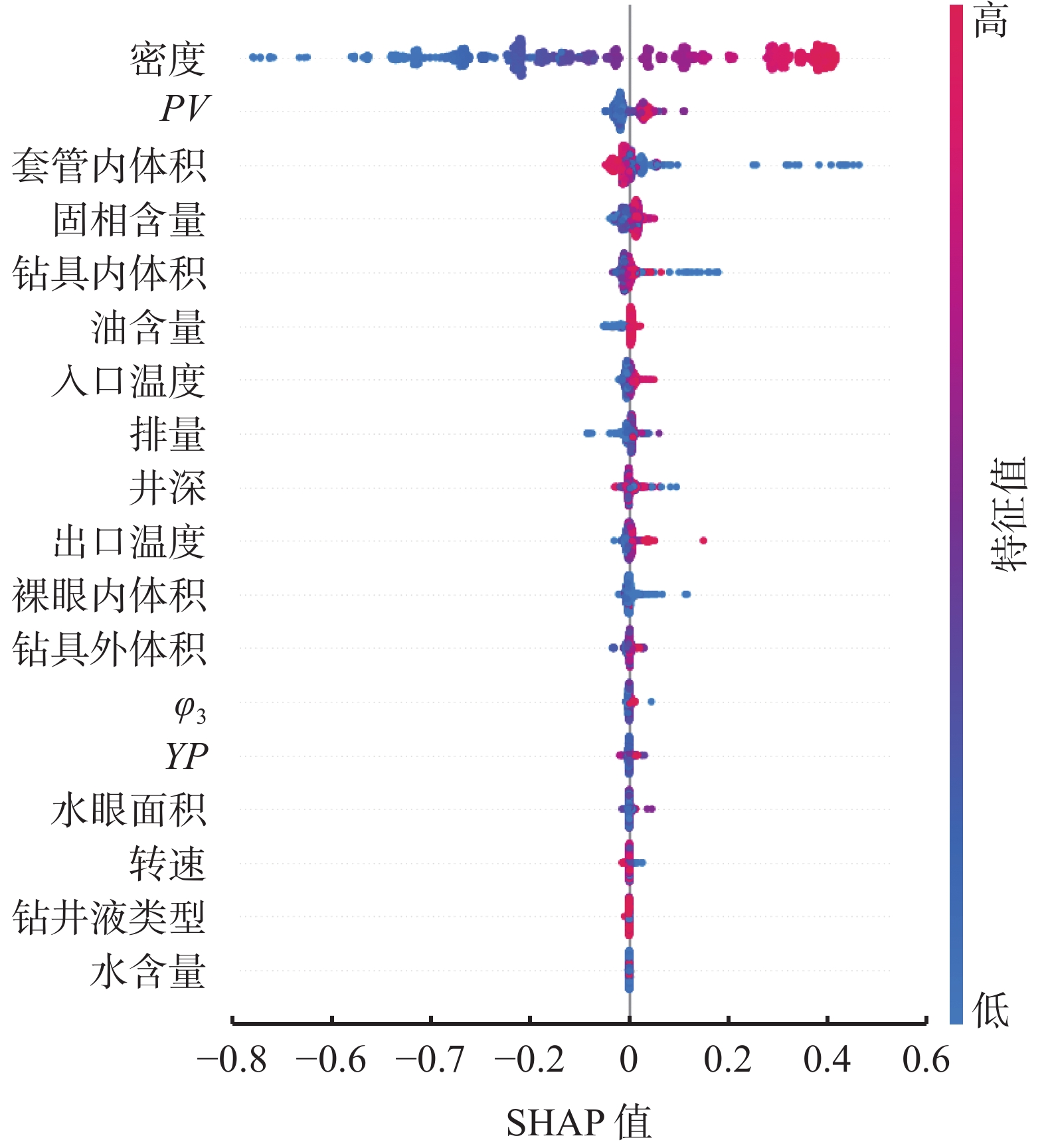
摘要: 当量钻井液循环密度(ECD)计算过于繁琐耗时,且其敏感性规律尚未得到明确认识。为此,采用ProHydraulic软件对克深区带的1928个数据点进行分析,以确定ECD的理论值,并建立了相关的特征参数。同时,利用可解释性机器学习方法SHAP对钻井液特性、钻进参数和环空容积等关键因素进行了敏感性分析。最终,利用线性回归构建克深区带计算ECD的经验公式,涵盖了12个主要特征参数。结果表明,该模型表现优异,测试集决定系数达到0.963,平均绝对误差仅为0.04,为实际工程应用推出了简明、高效的经验公式。Abstract: The calculation of equivalent circulation density (ECD) of drilling fluids is very cumbersome and time-consuming, and the pattern of sensitivity of the ECD has not been quite understood yet. To solve this problem, 1928 data from the Block Keshen were acquired and analyzed using the ProHydraulic software to calculate the theoretical ECD. Based on the calculation some characteristic parameters were determined. Key factors affecting the sensitivity of the ECDs of a drilling fluid, such as mud properties, drilling parameters and sizes of the annular spaces are analyzed using interpretable machine learning technology. Using linear regression, an empirical equation for calculating the ECDs of drilling fluids in the Block Keshen, which covers 12 main characteristic parameters, is constructed. ECD calculation with the model shows that the model gives results that fit the practical values with excellence. The coefficient of determination of the testing set is 0.963, and the average absolute error is only 0.04, indicating that this empirical equation is simple and efficient in ECD calculation in practical engineering application.
-
Key words:
- ECD /
- Sensitivity analysis /
- Interpretable machine learning /
- Linear regression model
-
表 1 博孜3-K2井ECD计算值与实测值 对比(基于ProHydraulic软件)
井深/
mρ出口/
g·cm−3计算值/(g·cm−3) ECD实测值/
g·cm−3相对误
差/%ESD ECD 5054 2.10 2.1390 2.1719 2.18 0.37 5433 2.18 2.2148 2.2803 2.26 0.90 5464 2.18 2.2177 2.2895 2.26 1.31 5767 2.18 2.2213 2.2725 2.25 1.00 5945 2.18 2.2211 2.2836 2.26 1.04 表 2 基于可解释性机器学习的ECD敏感性分析所采用的17个特征参数
参数 数据数量 均值 标准值 25%值 50%值 75%值 井深/m 1928 6809.003 00 834.103 20 6125 7138.2 7447 出口温度/℃ 1921 47.078 45 10.897 62 40 45 55 入口温度/℃ 1921 40.921 69 12.054 89 35 40 48 水眼面积/m3 1928 19.920 58 24.861 40 9.315 627 15.205 31 21.991 15 ρ/(g·cm-3) 1928 2.125 55 0.309 12 1.89 2.13 2.45 Vs/% 1926 40.191 07 8.557 10 33 40 49 油含量/% 1925 66.533 51 33.503 38 75 82 85 水含量/% 1925 33.475 84 33.499 20 15 18 25 YP/Pa 1928 6.307 26 3.322 03 4 5 7.5 PV/mPa·s 1928 56.978 48 29.863 78 32 45 83 φ3 1928 4.424 53 1.945 78 3 4 5 转速/(r·min-1) 1831 64.464 23 346.403 10 40 65 80 排量/(L·s-1) 1928 18.741 91 9.490 93 13 16 22 V套管内/m3 1928 290.783 10 59.615 21 243.771 90 318.505 328.689 60 V钻具内/m3 1928 62.839 57 14.635 11 53.315 13 65.614 68 71.946 99 V钻具外/m3 1927 92.858 40 15.098 63 81.452 69 93.326 67 101.928 10 V裸眼内/m3 1907 23.459 68 55.783 04 2.277 20 5.774 829 17.104 52 ECD/(g·cm-3) 1919 2.217 08 0.337 09 1.941 25 2.230 50 2.551 70 表 3 基于简化模型训练结果获得的参数回归系数对照表
参数 回归系数 ρ/(g·cm-3) 1.10 PV/mPa·s −1.11×10−4 V套管内/m3 −1.22×10−3 Vs/% −1.80×10−3 V钻具内/m3 −1.62×10−3 油含量/% −2.38×10−4 入口温度/℃ 2.04×10−3 排量/(L·s-1) 1.05×10−3 井深/m 4.31×10−5 出口温度/℃ 5.14×10−4 V裸眼内/m3 −4.17×10−4 V钻具外/m3 2.34×10−3 -
[1] BOURGOYNE A T, MILLHEIM K K, CHENEVERT M E, et al. Applied drilling engineering: 2[M]. Richardson, TX: Society of Petroleum Engineers Richardson, 1986. [2] 陈浩. 钻井过程中基于ECD的工程风险评价方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018.CHEN Hao. Research on drilling risk assessment during drilling process based on ECD[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2018. [3] 张更,李军,柳贡慧,等. 海上高温高压井环空ECD精细预测模型[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(6):698-704.ZHANG Geng, LI Jun, LIU Gonghui, et al. A precise model for prediction of annular ECD in offshore HTHP wells[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(6):698-704. [4] 马贤明, 管志川, 罗鸣, 等. 水平井钻井过程中ECD的动态预测方法研究[C]//2019第四届能源, 环境与自然资源国际会议论文集, 2019: 53-59.MA Xianming, GUAN Zhichuan, LUO Ming, et al. Study on the dynamic prediction method of ECD during the drilling process of horizontal wells[C]//Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Energy, Environment and Natural Resources, 2019: 53-59. [5] 翟羽佳,汪志明,郭晓乐. 深水钻井水力参数计算及优选方法[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(1):59-63,68.ZHAI Yujia, WANG Zhiming, GUO Xiaole. The method for calculation and optimization of deep water drilling hydraulic parameters[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(1):59-63,68. [6] 吕华东. 高温高压条件下的井低波动压力预测模型研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2014.LYU Huadong. Prediction model of surge pressure at high temperature and high pressure[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2014. [7] VAJARGAH A K, SULLIVAN G, OORT E V. Automated fluid rheology and ECD management[C]//SPE Deepwater Drilling and Completions Conference. Galveston, Texas, USA, 2016: SPE-180331-MS. [8] ASHENA R, BAHREINI H, GHALAMBOR A, et al. Investigation of parameters controlling equivalent circulating density ECD in managed pressure drilling MPD[C]//SPE International Conference and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control. Lafayette, Louisiana, USA, 2022: SPE-208869-MS. [9] PETRIE S W, DOLL R. Benefits of using continuous circulation systems in ERD wells to manage ECD, Bottom hole pressure and hole cleaning[C]//SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition. Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2021: SPE-202140-MS. [10] 王凯,和鹏飞,陈波,等. 基于Wellplan的ECD敏感性分析与精确预测技术[J]. 石油化工应用,2021,40(2):16-19,33.WANG Kai, HE Pengfei, CHEN Bo, et al. Sensitivity analysis and accurate prediction of ECD based on Wellplan[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2021, 40(2):16-19,33. [11] 高永德,董洪铎,胡益涛,等. 深水高温高压井钻井液当量循环密度预测模型及应用[J]. 特种油气藏,2022,29(3):138-143.GAO Yongde, DONG Hongduo, HU Yitao, et al. Prediction model and application of drilling fluid equivalent circulating density in deepwater High-Temperature and High-Pressure wells[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(3):138-143. [12] ABDELGAWAD K Z, ELZENARY M, ELKATATNY S, et al. New approach to evaluate the equivalent circulating density (ECD) using artificial intelligence techniques[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2019, 9(2):1569-1578. doi: 10.1007/s13202-018-0572-y [13] AHMED R, ENFIS M, MIFTAH-EL-KHEIR H, et al. The effect of drillstring rotation on equivalent circulation density: modeling and analysis of field measurements[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Florence, Italy, 2010: SPE-135587-MS. [14] ROBINSON T, GOMES D, MEOR HASHIM M M H, et al. Real-Time estimation of downhole equivalent circulating density ECD using machine learning and applications[C]//IADC/SPE International Drilling Conference and Exhibition. Galveston, Texas, USA, 2022: SPE-208675-MS. [15] GAMAL H, ABDELAAL A, ELKATATNY S. Machine learning models for equivalent circulating density prediction from drilling data[J]. ACS Omega, 2021, 6(41):27430-27442. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04363 [16] ALSAIHATI A, ELKATATNY S, GAMAL H, et al. A statistical machine learning model to predict equivalent circulation density ECD while drilling, based on principal components analysis PCA[C]//SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition. Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2021: SPE-202101-MS. [17] LUNDBERG S M, ERION G G, LEE S I. Consistent individualized feature attribution for tree ensembles[EB/OL]. (2019-03-07)[2023-05-05]. http://export.arxiv.org/abs/1802.03888v3. [18] WEISBERG S. Applied linear regression[M]. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. -





 下载:
下载: