| [1] |
WANG H, LI G, SHEN Z. A feasibility analysis on shale gas exploitation with supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. Energy Sources, 2012, 34:1426-1435. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2010.529570
|
| [2] |
ROGALA A, KRZYSIEK J, BERNACIAK M, et al. Non-aqueous fracturing technologiesfor shale gas recovery[J]. Physicochem Problems Mineral Process, 2012, 49(1):313-322.
|
| [3] |
LEE J Y, WEINGARTEN M, GE S. Induced seismicity: the potential hazard from shale gas development and CO2, geologic storage[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2016, 20(1):137-148. doi: 10.1007/s12303-015-0030-5
|
| [4] |
王香增,孙晓,罗攀,等. 非常规油气CO2压裂技术进展及应用实践[J]. 岩性油气藏,2019,31(2):4-10.WANG Xiangzeng, SUN Xiao, LUO Pan, et al. Progress and application of CO2 fracturing technology for unconventional oil and gas[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(2):4-10.
|
| [5] |
黄 程,霍丽如,吴辰泓. 基于非常规油气开发的CO2资源化利用技术进展及前景[J]. 非常规油气,2022,9(1):1-9.HUANG Cheng, HUO Liru, WU Chenhong. Progress and prospect of CO2 resource utilization technology based on unconventional oil and gas development[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2022, 9(1):1-9.
|
| [6] |
郭兴,孙晓,穆景福,等. 超临界CO2压裂井筒传热规律[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(6):782-789.GUO Xing, SUN Xiao, MU Jingfu, et al. Heat transfer in wellbores fractured with supercritical CO2 fracturing fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(6):782-789.
|
| [7] |
陈祉娉,王长权,位予瑄,等. 基于干法压裂的CO2与致密储层置换规律的研究[J]. 非常规油气,2021,8(6):106-111.CHEN Zhiping, WANG Changquan, WEI Yuxuan, et al. Study on replacement law of CO2 and tight reservoirbased on dry fracturing[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2021, 8(6):106-111.
|
| [8] |
杨洪,李彦林,郭庆,等. VF-8 清洁二氧化碳泡沫前置液压裂工艺在延长气井的应用[J]. 非常规油气,2015(4):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2015.04.009YANG Hong, LI Yanlin, GUO Qing, et al. Application of VF-8 clean CO2 foam pad fluid fracturing technology to Yanchang gas wells[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2015(4):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2015.04.009
|
| [9] |
穆景福,高志亮,张 力,等. 清水和液态CO2压裂对页岩破裂影响实验研究[J]. 非常规油气,2021,8(5):87-92.MU Jingfu, GAO Zhiliang, ZHANG Li, et al. Experimental study of the effect of water and liquid CO2 fracturing on shale fracture morphology[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2021, 8(5):87-92.
|
| [10] |
GUO X, NI H, LI M, et al. Experimental study on the influence of supercritical carbon dioxide soaking pressure on the mechanical properties of shale[J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 2018, 48(2):384-391. doi: 10.1007/s40098-017-0289-8
|
| [11] |
BINGBAI, HONG-JIANNI, XIANSHI, et al. The experimental investigation of effect of supercritical CO2 immersion on mechanical properties and pore structure of shale[J]. Energy, 2021, 228:1.
|
| [12] |
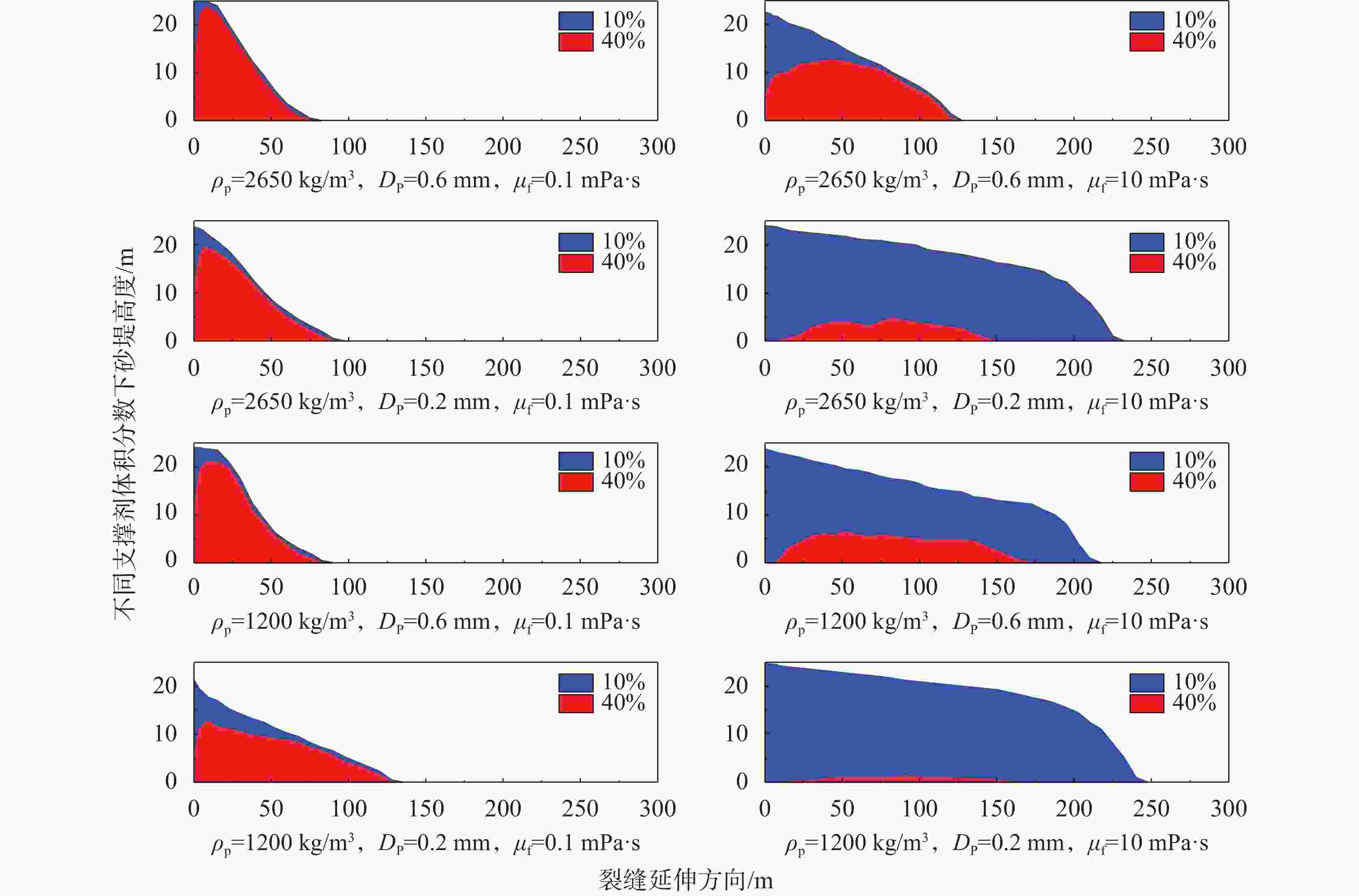
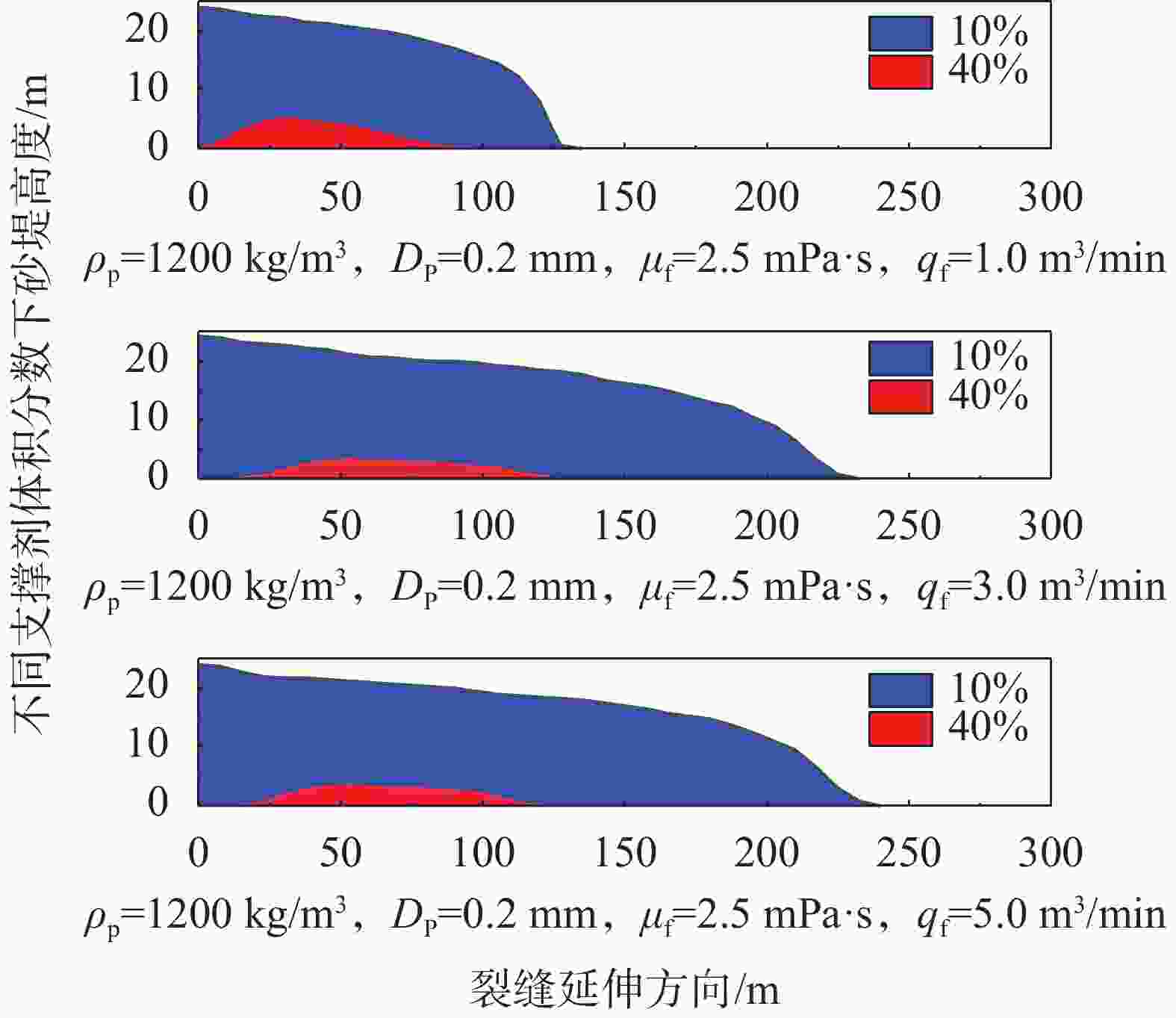
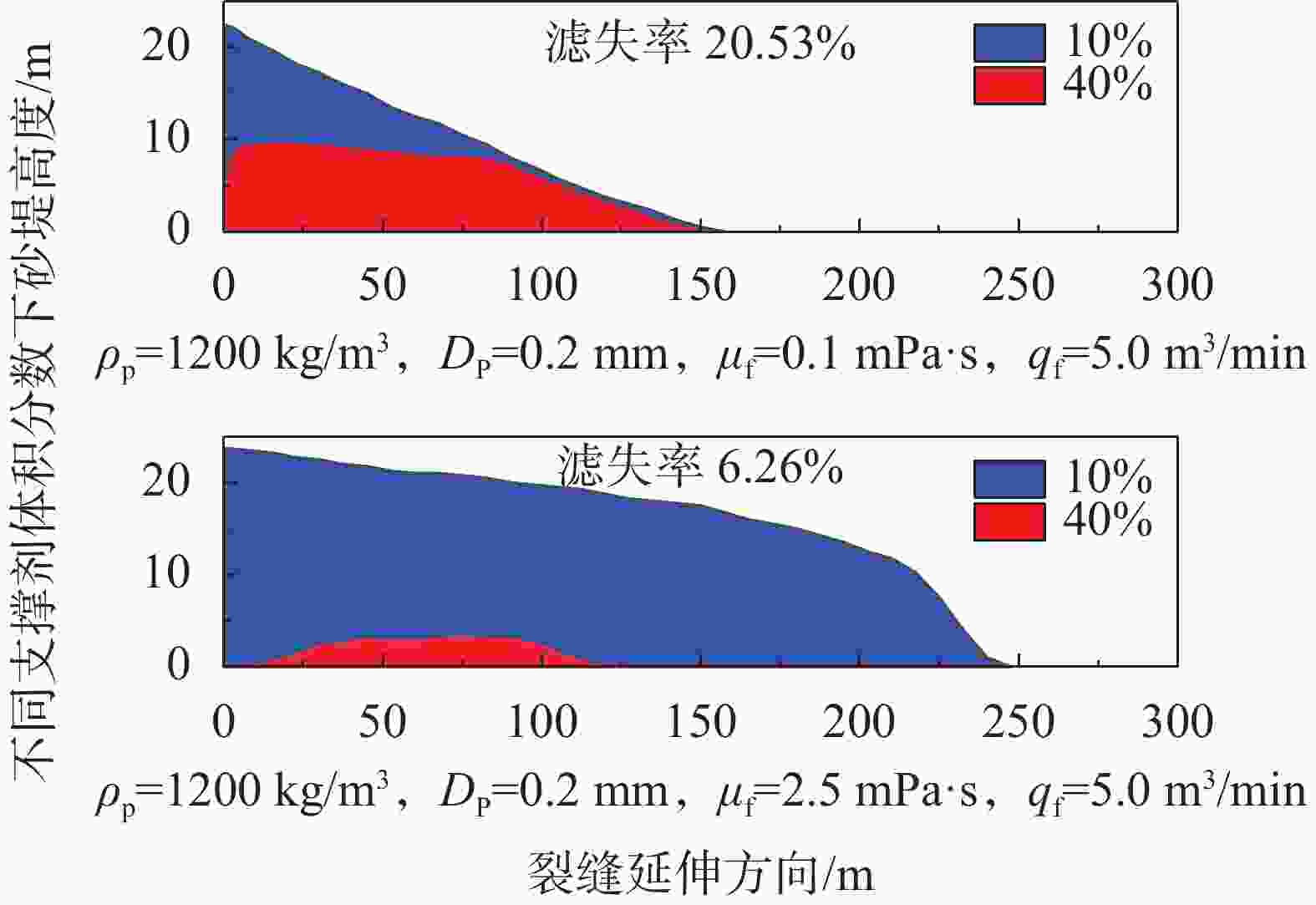
王猛,王海柱,李根生,等. 超临界CO2压裂缝内携砂数值模拟[J]. 石油机械,2018,46(11):72-78.WANG Meng, WANG Haizhu, LI Gensheng, et al. Numerical Study of Proppant Transport with Supercritical CO2 in Fracture[J]. CHINA PETROLEUM MACHINERY, 2018, 46(11):72-78.
|
| [13] |
ZENG J, LI H, ZHANG D. Numerical simulation of proppant transport in hydraulic fracture with the upscaling CFD-DEM method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 33:264-277.
|
| [14] |
JUNSHENG ZENG, HENG LI, DONGXIAO ZHANG. Numerical simulation of proppant transport in hydraulic fracture with the upscaling CFD-DEM method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2016, 33:264-277.
|
| [15] |
JUNSHENG ZENG, HENG LI, DONGXIAO ZHANG. Numerical simulation of proppant transport in propagating fractures with the multi-phase particle-in-cell method[J]. Fuel, 2019, 245:316-335. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.02.056
|
| [16] |
PATANKAR N A, JOSEPH D D. Lagrangian numerical simulation of particulate flows[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2001, 27(10):1685-1706. doi: 10.1016/S0301-9322(01)00025-8
|
| [17] |
CROWE CLAYTON T, SCHWARZKOPF JOHN D, SOMMERFELD MARTIN, et al. Multiphase flows with droplets and particles[M]. 2nd ed. CRC Press; 2012.
|
| [18] |
GU M, MOHANTY K K. Effect of foam quality on effectiveness of hydraulic fracturing in shales[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2014, 70:273-285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.05.013
|
| [19] |
ROOSTAEI M, NOURI A, FATTAHPOUR V. Numerical simulation of proppant transport in hydraulic fractures[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 163:119-138. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.044
|
| [20] |
O’ROURKE PJ, SNIDER DM. An improved collision damping time for MP-PIC calculations of dense particle flows with applications to polydisperse sedimenting beds and colliding particle jets[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(22):6014-6028. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.08.032
|
| [21] |
O’ROURKE PJ, SNIDER DM. A new blended acceleration model for the particle contact forces induced by an interstitial fluid in dense particle/fluid flows[J]. Powder Technol, 2014, 256:39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.01.084
|
| [22] |
SNIDER D M. An incompressible three-dimensional multiphase particle-in-cell model for dense particle flows[J]. Journal of computational physics, 2001, 170(2):523-549. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2001.6747
|
| [23] |
WEN C Y, YU Y H. Mechanics of Fluidization[J]. Chem. Eng. Process. Symp. Ser., 1966, 162:100-110.
|
| [24] |
VESOVIC V, WAKEHAM W A, OLCHOWY G A, et al. The transport properties of carbon dioxide[J]. Journalof Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1990, 19(3):763-808. doi: 10.1063/1.555875
|
| [25] |
PERKINS T K, KERN L R. Widths of hydraulic fractures[J]. Journal of petroleum technology, 1961, 13(9):937-949. doi: 10.2118/89-PA
|
| [26] |
NORDREN R P. Propagation of a vertical hydraulic fracture[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1972, 12(4):306-314.
|




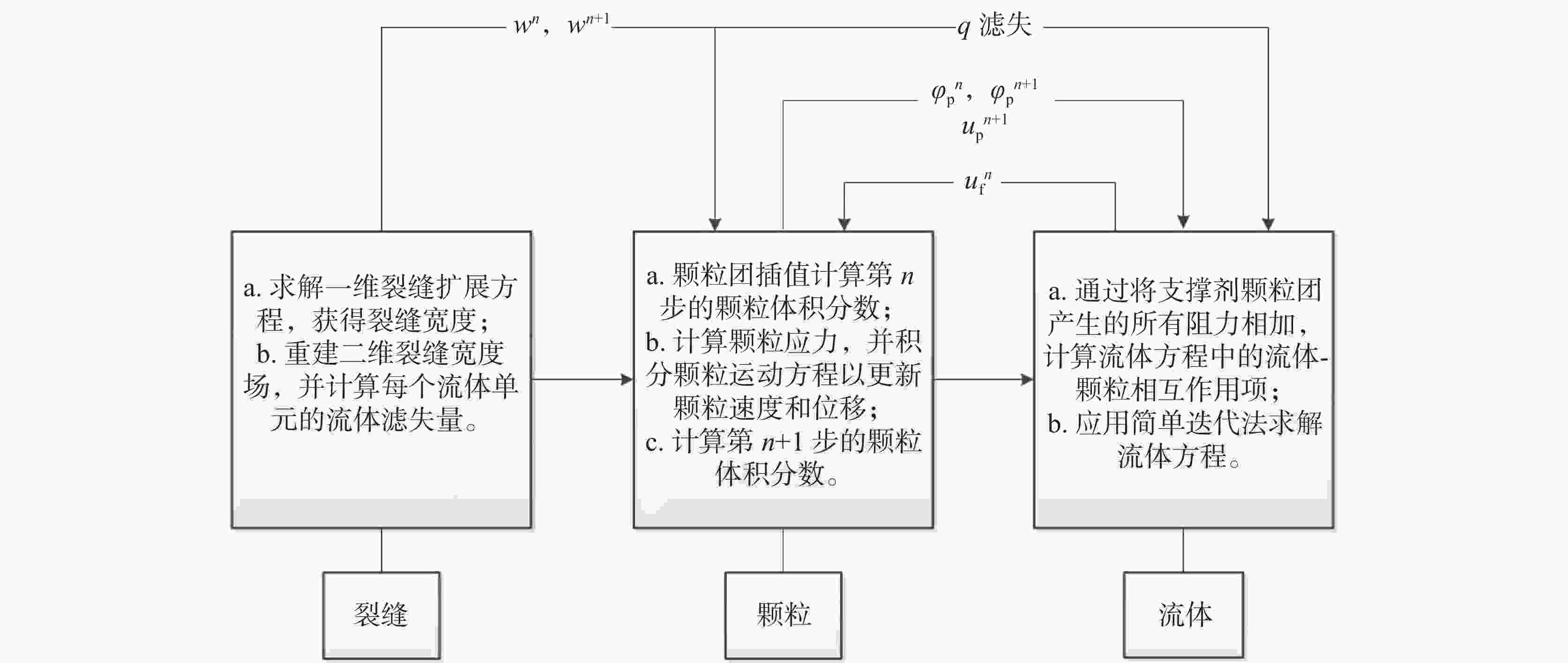
 下载:
下载: