Analyses of the Ballooning Effect and its Affecting Factors in Drilling Shallow Formations in Deep Water
-
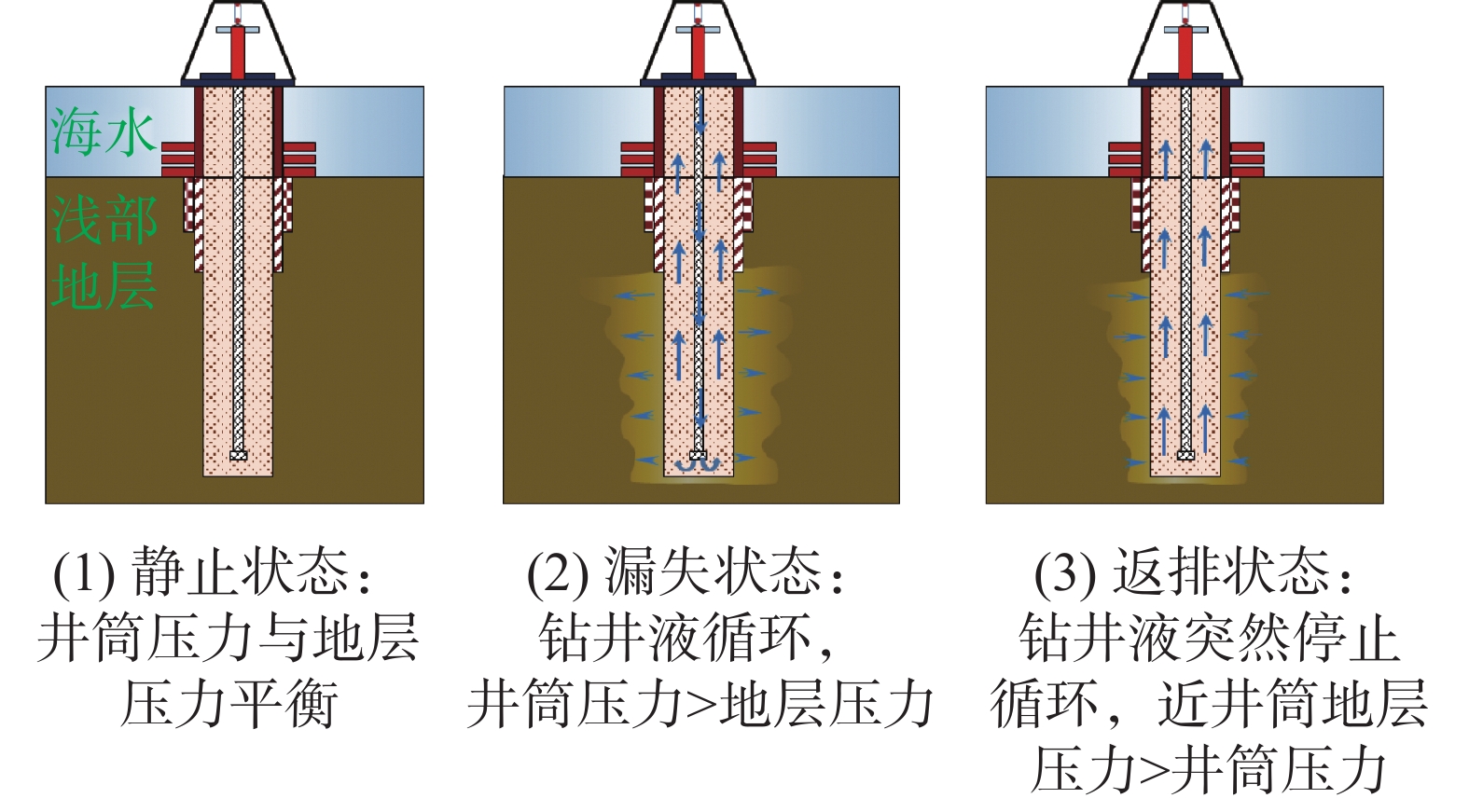
摘要: 对地层呼吸效应误判为井涌而采取压井措施容易造成恶性漏失,会提高深水作业的风险与成本,对深水钻井的安全高效造成了严重的危害。因此,对深水浅层呼吸效应机理开展研究,并利用COMSOL软件,模拟深水浅层钻井过程中呼吸效应的全过程,研究地层特性、钻井液性质和压差对呼吸效应的影响。模拟结果表明,深水浅层呼吸效应属于渗透性机理;低弹性模量、低泊松比、高孔高渗地层极易发生渗透性呼吸效应,而使用高黏度、高动切力钻井液,采用小压差(低密度钻井液、低排量等)形式钻进,有利于抑制呼吸效应的程度。因此,在低弹性模量、低泊松比、高孔高渗地层钻进时,需提前做好措施,如加入降滤失剂、降低泵速等,以减少地层呼吸效应带来的影响。研究成果能为深水浅层呼吸效应判别及预防和控制方案提供一定参考。Abstract: Ballooning effect encountered during drilling is easy to be taken as well kick and the well is then killed. This operation often results in severe mud losses, increasing the risks and costs and causing serious harm to the safety and efficiency of deep-water drilling. To solve this problem, the mechanisms of ballooning effect was studied, and the COMSOL software was used to simulate the whole process of ballooning during drilling in the shallow formations in deep water area. The effects of formation characteristics, drilling fluid properties and pressure differential on the ballooning effect were studied. The simulation results have shown that the ballooning effect taking place in the shallow formations in deep water area is a permeable mechanism. The permeable ballooning effect is very easy to happen in formations with low elastic modulus, low Poisson’s ratio, high porosity and high permeability. This kind of ballooning effect can be inhibited with high viscosity high yield point drilling fluids, and drilling with low pressure differentials (low density, low flow rate). Thus, when drilling formations with low elastic modulus, high Poisson’s ratio, low porosity and high permeability, measures should be ready in advance, for example, treating the mud with filter loss reducers, reducing pump rate, to minimize the impact of the ballooning effect. This study is of reference importance to the identification, prevention and plan for the controlling of ballooning effect encountered in shallow formations in deep water area.
-
表 1 模拟井参数及其数值
参数 值 参数 值 地层弹性模量E/GPa 3 钻井液黏度μ/Pa·s 0.02 地层泊松比v 0.3 钻井液动切力τ/Pa 3 地层孔隙度φ 0.2 地层孔隙压力pp/MPa 10 地层渗透率k/m2 1×10−12 井底循环压力pe/MPa 10.3 Biot系数α 0.8 井筒直径ϕ/m 0.2159 表 2 验证井参数及其取值
参数 值 参数 值 地层弹性模量E/GPa 3 钻井液黏度μ/mPa·s 12×10−3 地层泊松比v 0.35 钻井液动切力τ/Pa 3 地层孔隙度φ 0.4 Biot系数α 0.8 地层渗透率k/m2 3.2×10−12 井筒直径ϕ/m 0.66 井底循环压力pe/MPa 10.23 地层孔隙压力pp/MPa 9.89 表 3 模拟结果及误差分析
阶段 实际情况/m3 模拟情况/m3 误差/% 漏失阶段 3.96 3.78 4.55 反排阶段 1.35 1.21 10.37 总漏失 2.61 2.57 1.53 -
[1] 江怀友,潘继平,鲁庆江,等. 世界海洋石油工业勘探现状与方法[J]. 石油知识,2008(5):7-9.JIANG Huaiyou, PAN Jiping, LU Qingjiang, et al. Current situation and methods of offshore oil industry exploration in the world[J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2008(5):7-9. [2] 杨进,曹式敬. 深水石油钻井技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2008,30(2):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2008.02.002YANG Jin, CAO Shijing. Current situation and developing trend of petroleum drilling technologies in deep water[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2008, 30(2):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2008.02.002 [3] 李军,杨宏伟,张辉,等. 深水油气钻采井筒压力预测及其控制研究进展[J]. 中国科学基金,2021,35(6):973-983. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2021.06.016LI Jun, YANG Hongwei, ZHANG Hui, et al. Progress of basic research on wellbore pressure control in deepwater onl and gas drilling and production[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2021, 35(6):973-983. doi: 10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2021.06.016 [4] 高热雨. 深水地层呼吸效应机理及安全密度窗口优化研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2022.GAO Reyu. Formation mechanism of deep water borehole breathing and optimization method of safe density window[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2022. [5] LAVROV A, TRONVOLL J. Mechanics of borehole ballooning in naturally-fractured formations: SPE middle east oil and gas show and conference[C]//Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2005. [6] GILL J A. How borehole ballooning alters drilling responses[J]. Oil Gas J.(United States) , 1989. [7] HELSTRUP O A, RAHMAN M K, HOSSAIN M M, et al. A practical method for evaluating effects of fracture charging and/or ballooning when drilling high pressure, high temperature (HPHT) wells[C]//SPE/IADC drilling conference. OnePetro, 2001. [8] ATKIN T. Numerical modelling to estimate the amount of formation deformation and its effect on cement integrity[D]. University of Leoben, 2019. [9] ELMGERBI A, THONHAUSER G, ROOHI A, et al. General analytical solution for estimating the elastic deformation of an open borehole wall[J]. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2016, 7(1):1056. [10] BABU D. R. Effect of P–ρ–T behavior of muds on loss/gain during high-temperature deep-well drilling[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 1998, 20(1–2):49-62. doi: 10.1016/S0920-4105(98)00003-5 [11] AADNOY B. S. Modern well design[M]. CRC Press, 2010. [12] YUAN Z, MORRELL D, MAYANS A G, et al. Differentiate drilling fluid thermal expansion, wellbore ballooning and real kick during flow check with an innovative combination of transient simulation and pumps off annular pressure while drilling[C]//IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro, 2016. [13] 王欢欢,杨进,刘正礼,等. 深水浅层固井胶结强度影响因素分析[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2019,41(3):277-282. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2019.03.003WANG Huanhuan, YANG Jin, LIU Zhengli, et al. Analysis on the influential factors about the cementing strength of shallow cementing in deep water[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 41(3):277-282. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2019.03.003 [14] 闫博. 海底浅层土力学特性与声波特征关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.YAN Bo. Experimental study on the relations between acoustic velocity with physical and mechanical properties of seabed sediments[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. [15] 孙东征. 深水浅层安全钻井液密度窗口预测技术及工程应用[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2019,41(5):573-579. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2019.05.004SUN Dongzheng. The technology for predicting the safety density window of drilling fluidin deepwater shallow layers and its engineering application[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2019, 41(5):573-579. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2019.05.004 [16] 陈卓. 深水浅部弱固结地层力学性质研究及其在工程实践中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.CHEN Zhuo. Study on Mechanical Properties of Weakly Consolidated Deep Water Shallow Sediment and Its Application in Engineering[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. [17] 邹德永,赵建,郭玉龙,等. 渗透性砂岩地层漏失压力预测模型[J]. 石油钻探技术,2014,42(1):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2014.01.006ZOU Deyong, ZHAO Jian, GUO Yulong, et al. A model for predicting leak-off pressure in permeable-sandstone formations[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(1):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2014.01.006 [18] 孙玉学,李城里,白相双,等. 应用数值模拟软件探究动滤失影响因素[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(5):581-586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.05.010SUN Yuxue, LI Chengli, BAI Xiangshuang, et al. Study on factors affecting filtration property of drilling fluid with numerical simulation software[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(5):581-586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.05.010 [19] 屈亚光,巩旭,石康立,等. 页岩储层压裂液渗吸及返排机理研究进展[J]. 当代化工,2020(11):2532-2535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.11.038QU Yaguang, GONG Xu, SHI Kangli, et al. Research progress of imbibition and backflow mechanism of fracturing fluids in shale reservoirs[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020(11):2532-2535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.11.038 [20] LIETARD O. Permeabilities and skins in naturally fractured reservoirs: An overview and an update for wells at any deviation[C]//SPE European Formation Damage Conference. OnePetro, 1999. -





 下载:
下载: