Settling Behavior and Drag Coefficient Model of Rock Cuttings of Varied Shapes
-
摘要: 油气钻井中,岩屑颗粒在井筒中自由沉降会引起沉砂卡钻等问题。为了探究岩屑颗粒沉降规律,开展了模拟岩屑颗粒自由沉降实验。利用沉降实验数据和图像处理技术,计算出10种不同形状颗粒在9种非牛顿流体中的沉降末速度与曳力系数,研究了颗粒形状和流变性对沉降的影响规律,并探究了现有曳力系数模型对非球形颗粒在非牛顿流体中的适用性。结果表明,颗粒偏离球形程度越大,在流体中越难沉降。流体黏度增加可有效抑制沉降的发生,且流体非牛顿性越强,对沉降的抑制作用越明显。现有曳力系数模型不适合描述非牛顿流体中非球形颗粒沉降规律,因此,构建了一种新的形状因子,并结合该形状因子建立了新的曳力系数模型。误差分析结果显示,新模型对沉降实验测量数据具有良好的拟合性,决定系数R2大于0.99。较现有模型预测精度提高了50.5%,预测真实岩屑颗粒曳力系数的误差在15%以内,可较好地描述不同形状岩屑颗粒的沉降曳力系数规律,对提高钻井过程中颗粒流体稳定性具有重要理论和现实意义。Abstract: In oil and gas drilling, free settling of drilled cuttings along the wellbore may cause pipe sticking. To investigate the settling behavior of the cuttings particles, laboratory experiment was performed to simulate the free settling of drilled cuttings. Using the data collected in the experiment and image processing technology, the final settling velocities and drag coefficients of 10 kinds of particles of varied shapes in 9 non-Newtonian fluids were calculated and the effects of the particle shape and rheology of the fluids on the settling behavior of the particles were investigated. The adaptability of the existing drag coefficient models to the settling of non-spherical particles in non-Newtonian fluids was also studied. The results of the studies show that the higher the non-sphericity of the particles, the more difficult for them to settle in the fluids. Increase in the viscosity of the fluid can effectively hinder the settling of the particles, and the stronger the non-Newtonian property of the fluids, the stronger the hindrance of the fluids on the settling of the particles. The existing drag coefficient models are not suitable for describing the settling behavior of non-spherical particles in non-Newtonian fluids. To solve this problem, a new shape factor is presented to build a new drag coefficient model. Results of the error analyses of the model show that the new model has excellent fit to the data measured in settling experiment; the coefficient of determination R2 is greater than 0.99. Compared with the existing model the prediction accuracy of the new model is increased by 50.5%, and errors in predicting the drag coefficient of real rock particles are less than 15%. This new model can be used to better describe the settling drag coefficient of rock particles of varied shapes, and has both theoretical and practical significance to improving the stability of rock particles in drilling fluid during drilling operation.
-
Key words:
- Oil and gas drilling /
- Rock particles /
- Free settlement /
- Shape factor /
- Drag coefficient model
-
表 1 实验溶液组分和密度
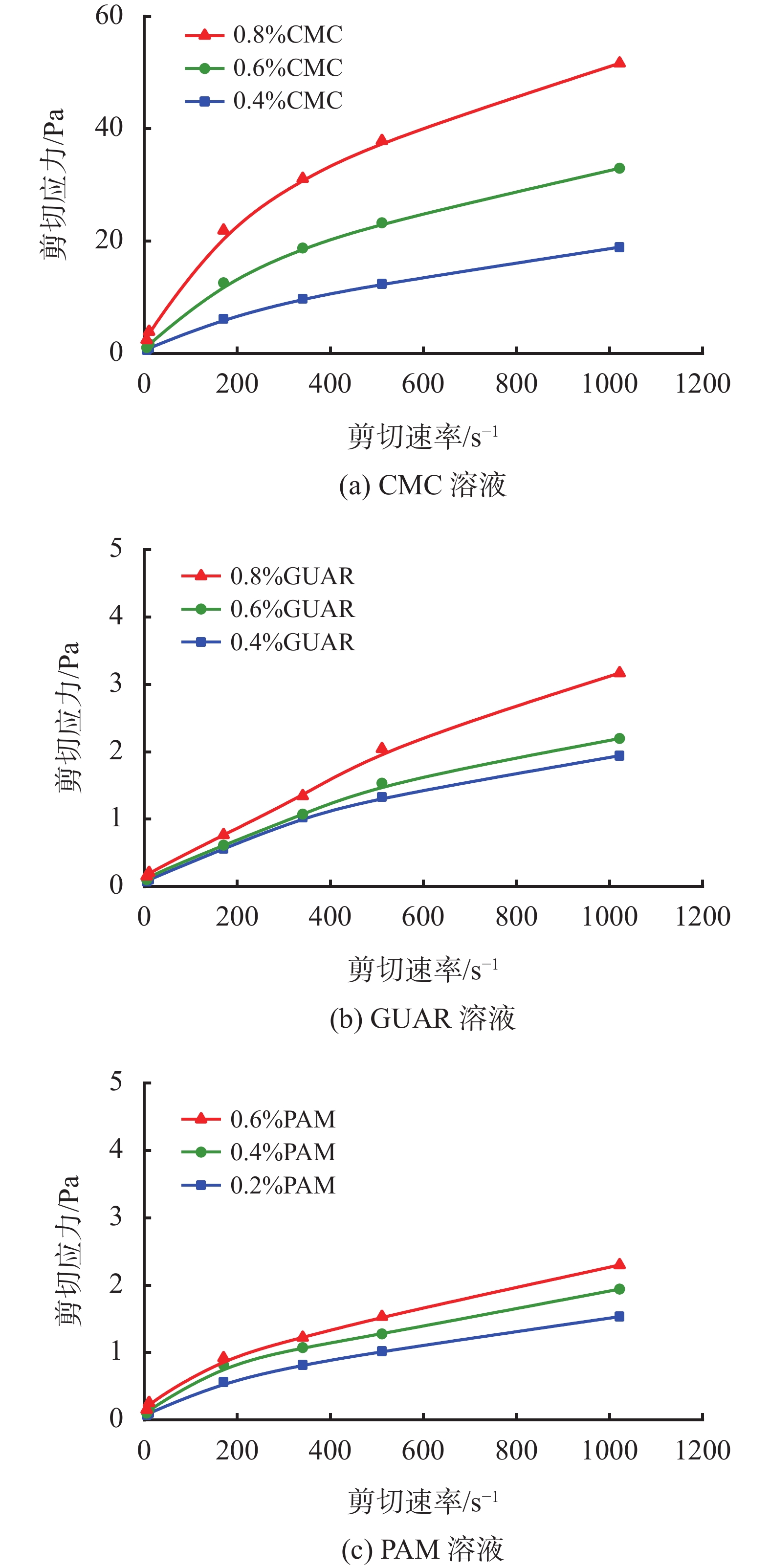
溶液 ρ/(kg·m−3) 溶液 ρ/(kg·m−3) 清水 998.7 0.08%GUAR 1026 0.4%CMC 1025.0 0.12%GUAR 1027 0.6%CMC 1026.0 0.2%PAM 1025 0.8%CMC 1027.0 0.4%PAM 1026 0.04%GUAR 1025.0 0.6%PAM 1027 表 2 实验流体流变参数
溶液 n K/(Pa·sn) 溶液 n K/(Pa·sn) 清水 1.000 0.001 08 0.08%GUAR 0.646 0.025 37 0.40%CMC 0.622 0.254 00 0.12%GUAR 0.711 0.023 44 0.60%CMC 0.551 0.734 70 0.20%PAM 0.557 0.032 75 0.80%CMC 0.499 1.654 00 0.40%PAM 0.523 0.051 04 0.04%GUAR 0.629 0.025 09 0.60%PAM 0.542 0.052 55 表 3 不同形状颗粒形状因子计算结果
颗粒形状 投影面最长轴长度/m 投影面中间轴长度/m 投影面最短轴长度/m 球形度$\varPhi $ 扁平度Fc 新的形状因子${\varPhi _F}$ 球状 0.0112 0.0112 0.0112 1.000 1.000 1.000 椭球状1 0.0105 0.0105 0.0105 0.993 1.000 0.996 椭球状2 0.0100 0.0100 0.0100 0.972 1.000 0.986 椭球状3 0.0097 0.0097 0.0097 0.971 1.000 0.985 八面体状 0.0164 0.0164 0.0164 0.854 1.000 0.924 类盘状1 0.0200 0.0100 0.0050 0.803 0.354 0.533 类盘状2 0.0250 0.0080 0.0050 0.789 0.354 0.528 类盘状3 0.0500 0.0040 0.0050 0.784 0.354 0.526 类圆柱状1 0.0128 0.0100 0.0040 0.639 0.354 0.476 类圆柱状2 0.0166 0.0030 0.0025 0.634 0.354 0.474 圆柱状 0.0200 0.0200 0.0010 0.471 0.050 0.153 盘状 0.0100 0.0100 0.0010 0.471 0.100 0.217 表 4 新的形状因子进行多元非线性拟合结果
a b c d e R2 15.6 0.763 0.267 5904 0.046 0.993 表 5 曳力系数模型预测误差结果
经验模型 预测误差 r s1 s2 Haider模型 52.41% 41.44 5.52 Ganser模型 46.72% 33.18 3.068 新的曳力系数模型 22.10% 6.55 1.59 -
[1] X ZHU, Y H ZENG. Settling velocity of non-spherical hydrochorous seeds[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2017(8):99-107. [2] 朱坤娥,秦树辰,郑朝振,等. 浸出矿浆固液分离过程中颗粒的沉降行为研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分),2019(11):7-11.ZHU Kun’e, QIN Shuchen, ZHENG Chaozhen, et al. Study on particle settlement behavior of leachate slurry during solid-liquid separation[J]. Non-ferrous Metals (Smelting Section) , 2019(11):7-11. [3] 马林虎. 钻斜井中防止岩屑沉积的研究[J]. 钻采工艺,1992,15(1):4-7.MA Linhu. Research on preventing cuttings deposition in inclined well drilling[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 1992,15(1):4-7. [4] 刘建坤,吴峙颖,吴春方,等. 压裂液悬砂及支撑剂沉降机理实验研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(3):378-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.03.020LIU Jiankun, WU Zhiying, WU Chunfang, et al. Experiment study on the mechanisms of sand suspension and settling of proppant in fracturing fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(3):378-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.03.020 [5] 潘谊党,于培志,马京缘. 高密度钻井液加重材料沉降问题研究进展[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(1):1-9.PAN Yidang, YU Peizhi, MA Jingyuan. Review on settlement problem of drilling fluid weighting materials[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(1):1-9. [6] 霍洪俊,王瑞和,倪红坚,等. 超临界二氧化碳在水平井钻井中的携岩规律研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2014,42(2):12-17.HUO Hongjun, WANG Ruihe ,NI Hongjian, et al. Cuttings carrying pattern of supercritical carbon dioxide in horizontal wells[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(2):12-17. [7] 李莅临, 杨进, 路保平, 等. 深水水合物试采过程中地层沉降及井口稳定性研究[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2020, 48(5): 61-68.LI Lilin, YANG Jin, LU Baoping, et al. Research on stratum settlement and wellhead stability in deep water during hydrate production testing[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2020, 48(5): 61-68. [8] STOKES G G. On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums[J]. Mathematical and Physical Papers, 1851, 3:1-10. [9] RUBEY W W. Settling velocity of gravel, sand, and silt particles[J]. American Journal of Science, 1933(148):325-338. [10] HAIDER A, LEVENSPIEL O. Drag coefficient and terminal velocity of nonspherical particles[J]. Powder Technology, 1989(1):63-70. [11] GANSER G H. A rational approach to drag prediction of spherical and nonspherical particles[J]. Powder Technology, 1993(2):143-152. [12] CAMENEN B B R D. Simple and general formula for the settling velocity of particles[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007(2):229-233. [13] 孙晓峰,纪国栋,冯松林,等. 幂律流体中岩屑颗粒沉降速度实验[J]. 断块油气田,2016(1):120-124. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201601027SUN Xiaofeng, JI Guodong, FENG Songlin, et al. Experimental study on the sedimentation velocity of cuttings in power law fluid[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016(1):120-124. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt201601027 [14] 范茏,杨超,禹耕之,等. 大长径比细长颗粒的沉降实验和曳力系的关联[J]. 化工学报,2003(10):1501-1503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2003.10.009FAN Long, YANG Chao, YU Geng, et al. Experimental study on the settlement of slender particles with large aspect ratio and its correlation with drag system[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2003(10):1501-1503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2003.10.009 [15] CHHABRA R P. Motion of spheres in power law (viscoinelastic) fluids at intermediate Reynolds numbers: a unified approach[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing, 1990(2):89-94. [16] COREY A T. Influence of shape on the fall velocity of sand grains[D]. Colorado State University, 2019. [17] BAGHERI G H G B, BONADONNA C, MANZELLA I, et al. On the characterization of size and shape of irregular particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2015(12):141-153. [18] XIANZHI S , ZHENGMING X. A new model for predicting drag coefficient and settling velocity of spherical and non-spherical particle in Newtonian fluid[J]. Powder Technology, 2017(321):242-250. -





 下载:
下载: