A Model for Hard Brittle Mudstone Collapse Pressure Computation Based on Rock Dilation Strength Criteria
-
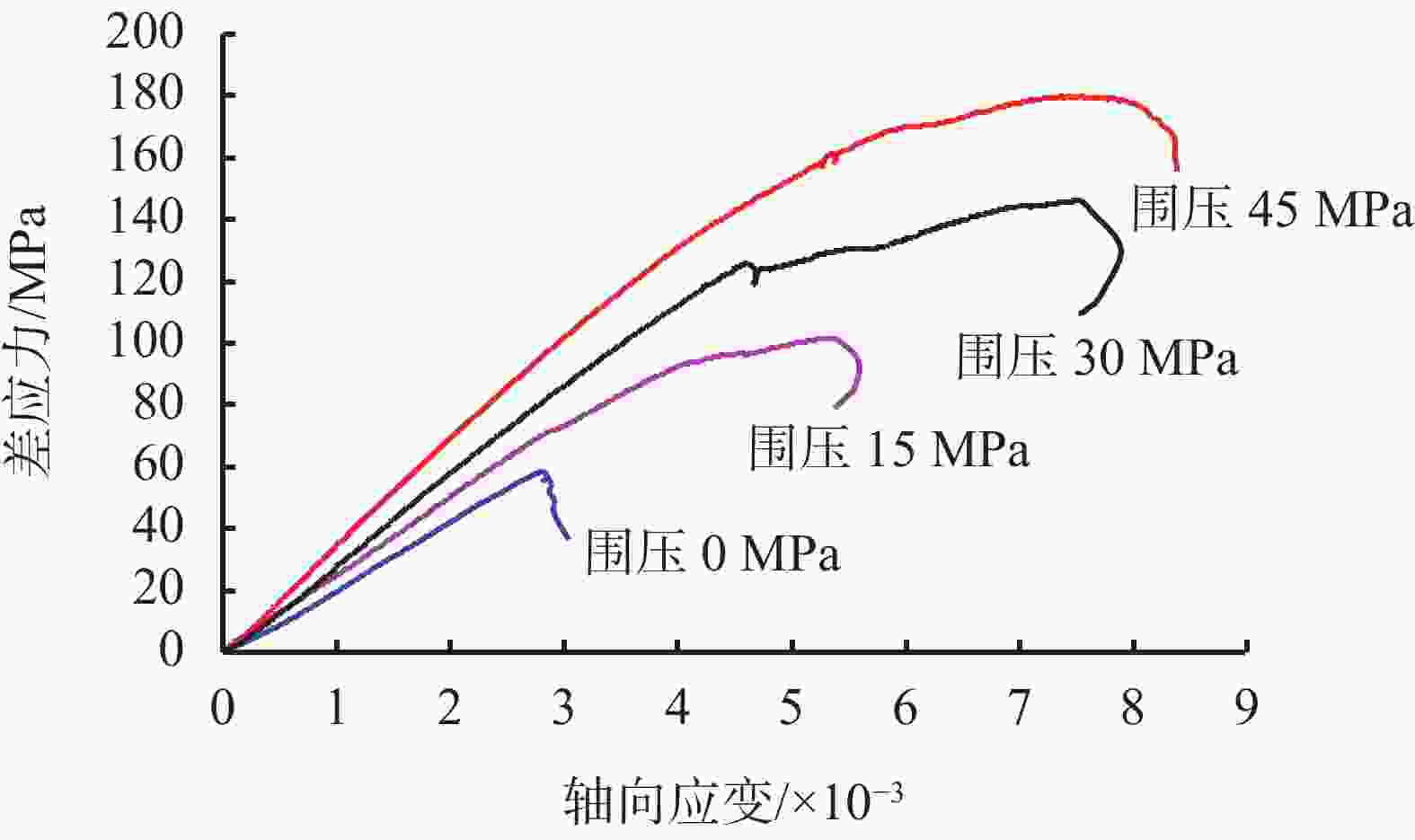
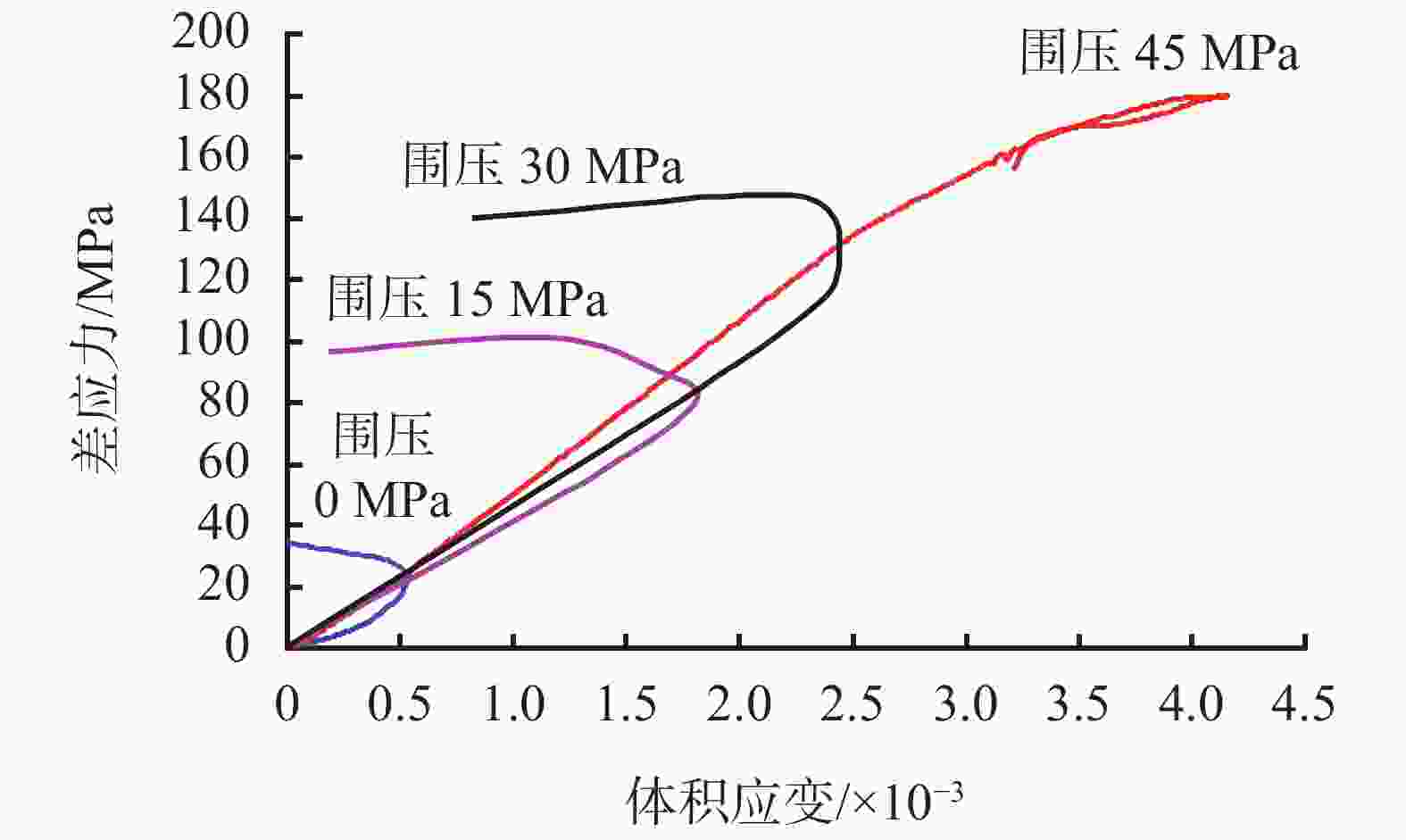
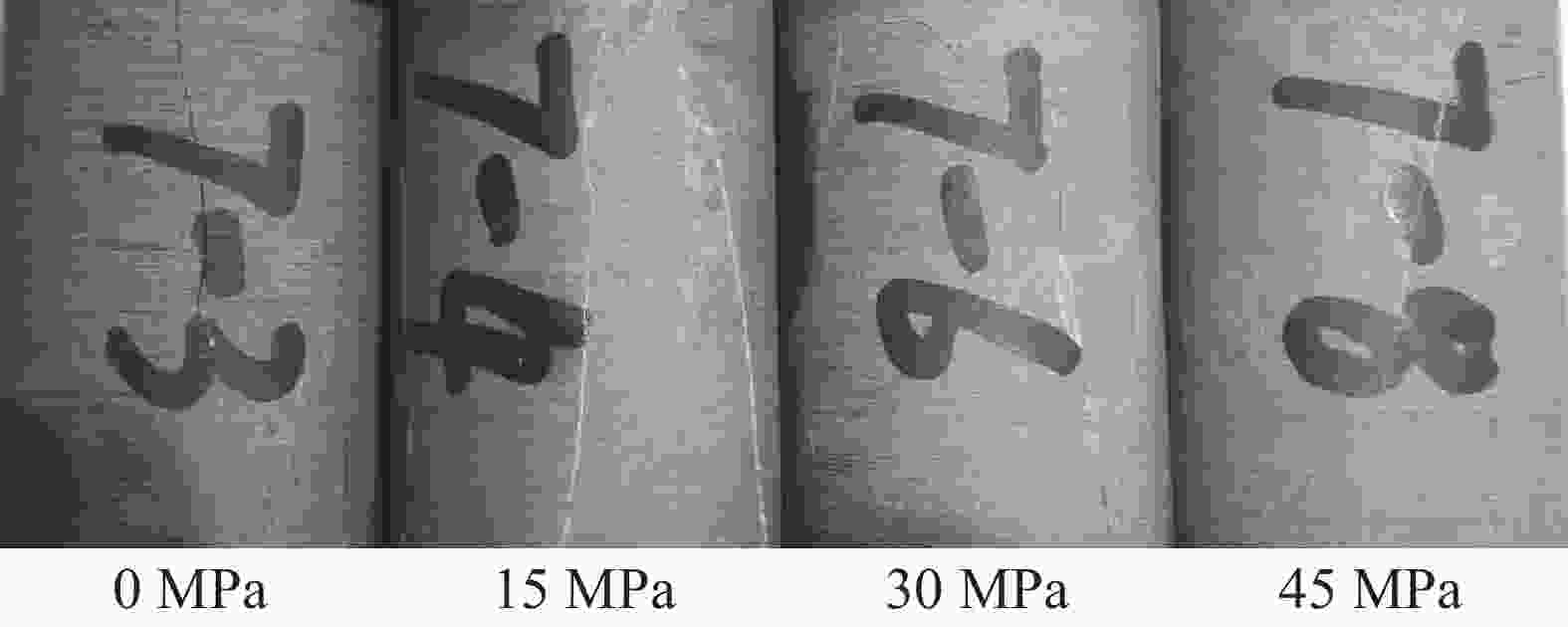
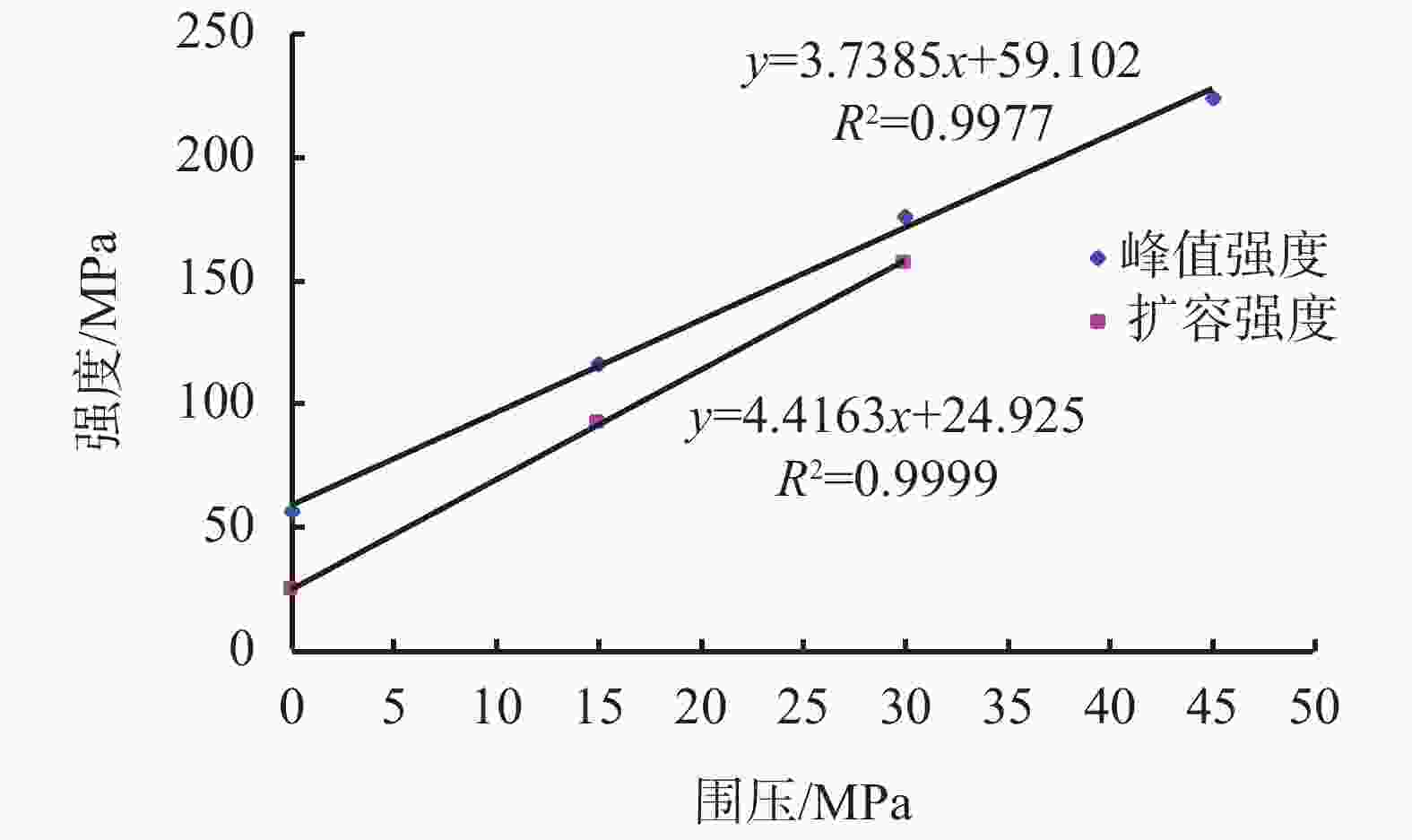
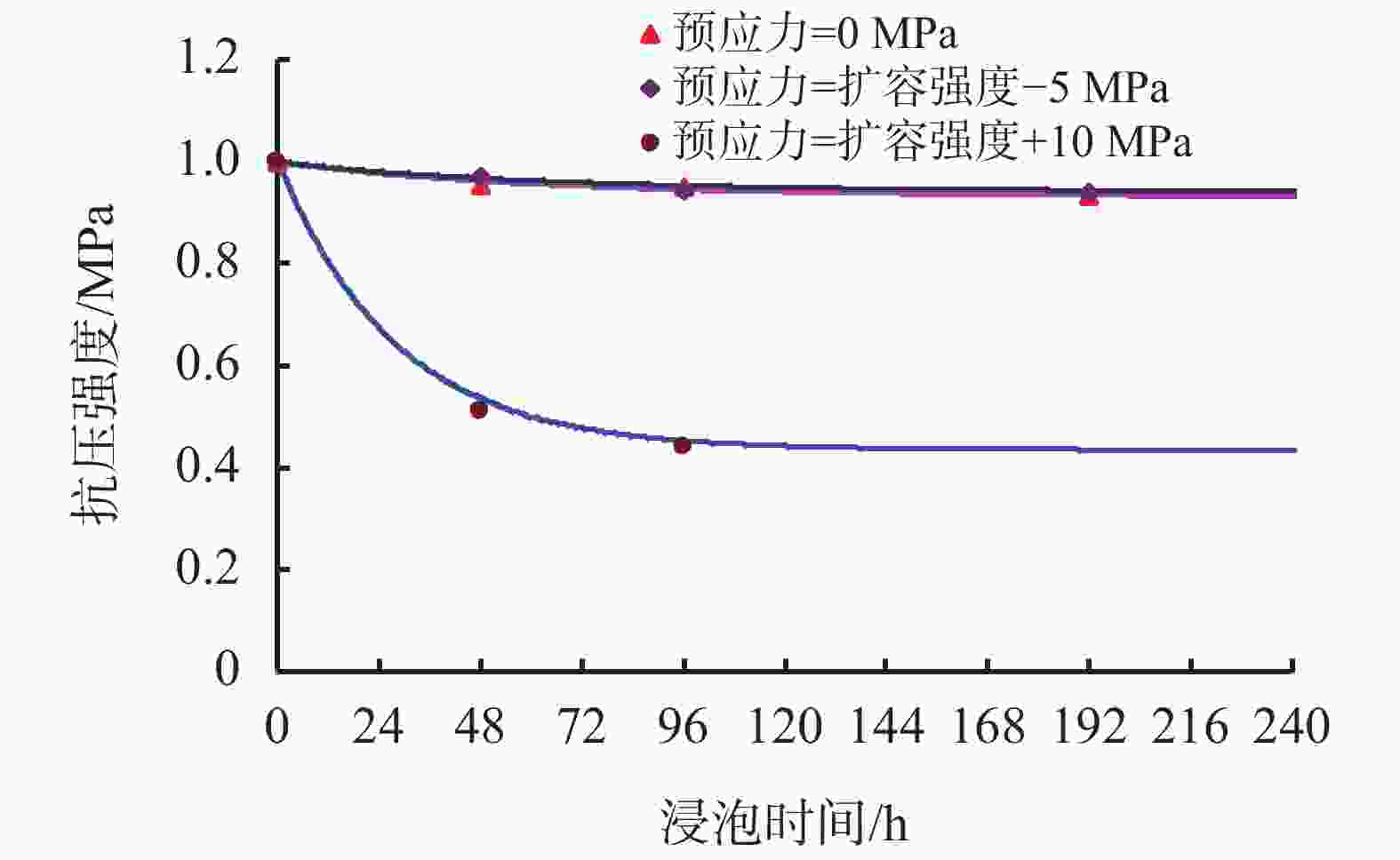
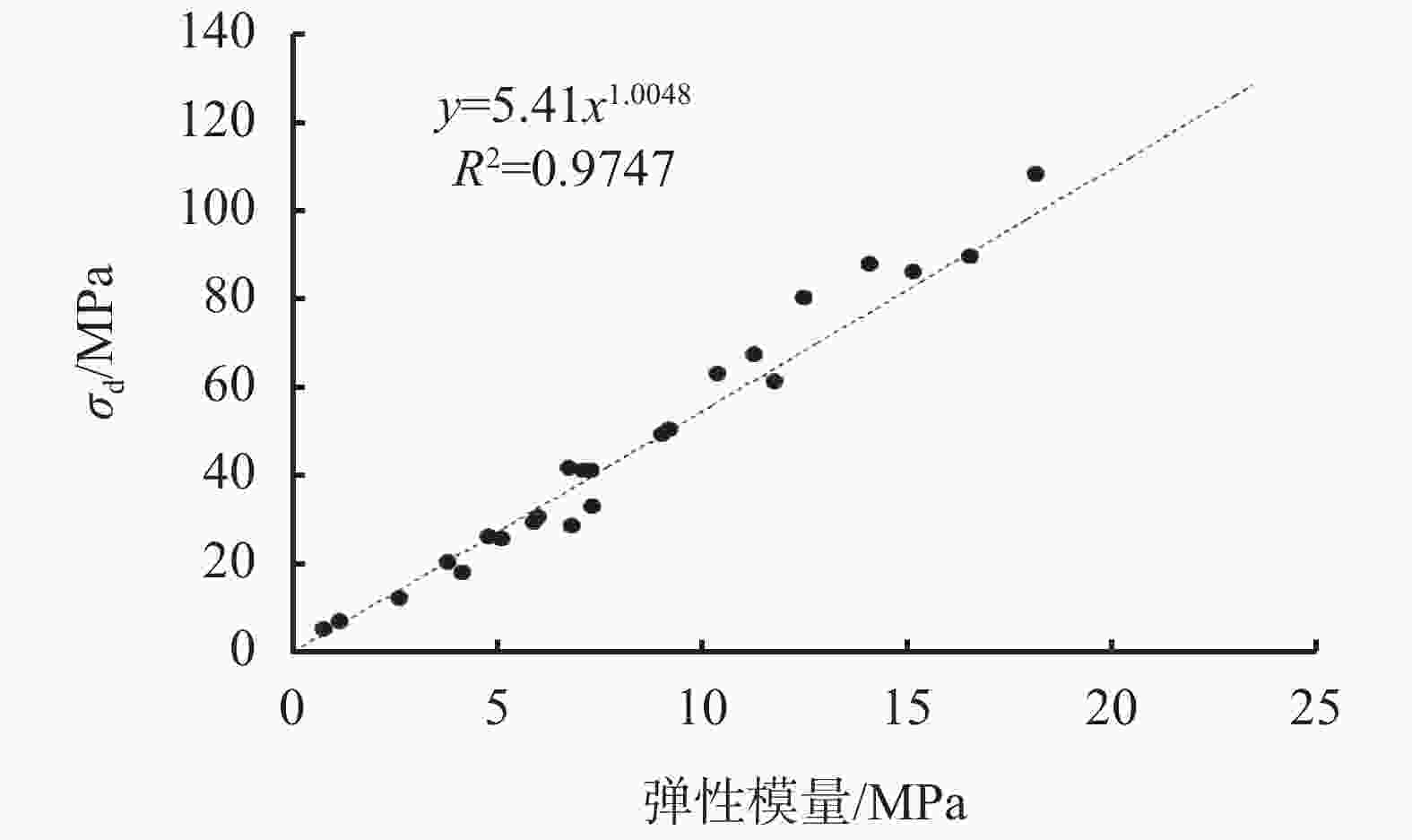
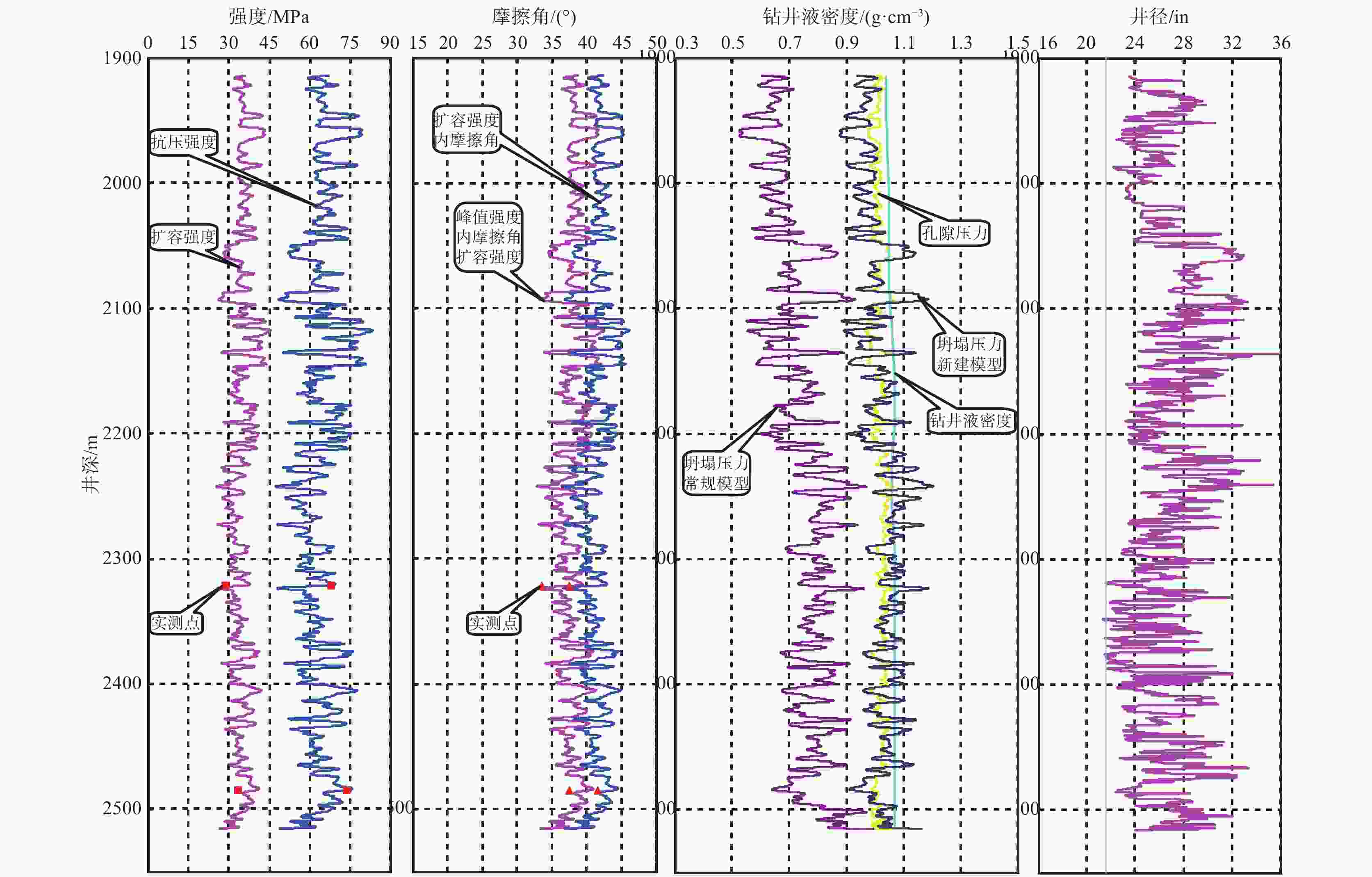
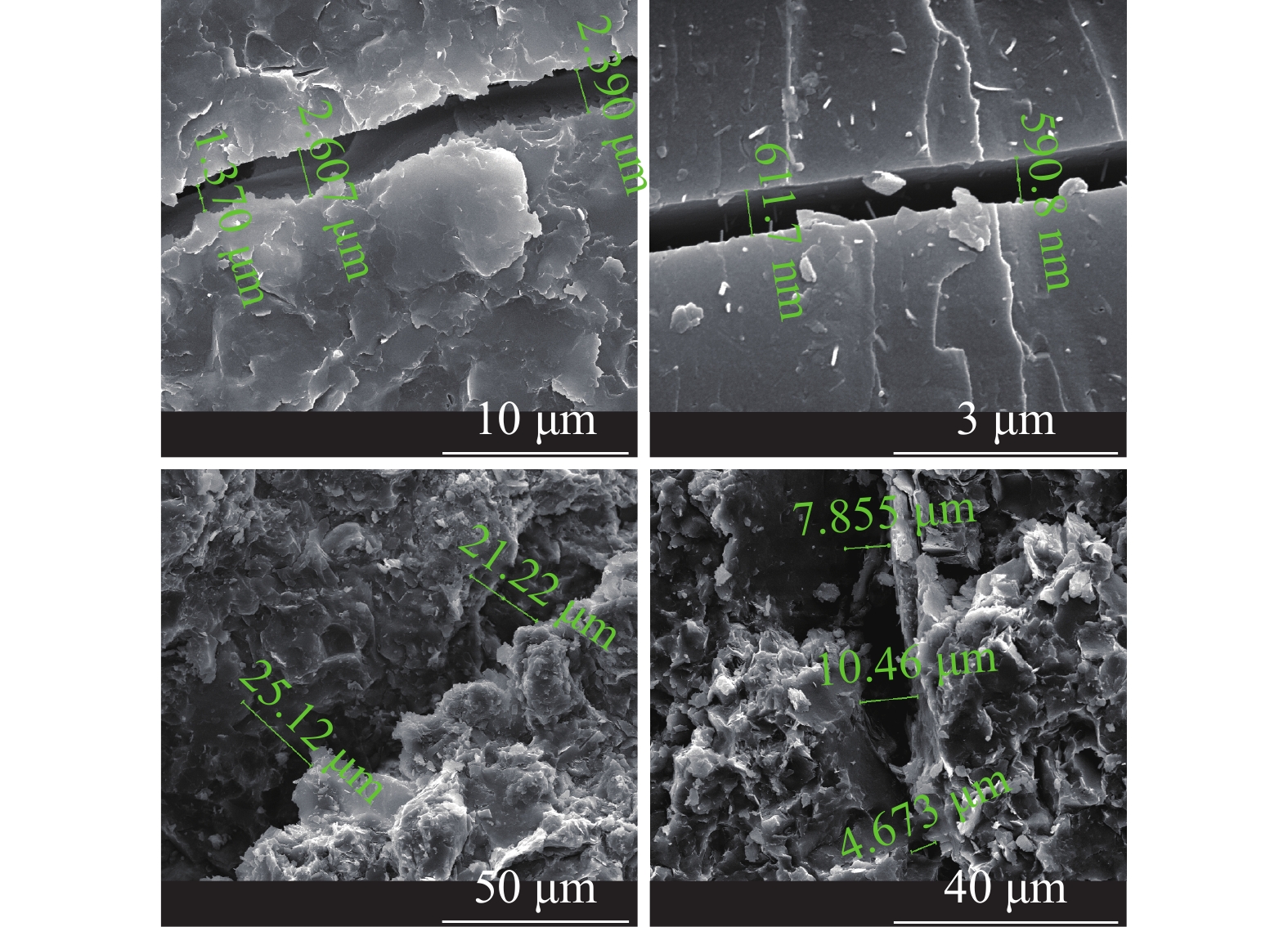
摘要: 在低围压下,硬脆性泥岩在应力状态达到峰值强度前易发生扩容,当应力状态超过扩容强度后,钻井液水化作用对岩石强度的削弱增快增大,引起井壁坍塌,需制定合理的钻井液密度保持井壁稳定性。采用实验研究和理论分析相结合的方法,对硬脆性泥岩组构特征、水理性质、变形规律、强度准则和预应力后的浸泡钻井液强度变化规律进行研究,推导了基于扩容强度准则的硬脆性泥岩的井壁坍塌压力计算模型和参数计算方法,并进行了实例分析。结果表明,钻井液密度高于以峰值强度为准则计算的坍塌压力,低于以扩容强度为准则的坍塌压力,导致井周地层进入扩容状态,井周地层产生应力诱导微裂隙,激发了钻井液水化作用是井壁坍塌的根源。以扩容强度为准则确定坍塌压力,制定钻井液密度更加合理。Abstract: Under low confining pressures, a hard brittle mudstone is easy to dilate before the stress acted on the mudstone reaches its peak value. When the stress is greater than the dilation strength of the shale, the weakening of the mudstone by the hydration of the drilling fluid becomes fast and outstanding, resulting in borehole collapse. To avoid borehole collapse, a reasonable mud weight should be used. Through laboratory experiment and theoretical analysis, studies were conducted on the factors such as the fabric characteristics, hydrophysical properties, deforming patterns and strength criteria of hard brittle mudstones, as well as the change of strengths of mudstones after unloading prestress in a drilling fluid. A computation model and parameter computing method based on rock dilation strength criteria were developed for the collapse pressure of a borehole penetrating hard brittle mudstones, and a case study was conducted. The study results show that the mud weight is greater than the collapse pressure calculated on the basis of peak strength criteria and is lower than the collapse pressure calculated on the basis of dilation strength criteria, the formation around the borehole is in a state of dilation, and stress-induced micro fractures are generated around the wellbore, which stimulates drilling fluid hydration, and this is the root cause for borehole collapse. Based on this knowledge, mud weight determined on the basis of dilation strength criteria is more reasonable.
-
[1] BRADLEY W B. Mathematical concept-stress cloud-can predict borehole failure[J]. Oil Gas J. ;(United States) , 1979, 77:88-92. [2] AADNOY B S, CHENEVERT M E. Stability of highly inclined boreholes (includes associated papers 18596 and 18736)[J]. SPE Drilling Engineering, 1987, 2(4):364-374. doi: 10.2118/16052-PA [3] YEW C H, LIU G. Pore fluid and wellbore stabilities[C]//International Meeting on Petroleum Engineering. Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1992. [4] BAI M, ABOUSLEIMAN Y. Thermoporoelastic coupling with application to consolidation[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 1997, 21(2):121-132. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9853(199702)21:2<121::AID-NAG861>3.0.CO;2-W [5] WANG Y, DUSSEAULT M B. A coupled conductive-convective thermo-poroelastic solution and implications for wellbore stability[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2003, 38(3):187-198. [6] CHENEVERT M E. Shale alteration by water adsorption[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1970, 22(9):1,141-1,148. doi: 10.2118/2401-PA [7] HALE A H, MODY F K, SALLSBURY D P. The influence of chemical potential on wellbore stability[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 1993, 8(3):207-216. [8] VAN OORT E. Physico-chemical stabilization of shales[C]//SPE international symposium on oilfield chemistry. 1997: 523-538. [9] VAN OORT E. Physico-chemical stabilization of shales[C]//SPE international symposium on oilfield chemistry. 1997: 523-538. [10] CHOI S K, TA C P, FREIJ-AYOU R. A Coupled mechanical-thermal-physico-chemical model for the study of time-dependent wellbore stability in shales[J]. Elsevier Geo-Engineering Book Series, 2004, 2:581-586. [11] CHEN G, CHENEVERT M E, SHARMA M M, et al. A study of wellbore stability in shales including poroelastic, chemical, and thermal effects[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2003, 38(3):167-176. [12] ZHOU X, GHASSEMI A. Finite element analysis of coupled chemo-poro-thermo-mechanical effects around a wellbore in swelling shale[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2009, 46(4):769-778. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.11.009 [13] CHAI Z Y, KANG T H, FENG G R. Effect of aqueous solution chemistry on the swelling of clayey rock[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 93:12-16. [14] KAARSBERG E A. Introductory studies of natural and artificial argillaceous aggregates by sound-propagation and X-ray diffraction methods[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1959, 67(4):447-472. doi: 10.1086/626597 [15] JOHNSTON J E, CHRISTENSEN N I. Seismic anisotropy of shales[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B4):5991-6003. doi: 10.1029/95JB00031 -





 下载:
下载: