A New Reservoir Wettability Characterization Method for Fracturing Fluid Performance
-
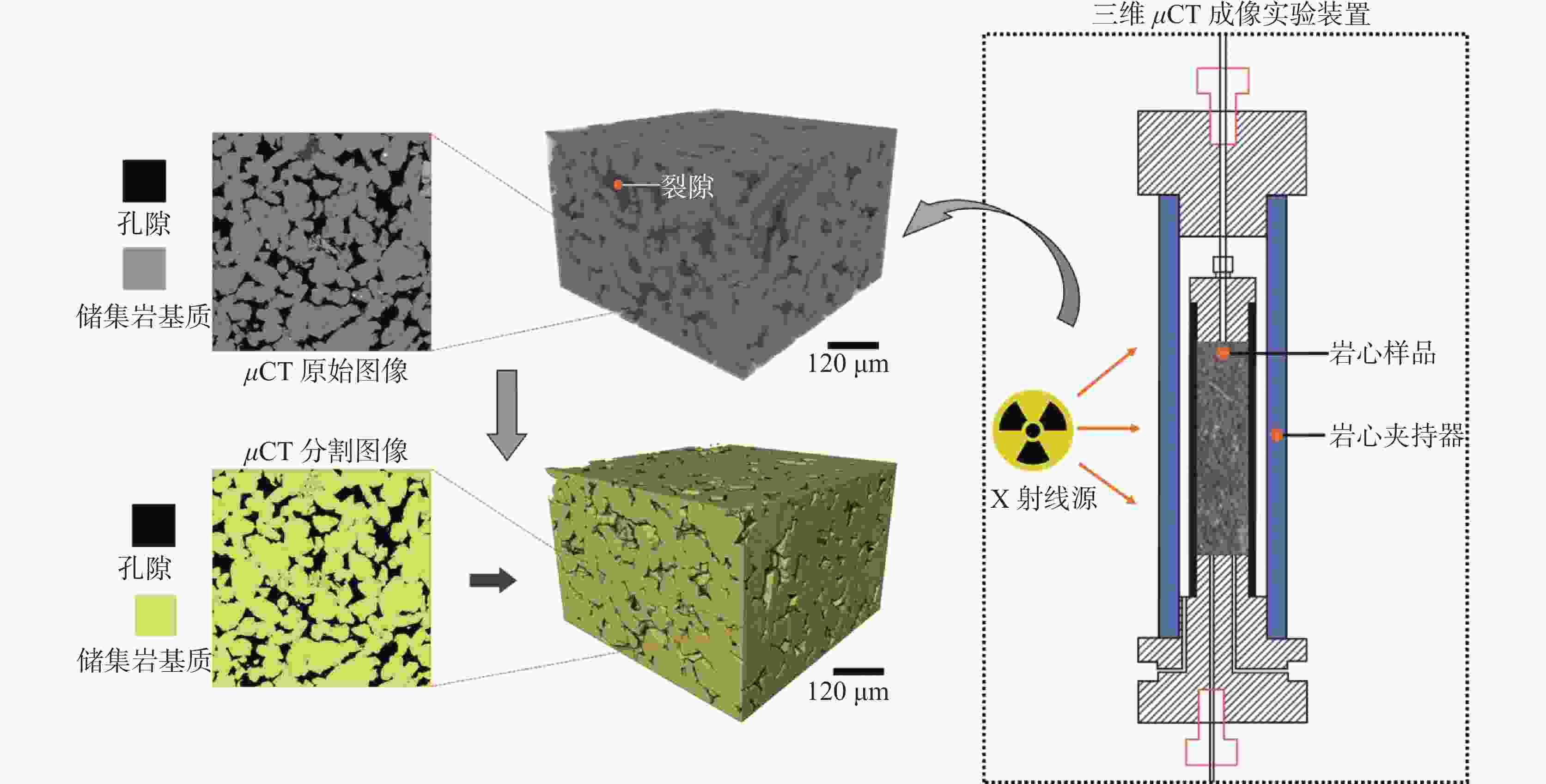
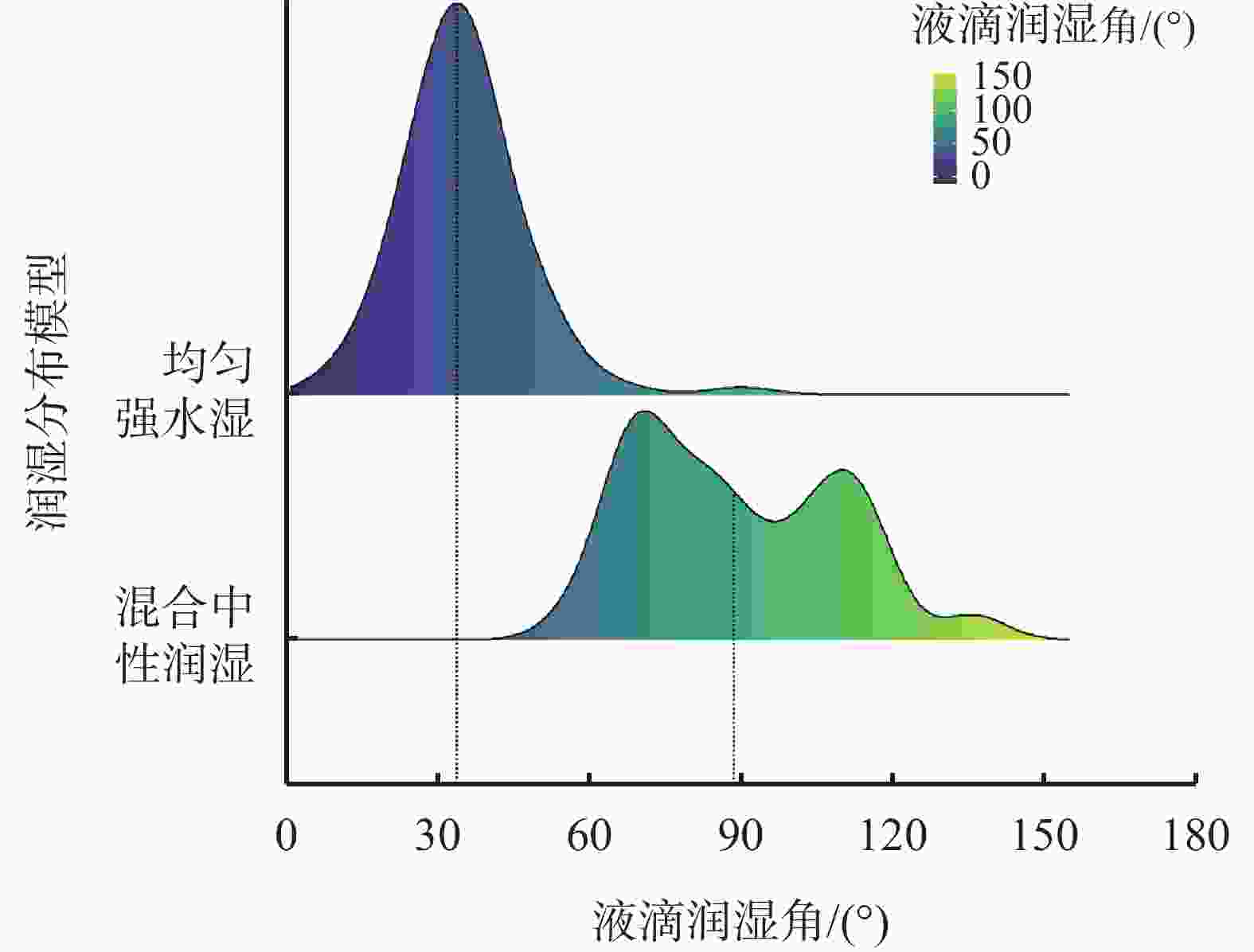
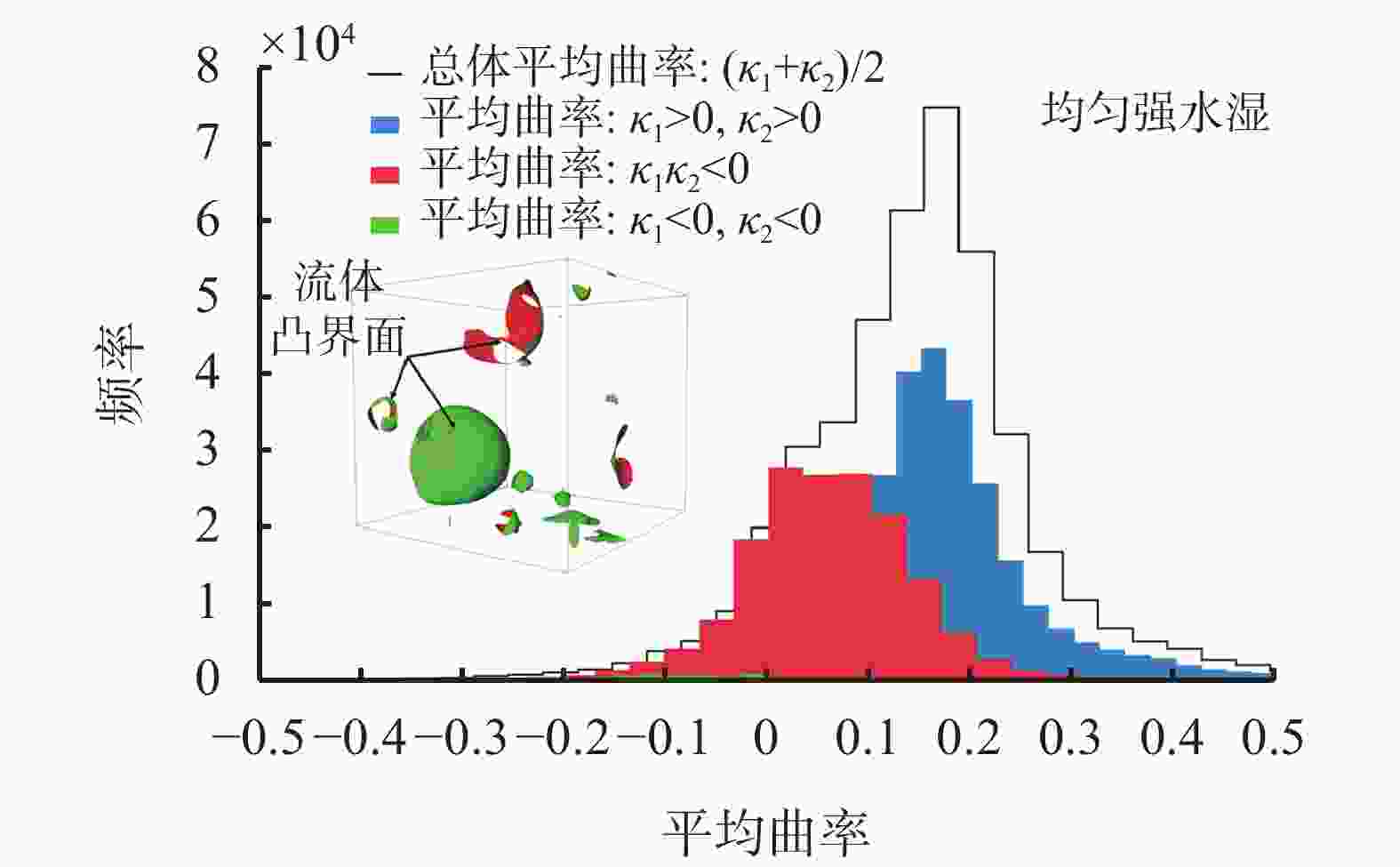
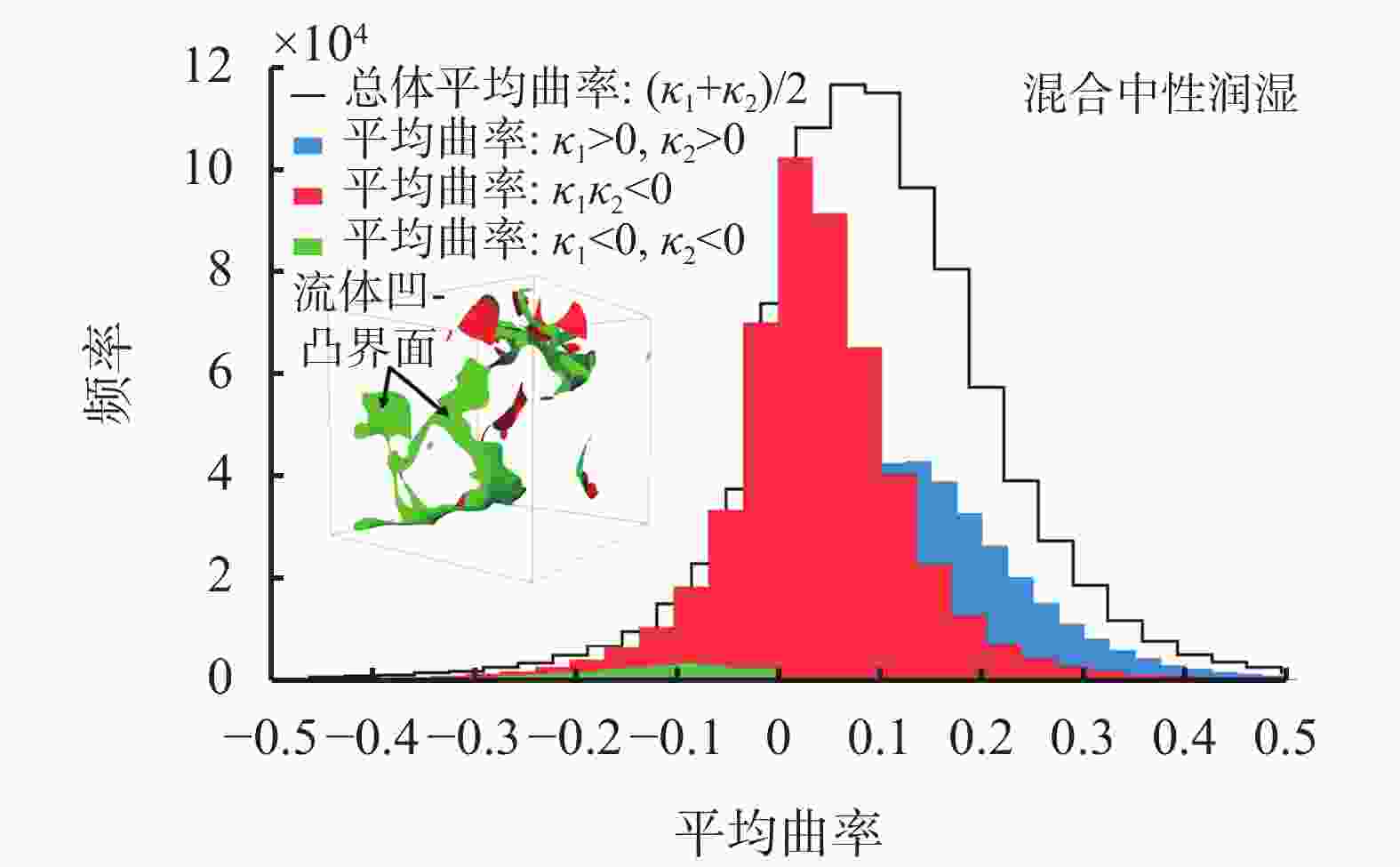
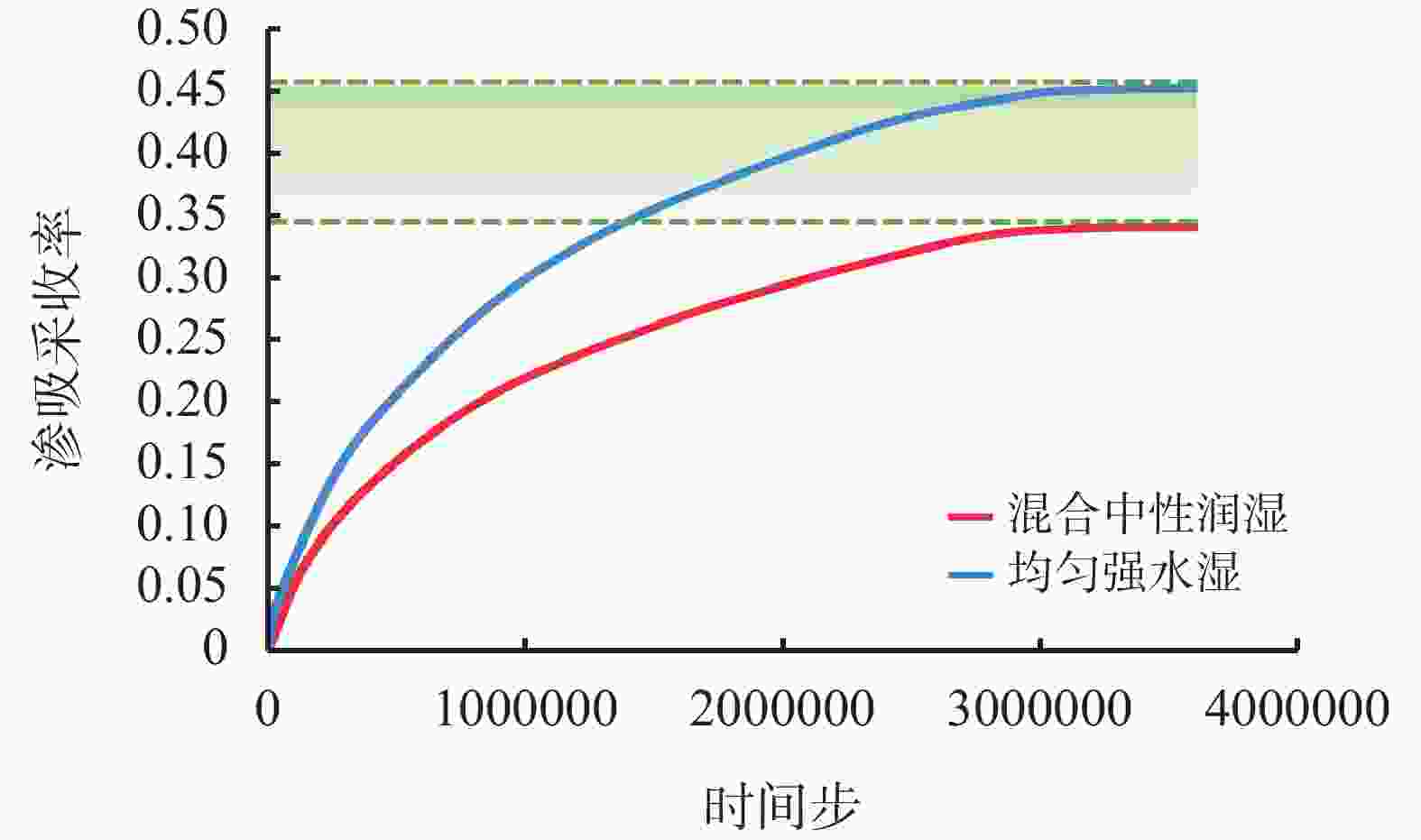
摘要: 非常规油气储层具有孔隙结构复杂、非均质性强以及渗透率低等特点,压裂液在裂隙中的渗流侵入机制由毛细管压力与储层润湿性主导。因此,精确的原位润湿性表征对评价压裂液性能、构建完善的焖井渗吸驱油工艺以及优化压裂液配方等方面具有重要意义与工程应用价值。基于拓扑几何学Gauss-Bonnet定理和三维微观CT成像试验,建立了储层原位润湿性评价新方法。利用数字岩心重构模型和格子玻尔兹曼方法,模拟了压裂液在真实地层内的渗吸驱油过程,研究了储集岩不同的润湿分布对压裂液性能的影响机制。研究结果表明,基于拓扑几何学的润湿性表征方法的精度高达95%以上,同时可实现表征储集岩不同润湿特征的目的。同时,均匀强水湿状态下致密油的采出程度比混合中性润湿状态高33.8%,其渗吸驱油的效果更佳。储层的原始润湿状态通常具有混合润湿的特征,因此需要优化压裂液配方使储层岩石达到润湿改性和增加致密油采出程度的目的。Abstract: Unconventional reservoirs have characteristics of complex pore geometry, high heterogeneity and low permeability. The wetting behavior between the fluid and solid is the dominant factor that controlling the static and dynamic fluid displacements, which is of great crucial for evaluating the fracturing fluid performance, enhancing the oil recovery during the fracturing fluid imbibition, and optimizing the fracturing fluid formulation. In this paper, we propose a new in-situ wettability characterization method based on the Gauss-Bonnet theorem and 3D micro-computed tomography experiments. In addition, we systematically analyze the effect of complex wetting condition on fracturing fluid performance during the imbibition process of fracturing fluids by applying digital rock technology and lattice-Boltzmann method simulations. It is elucidated that the wettability characterization method by the topological principles is more accurate than in-situ microscopic contact angles, of which accuracy is higher than 95%. It is also capable of characterizing the wettability that is influenced by different wetting characteristics. Simultaneously, the tight oil recovery in the homogeneous water-wet reservoir is 33.8% higher than that of mixed-wet reservoirs, which leads to a better performance of fracturing fluid. The initial condition of reservoir is commonly mixed-wet. Therefore, the formulation of fracturing fluid needs to be optimized to reduce the rock wettability and enhance tight oil recovery.
-
Key words:
- Wettability /
- Oil displacement /
- Contact angle /
- Fracturing fluid /
- Imbibition
-
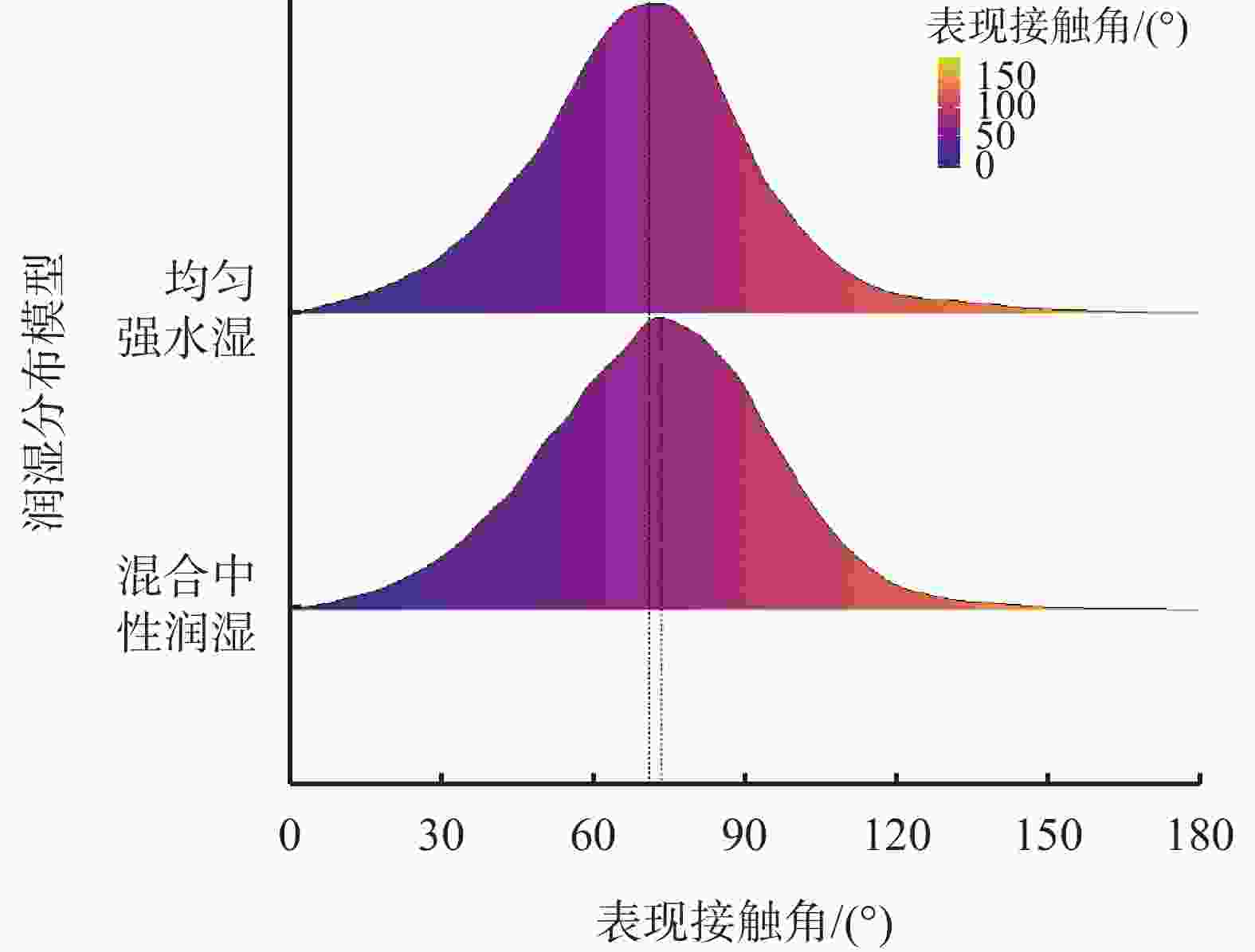
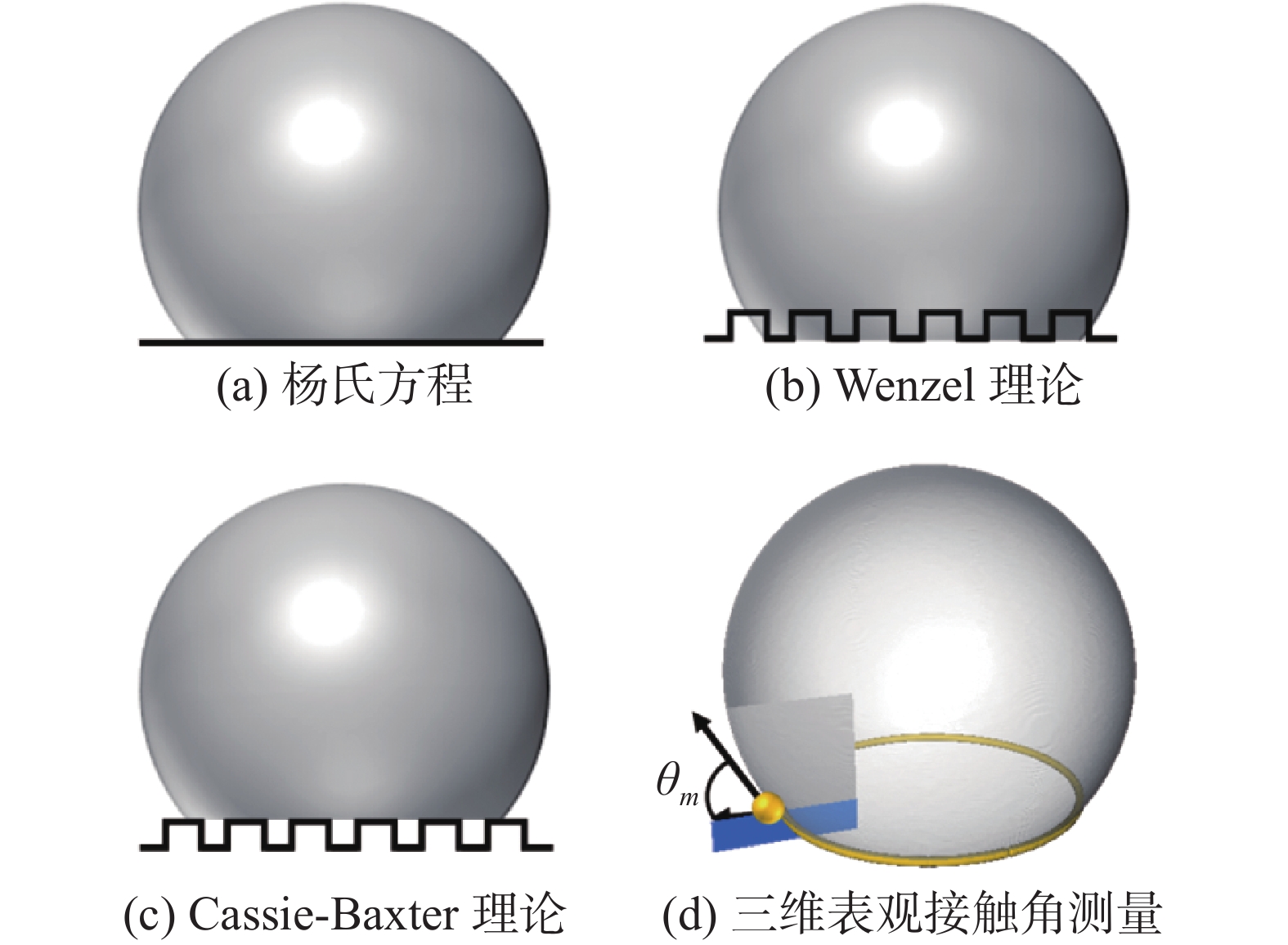
表 1 不同润湿分布模型的本征接触角、 平均θc以及平均θm的表征结果
润湿分布模型 $ {\theta _{\text{in}} } $ $ \overline {\theta _{\text{c}} } $ $ \overline {\theta _{\text{m}} } $ 均匀强水湿 45.57° 34.23° 69.73° 混合中性润湿 84.26° 88.57° 72.12° -
[1] DE GENNES P G. Wetting: Statics and dynamics[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1985, 57(3):827-863. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.57.827 [2] BONN D, EGGERS J, INDEKEU J, et al. Wetting and spreading[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2009, 81(2):739-805. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.81.739 [3] RABBANI H S, ZHAO B Z, JUANES R, et al. Pore geometry control of apparent wetting in porous media[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8:15729. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34146-8 [4] 刘秀婵,陈西泮,刘伟,等. 致密砂岩油藏动态渗吸驱油效果影响因素及应用[J]. 岩性油气藏,2019,31(5):114-120.LIU Xiuchan, CHEN Xipan, LIU Wei, et al. Influencing factors of dynamic imbibition displacement effect in tight sandstone reservoir and application[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(5):114-120. [5] 李小兵,刘莹. 微观结构表面接触角模型及其润湿性[J]. 材料导报,2009,23(24):101-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2009.24.029LI Xiaobing, LIU Ying. Contact angle model and wettability on the surfaces with microstructures[J]. Materials Reports, 2009, 23(24):101-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2009.24.029 [6] 朱定一,张远超,戴品强,等. 润湿性表征体系及液固界面张力计算的新方法(II)[J]. 科学技术与工程,2007,7(13):3063-3069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2007.13.005ZHU Dingyi, ZHANG Yuanchao, DAI Pinqiang, et al. Novel characterization of wetting propertiesand the calculationof liquid-solid interface tension (Ⅱ)[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2007, 7(13):3063-3069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2007.13.005 [7] 林伯韬,史璨,于光哲,等. 风城陆相稠油油砂亲水性及润湿性机理研究[J]. 石油科学通报,2017,2(3):355-363.LIN Botao, SHI Can, YU Guangzhe, et al. Wettability and hydrophilicity of Fengcheng terrestrial oil sand[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2017, 2(3):355-363. [8] 王飞,阮颖琪,陈巧韵,等. 考虑压裂液渗吸换油效应的压裂焖井压降模型[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(6):1250-1257. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.06.17WANG Fei, RUAN Yingqi, CHEN Qiaoyun, et al. A pressure drop model of post-fracturing shut-in considering the effect of fracturing-fluid imbibition and oil replacement[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6):1250-1257. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.06.17 [9] SUN C, MCCLURE J E, MOSTAGHIMI P, et al. Probing effective wetting in subsurface systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(5):e2019GL086151. [10] 管自生,张强. 激光刻蚀硅表面的形貌及其对浸润性的影响[J]. 化学学报,2005,63(10):880-884. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2005.10.002GUAN Zisheng, ZHANG Qiang. Effect of topography on wettability of pulse laser-ablated Si surface[J]. Acta Chimica Sinca, 2005, 63(10):880-884. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2005.10.002 [11] 杨永飞,姚军,VAN DIJKE M I J. 油藏岩石润湿性对气驱剩余油微观分布的影响机制[J]. 石油学报,2010,31(3):467-470. doi: 10.7623/syxb201003021YANG Yongfei, YAO Jun, VAN DIJKE M I J. Effect of reservoir rock wettability on microcosmic distribution of residual oil after gas displacement[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(3):467-470. doi: 10.7623/syxb201003021 [12] 高党鸽,李鹏宇,苏莹,等. 特殊润湿性油水分离材料的研究进展[J]. 精细化工,2021,38(9):1746-1756.GAO Dangge, LI Pengyu, SU Ying, et al. Research progress of oil water separation materials with special wettability[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2021, 38(9):1746-1756. [13] YOUNG T. III. An essay on the cohesion of fluids[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1805, 95:65-87. doi: 10.1098/rstl.1805.0005 [14] WENZEL R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28(8):988-994. [15] CASSIE A B D, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1944, 40:546-551. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [16] ANDREW M, BIJELJIC B, BLUNT M J. Pore-scale contact angle measurements at reservoir conditions using x-ray microtomography[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2014, 68:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.02.014 [17] ALRATROUT A, RAEINI A Q, BIJELJIC B, et al. Automatic measurement of contact angle in pore-space images[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2017, 109:158-169. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.07.018 [18] SCANZIANI A, SINGH K, BLUNT M J, et al. Automatic method for estimation of in situ effective contact angle from x-ray micro tomography images of two-phase flow in porous media[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 496:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.02.005 [19] DALTON L E, TAPRIYAL D, CRANDALL D, et al. Contact angle measurements using sessile drop and micro-ct data from six sandstones[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2020, 133(1):71-83. doi: 10.1007/s11242-020-01415-y [20] JOHNSON JR R E, DETTRE R H. Contact angle hysteresis. III. Study of an idealized heterogeneous surface[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1964, 68(7):1744-1750. doi: 10.1021/j100789a012 [21] MORROW N R. Physics and thermodynamics of capillary action in porous media[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1970, 62(6):32-56. [22] AMOTT E. Observations relating to the wettability of porous rock[J]. Transactions of the AIME, 1959, 216(1):156-162. doi: 10.2118/1167-G [23] TIAB D, DONALDSON E C. Petrophysics: Theory and practice of measuring reservoir rock and fluid transport properties [M]. Houston: Gulf Professional Publishing, 2015. [24] DONALDSON E C, THOMAS R D, LORENZ P B. Wettability determination and its effect on recovery efficiency[J]. SPE Journal, 1969, 9(1):13-20. [25] BLUNT M J, LIN Q, AKAI T, et al. A thermodynamically consistent characterization of wettability in porous media using high-resolution imaging[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 552:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.05.026 [26] MASCINI A, CNUDDE V, BULTREYS T. Event-based contact angle measurements inside porous media using time-resolved micro-computed tomography[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 572:354-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.099 [27] ARMSTRONG R T, SUN C, MOSTAGHIMI P, et al. Multiscale characterization of wettability in porous media[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2021, 140(1):215-240. doi: 10.1007/s11242-021-01615-0 [28] SUN C, MCCLURE J, BERG S, et al. Universal description of wetting on multiscale surfaces using integral geometry[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 608:2330-2338. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.152 [29] CHERN S-S. A simple intrinsic proof of the gauss-bonnet formula for closed riemannian manifolds[J]. Annals of Mathematics, 1944, 45(4):747-752. doi: 10.2307/1969302 [30] SUN C, MCCLURE J E, MOSTAGHIMI P, et al. Linking continuum-scale state of wetting to pore-scale contact angles in porous media[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 561:173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.105 [31] MCCLURE J E, ARMSTRONG R T, BERRILL M A, et al. Geometric state function for two-fluid flow in porous media[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2018, 3(8):084306. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevFluids.3.084306 [32] MCCLURE J E, LI Z, BERRILL M, et al. The LBPM software package for simulating multiphase flow on digital images of porous rocks[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2021, 25(3):871-895. doi: 10.1007/s10596-020-10028-9 [33] MCCLURE J E, PRINS J F, MILLER C T. A novel heterogeneous algorithm to simulate multiphase flow in porous media on multicore cpu-gpu systems[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2014, 185(7):1865-1874. doi: 10.1016/j.cpc.2014.03.012 [34] ARMSTRONG R T, MCCLURE J E, BERILL M A, et al. Flow regimes during immiscible displacement[J]. Petrophysics, 2017, 58(1):10-18. -




 下载:
下载: