Study on Viscoelastic Sand-carrying Mechanism and Imbibition Performance of Nano Variable-viscosity Slickwater
-
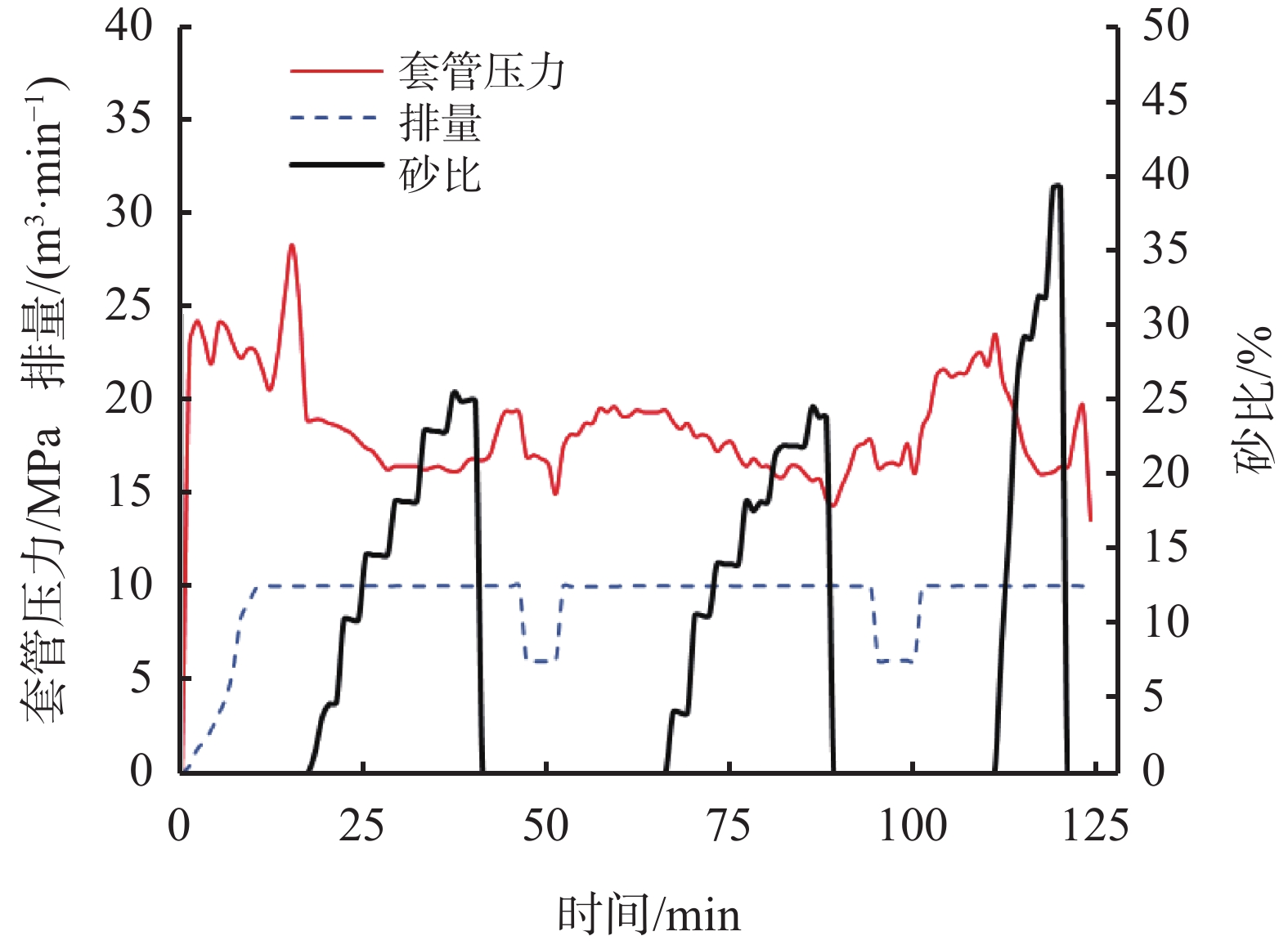
摘要: 纳米变黏滑溜水作为一种具有良好携砂性能和渗吸置换作用的新型压裂液体系,已成功应用于长庆油田页岩油体积压裂施工,现场试验结果表明其具有良好的携砂性能以及增产效果,40 %砂比条件下加砂过程压力平稳,压裂施工完成后单井日产油量可达11.31 t,但其携砂机理与渗吸性能尚不明确。因此对现场使用浓度的纳米变黏滑溜水与常规EM30S可交联滑溜水体系进行室内实验研究,通过动态携砂运移、透射电镜(TEM)、流变性能评价以及储层温压条件下的带压渗吸等实验方法,揭示了纳米变黏滑溜水的携砂机理并评价了其渗吸性能。实验结果表明,滑溜水弹性模量与黏性模量的交点值反映了滑溜水溶液的携砂性能,交点值越小,其弹性携砂性能越强;相同黏度下的纳米变黏滑溜水CNI体系黏弹模量交点值仅为0.0741 Hz,远低于现场用滑溜水EM30S的0.181 Hz,致使其静态和动态弹性携砂性能远高于EM30S;电镜结果表明纳米乳液与变黏滑溜水存在强化缔合结构是滑溜水的弹性携砂性能增强的主要原因。此外,带压渗吸实验结果显示,纳米变黏滑溜水具有良好的渗吸置换性能,能够置换出页岩纳米孔隙中的原油,整体采收率可达36 %;其中,不同孔隙类型的采收率排序依次为:介孔>微孔>宏孔。Abstract: As a new fracturing fluid system with good sand-carrying performance and imbibition displacement, nano variable-viscosity slickwater has been successfully applied to shale oil volume fracturing in Changqing Oilfield. The field test results show that it has good sand-carrying performance and stimulation effect. Under the condition of 40 % sand ratio, the pressure of sand adding process is stable, and the daily oil production of a single well can reach 11.31 tons after fracturing construction, but its sand-carrying mechanism and imbibition performance are not clear. In this paper, the laboratory experimental study on the field concentration of nano variable-viscosity slickwater and the conventional EM30S crosslinkable slickwater system is carried out. Through the experimental methods of dynamic sand-carrying migration, transmission electron microscope (TEM), rheological property evaluation, and pressurized imbibition under the condition of reservoir temperature and pressure, the sand-carrying mechanism of nano variable-viscosity slickwater is revealed and its imbibition performance is evaluated. The experimental results show that the intersection value of elastic modulus and viscous modulus of slickwater reflects the sand-carrying capacity of slickwater solution. The smaller the intersection value is, the stronger the elastic sand-carrying capacity is; Under the same viscosity, the intersection value of viscoelastic modulus of nano variable-viscosity slickwater CNI system is only 0.0741 Hz, which is far lower than 0.181 Hz of field slickwater EM30S, resulting in its static and dynamic elastic sand-carrying performance much higher than EM30S; TEM results show that the strengthening association structure between nano emulsion and variable-viscosity slickwater is the main reason for the enhancement of elastic sand-carrying performance of slickwater. In addition, the results of pressure imbibition experiment show that the nano variable-viscosity slickwater has good imbibition displacement performance, and can replace the crude oil in the nano pores of shale, and the overall recovery can reach 36%. Among them, the order of recovery efficiency of different pore types is: mesopore > micropore > macropore.
-
表 1 两种滑溜水的模量和沉降时间、平衡高度比较(1 Hz对应,20 L/min排量、40%砂比)
滑溜水及其浓度 交点/ Hz G’/ Pa 沉降时
间/s砂堤平衡
高度/ cm0.10% CNI-A+
0.10% CNI-B0.0800 0.284 57.18 23 0.10% CNI-A+
0.30% CNI-B0.0741 0.4628 223.10 15 0.10% CNI-A+
0.60% CNI-B0.0100 3.444 1041.06 8 表 2 岩心物性参数
岩心编号 长度/
cm直径/
cm孔隙度/
%渗透率/
mD1 5.030 2.54 8.3356 0.030 8 2 5.010 2.52 8.3212 0.030 3 表 3 核磁扫描横向弛豫时间与孔隙半径转换
T2/ms R/nm 孔隙类型 0.01≤T2≤0.1 R<2 微孔 0.1<T2≤2.5 2<R≤50 介孔 T2>2.5 R>50 宏孔 -
[1] 张锋三,沈一丁,王磊,等. 聚丙烯酰胺压裂液减阻剂的合成及性能[J]. 精细化工,2016(35):1422-1427.ZHANG Fengsan, SHEN Yiding, WANG Lei, et al. Synthesis and properties of polyacrylamide fracturing fluid drag reducer[J]. Fine Chemical Industry, 2016(35):1422-1427. [2] 姜在兴,张文昭,梁超,等. 页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J]. 石油学报,2014,35(1).JIANG Zaixing, ZHANG Wenzhao, LIANG Chao, et al. Basic characteristics and evaluation elements of shale oil reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2014, 35(1). [3] SCANLON B R, et al. Comparison of water use for hydraulic fracturing for unconventional oil and gas versus conventional oil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014. [4] GUO J, YANG L, WANG S. Adsorption damage and control measures of slick-water fracturing fluid in shale reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(2):148-154. [5] 杜凯,黄凤兴,伊卓,等. 页岩气滑溜水压裂用降阻剂研究与应用进展[J]. 中国科学:化学,2014,44(11):1696-1704.DU Kai, HUANG Fengxing, YI Zhuo, et al. Research and application progress of resistance reducer for shale gas slick water fracturing[J]. Chinese Science:Chemistry, 2014, 44(11):1696-1704. [6] 张文龙,伊卓,杜凯,等. 水溶性减阻剂在页岩气滑溜水压裂中的应用进展[J]. 石油化工,2015,44(1):121-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2015.01.034ZHANG Wenlong, YI Zhuo, DU Kai, et al. Application progress of water-soluble drag reducer in shale gas slick water fracturing[J]. Petrochemical Industry, 2015, 44(1):121-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2015.01.034 [7] 李永飞,王彦玲,曹勋臣,等. 页岩储层压裂用减阻剂的研究及应用进展[J]. 精细化工,2018,35(1):7-15.LI Yongfei, WANG Yanling, CAO Xunchen, et al. Research and application progress of drag reducer for shale reservoir fracturing[J]. Fine Chemical Industry, 2018, 35(1):7-15. [8] BRITT L, SMITH M, HADDAD Z, et al. Waterfracs: We do need proppant after all[C]. SPE 102227, 2006. [9] CHUNG H, HU T, YE X, et al. A friction reducer: self-cleaning to enhance conductivity for hydraulic fracturing[C]. SPE 170602, 2014. [10] 郭钢. 长庆油田致密油全程携砂低黏滑溜水压裂液减阻剂合成及应用[C]// 2017IPPTC国际石油石化技术会议.GUO Gang. Synthesis and application of drag reducer for full process sand carrying low viscosity slick water fracturing fluid in Changqing Oilfield [C]// 2017 ipptc International Petroleum and Petrochemical Technology Conference. [11] GOMAA A, GUPTA D, CARMAN P. Proppant transport? Viscosity is not all it’s cracked up to be[C]. SPE 173323, 2015. [12] 霍丙夏. 快速增黏滑溜水降阻剂的研制[D]. 天津科技大学, 2016.HUO Bingxia. Development of fast viscosity increasing slickwater drag reducer[D]. Tianjin University of science and technology, 2016 [13] LIU JUNRONG, JAMES J SHENG. Investigation of countercurrent imbibition in oil-wet tight cores using NMR technology[J]. SPE J, 2020, 25:2601-2614. [14] JIANG, YUN, SHI, et al. Experimental study on spontaneous imbibition under confining pressure in tight sandstone cores based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurements[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018. [15] 温庆志,翟恒立,罗明良,等. 页岩气藏压裂支撑剂沉降及运移规律实验研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2012,19(6):4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.025WEN Qingzhi, ZHAI Hengli, LUO Mingliang, et al. Experimental study on fracturing proppant settlement and migration in shale gas reservoir[J]. Oil and Gas Geology and Recovery, 2012, 19(6):4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2012.06.025 [16] 王海燕,霍丙夏,郭丽梅,等. 快速增黏滑溜水降阻剂的性能研究[J]. 应用化工,2016,45(12):2229-2233,2237.WANG Haiyan, HUO Bingxia, GUO Limei, et al. Study on the performance of rapid viscosity increasing slick water drag reducer[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(12):2229-2233,2237. [17] ESHRATI M, AL-HASHMI AR, AL-WAHAIBI T, et al. Drag reduction using high molecular weight polyacrylamides during multiphase flow of oil and water: A parametric study[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 135:403-409. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.09.028 [18] DAI C, WANG X, LI Y, et al. Spontaneous imbibition investigation of self-dispersing silica nanofluids for enhanced oil recovery in low-permeability cores[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(3):2663-2668. [19] LI Y, Dai C, ZHOU H, et al. Investigation of spontaneous imbibition by using a surfactant-free active silica water-based nanofluid for enhanced oil recovery[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 32(1):287-293. [20] 李继山. 表面活性剂体系对渗吸过程的影响 [D]. 廊坊: 中国科学院研究生院(渗流流体力学研究所), 2006.LI Jishan. Effect of surfactant system on infiltration process [D]. Langfang: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of seepage hydrodynamics), 2006. -





 下载:
下载: