Development and Application of a Protective Agent for Tight Oil and Gas Reservoirs
-
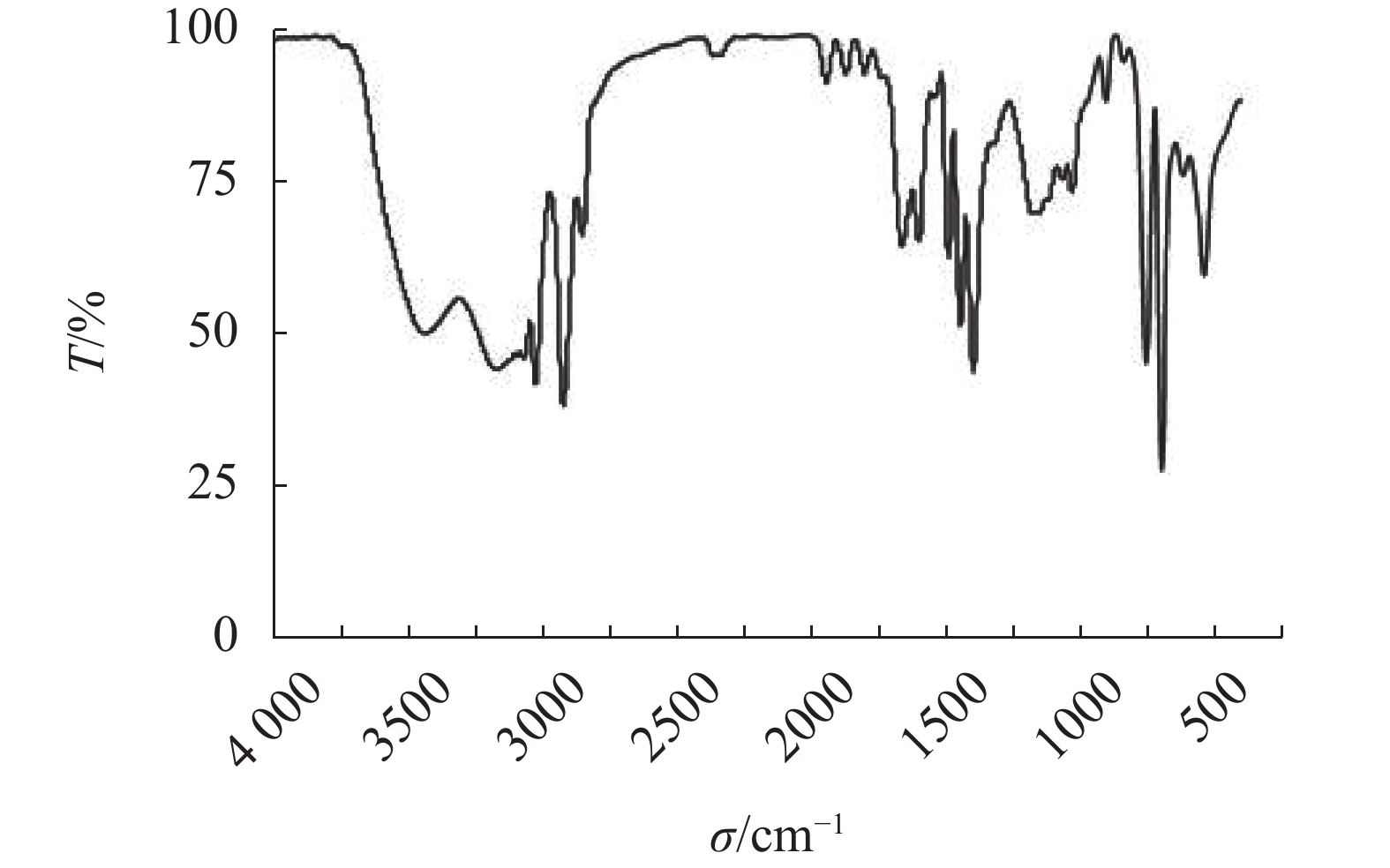
摘要: 在新疆本布图油田的勘探开发过程中,时常发生水层及油气层井段井径不规则,严重影响固井质量,损害了油气层。为了钻采过程中满足对本布图油田储层保护的要求,采用无肥皂乳液聚合法合成了聚合物弹性微球NWL,并对其进行了表征,另外优选了防水锁剂。将NWL、防水锁剂、微米级的刚性酸溶性颗粒(CaCO3)、石油树脂C9按照一定比例进行复配,得到了储层保护剂CBJ。并评价了CBJ与地层裂缝孔隙适配性、酸溶性与油溶性、与现有钻井液配伍性的评价和储层保护效果,并进行了现场实验。结果表明,CBJ满足地层裂缝孔隙封堵粒径大小的要求,具有良好的酸溶性与油溶性,API滤失量下降了20%左右,渗透率恢复值达80%以上,现场实验效果良好。研究结果表明,CBJ具有良好的储层保护性能,能够因地制宜地保护本布图油田储层,最大限度地提高油井产量。Abstract: In developing the Benbutu oilfield in Xinjiang, hole size irregularities were often encountered in the water- and hydrocarbon-containing sections, and these greatly affect the quality of the cementing job and damage the reservoirs. To protect the oil and gas reservoirs in the Benbutu oilfield, an elastic polymer microsphere NWL was developed through soap-free emulsion polymerization and was characterized. A reservoir protective agent CBJ was formulated with NWL, a selected anti water-block agent, a kind of rigid acid soluble nanometer particles (CaCO3) and a petroleum resin in a certain quantity ratio. Laboratory experiment was conducted to evaluate CBL in the aspects such as: the compatibility of CBL with the sizes of formation fractures, the acid solubility and oil solubility of CBL, the compatibility of CBL with the drilling fluids presently used, and the reservoir protection performance of CBL. CBL was also tested in field operations. CBL has the particle size distribution that is suitable for plugging formation fractures, good acid solubility and oil solubility. Drilling fluids treated with CBL have filtration rate reduced by about 20%, and percent permeability recovery by more than 80%. Field application and laboratory study show that CBL has good reservoir protection effect, it can be used to protect the reservoirs of Benbutu oilfield in accordance with the local conditions and maximize the production of oil wells.
-
表 1 防水锁剂的表面张力测定
样品 CMC/% σCMC/(mN·m−1) 与模拟地层水配伍性 PFWD 0.50 35.29 好 JPZ-2 0.20 54.43 好 JZP-3 0.20 47.83 较好 OP-10 0.20 31.21 好 OP-15 0.20 32.64 好 XY-W 0.20 28.65 好 SATRO 0.20 31.01 好 S2 0.40 40.14 好 S3 0.75 40.14 好 F4 0.15 31.73 好 F5 0.25 31.06 不好 F6 0.50 37.74 好 F7 0.75 42.07 好 F9 0.75 42.07 好 F10 0.50 34.86 良 HAR 0.50 30.62 好 表 2 表面活性剂起泡及乳化性能的评价
表面活性剂 加量/% 起泡性能 乳化性能 浊度 PFWD 1.0 弱 轻度乳化 11.1 OP-10 1.0 强 严重乳化 16.5 XY-W 0.5 强 严重乳化 39.5 SATRO 1.0 弱 轻度乳化 8.5 F4 1.0 强 明显乳化 42.3 F10 0.5 强 严重乳化 36.7 HAR 0.5 不起泡 不产生乳化 2.0 表 3 本部图油田储层不同层孔喉分布区间表
孔喉缝隙/μm 不同层位孔喉缝隙百分比/% 26-3 26-2 1-2 19-2 7-2 57-1 42-3 25-1 5-2 1-1 T15 14-1 平均 >75 0.38 0.39 0.40 0.38 1.20 0.52 0.35 0.71 0.61 0.66 0.30 0.51 0.53 75~30 0.37 0.08 0.20 0.26 0.09 0.13 0.26 0.19 0.06 0.20 0.30 0.18 0.19 30~15 0.51 0.24 0 0.13 0.09 0.40 0 0.25 0.06 0.07 0 0.22 0.16 10~15 0.37 0.39 0.27 0.31 0 0.01 0.26 0.20 0.30 0.20 0.30 0.12 0.23 10~7.5 0.13 0 0.34 0.07 0.10 0.12 0.35 0.32 0 0.19 0.08 0.07 0.15 >7.5 1.76 1.10 1.21 1.15 1.48 1.18 1.22 1.67 1.03 1.31 0.98 1.20 1.27 7.5-2.5 0.37 0.63 0.79 10.62 4.15 5.94 0.96 0.32 0.73 0.79 1.12 14.01 3.37 2.5~0.94 1.13 4.32 21.37 21.98 29.80 22.49 18.05 23.10 17.29 22.02 15.47 20.23 18.10 0.94~0.44 5.40 24.44 12.93 13.98 14.21 12.43 10.64 16.68 12.56 14.00 12.31 12.30 13.49 0.44~0.11 22.47 29.86 22.29 21.74 21.23 21.58 19.63 23.93 21.72 20.59 19.52 18.12 21.89 0.11~0.02 15.82 19.88 15.77 12.31 11.07 15.56 20.14 17.74 18.87 18.87 14.86 11.09 16.00 <0.02 53.05 19.77 25.64 18.22 18.06 20.82 29.36 16.56 27.80 22.41 35.74 23.15 25.88 注:M-m为孔喉缝隙最大值-孔喉缝隙最小值 表 4 室温下油气层保护剂CBJ在煤油中随时间的溶解率
t/
hI号暂堵剂 Ⅱ号暂堵剂 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 油溶率/% 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 油溶率/% 1 19.8 溶液澄清 1.0 19.8 溶液澄清 1.0 12 19.5 溶液澄清 2.5 19.4 溶液澄清 3.0 24 19.2 溶液澄清 4.0 19.1 溶液微浑浊 4.5 48 18.8 溶液微浑浊 6.0 18.9 溶液微浑浊 5.5 72 18.4 溶液微浑浊 8.0 18.5 溶液微浑浊 7.5 表 5 80 ℃下油气层保护剂CBJ在煤油中随时间的溶解率
t/
hI号暂堵剂 Ⅱ号暂堵剂 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 油溶率/% 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 油溶率/% 1 19.7 溶液澄清 1.5 19.7 溶液澄清 1.5 12 19.4 溶液澄清 3.0 19.3 溶液澄清 3.5 24 19.1 溶液澄清 4.5 19.0 溶液澄清 5.0 48 18.6 溶液微浑浊 7.0 18.6 溶液微浑浊 7.0 72 18.1 溶液微浑浊 9.5 18.2 溶液微浑浊 9.0 表 6 室温下油气层保护剂CBJ在15%HCl中随时间的溶解率
t/h I号暂堵剂 Ⅱ号暂堵剂 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 酸溶率/% 溶解后重量/g 溶液状态 酸溶率/% 1 10.2 溶液澄清 49.0 10.0 溶液澄清 50.0 12 5.3 溶液澄清 73.5 5.2 溶液澄清 74.0 24 3.8 溶液澄清 81.0 3.8 溶液澄清 81.0 48 3.7 溶液澄清 81.5 3.7 溶液澄清 81.5 72 3.6 溶液澄清 82.0 3.7 溶液澄清 81.5 表 7 油气层保护剂CBJ与河南钻井液的配伍性
CBJ/
%老化
条件AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/PaFLAPI/
mLpH 0 老化前 31.0 20.5 10.5 3.0/8.5 5.0 9 120 ℃、16 h 33.5 22.0 11.5 3.0/9.0 10.6 9 1 老化前 34.0 22.5 11.5 3.0/8.5 4.7 9 120 ℃、16 h 35.5 23.5 12.0 3.0/9.5 8.5 9 2 老化前 35.0 23.0 12.0 3.0/8.5 4.2 9 120 ℃、16 h 36.5 23.5 13.5 3.0/9.5 6.1 9 3 老化前 35.5 23.0 12.5 3.0/8.5 3.0 9 120 ℃、16 h 37.5 24.5 13.0 3.0/9.5 5.4 9 表 8 钻井液暂堵深度评价
钻井液体系类型 岩心编号 岩心长度Lo/
cmK0/
mD截取长度Li/
cm截取后剩下段渗透率Ki/
mD侵入深度/
cm河南钻井液 253 5.96 0.129 3.12 0.121 ≥3.0 河南钻井液+2%CBJ 75 6.12 0.125 1.10 0.120 ≤1.10 表 9 CBJ加量对河南钻井液体系的储层保护效果
CBJ/
%岩心 K0/
mDKd/
mDKd/K0/
%暂堵实验条件 压差/MPa t/min T/℃ 0 368 0.122 0.0879 72.00 3.5 120 90 1 210 0.157 0.1250 79.62 3.5 120 90 2 342 0.206 0.1750 84.95 3.5 120 90 3 313 0.125 0.1080 86.40 3.5 120 90 表 10 现场钻井液性能
井深/
mρ/
g·cm−3FLAPI/
mLPV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/PaCs/
%pH 固相含量/
%摩擦
系数2500 1.11 5.3 21.3 9 2.0/8.0 0.2 10.0 4.0 0.3946 2615 1.12 5.2 20.9 10 4.0/10.5 0.2 9.0 4.5 0.4017 2636 1.13 5.4 21.1 12 3.0/9.5 0.2 8.5 5.0 0.3946 2880 1.13 5.0 21.7 11 2.5/9.5 0.3 9.0 5.0 0.4017 3009 1.14 5.4 23.7 12 2.0/8.0 0.3 9.0 5.5 0.3946 3140 1.15 5.3 23.5 12 2.5/8.0 0.2 9.0 5.0 0.4017 3314 1.15 5.4 23.3 11 2.5/8.0 0.2 8.5 5.5 0.4017 3423 1.15 5.2 23.3 13 2.5/8.0 0.2 9.0 5.0 0.4017 3554 1.14 5.4 24.1 12 3.0/9.5 0.3 9.0 5.0 0.4017 3671 1.14 5.4 23.7 13 3.0/9.5 0.2 9.0 5.0 0.4017 3795 1.15 5.3 24.4 12 3.0/9.5 0.2 9.0 5.0 0.4017 -
[1] 董兵强,邱正松,王伟吉,等. 新型页岩气储层保护剂SDME-2的制备及特性[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报,2015,28(6):61-65.DONG Bingqiang, QIU Zhengsong, WANG Weiji, et al. Preparation and properties of a new shale gas reservoir protectant SDME-2[J]. Journal of Petroleum and Chemical Engineering, 2015, 28(6):61-65. [2] 卓绿燕,谭晓峰,任艳增,等. 大港油田钻进过程中油气层保护技术研究[J]. 天津化工,2017,31(6):36-38.ZHUO Lyuyan, TAN Xiaofeng, REN Yanzeng, et al. Study on oil and gas layer protection technology during drilling in Dagang oilfield[J]. Tianjin Chemical Industry, 2017, 31(6):36-38. [3] 王瑜,梁大川,王博,等. 钻井液高温保护剂EGC-D的评价[J]. 化学世界,2019,60(7):457-464.WANG Yu, LIANG Dachuan, WANG Bo, et al. Evaluation of drilling fluid high temperature protective agent EGC-D[J]. Chemical World, 2019, 60(7):457-464. [4] 王双威,张闯,张洁,等. 狮子沟构造带裂缝储层保护钻井液配方[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(19):7991-7996.WANG Shuangwei, ZHANG Chuang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Drilling fluid formulation for fracture reservoir protection in the Shizigou structural belt[J]. Science technology and engineering, 2021, 21(19):7991-7996. [5] AZIMI DIJVEJIN Z, GHAFFARKHAH A, SADEGHNEJAD S, et al. Effect of silica nanoparticle size on the mechanical strength and wellbore plugging performance of SPAM/chromium (III) acetate nanocomposite gels[J]. Polymer Journal, 2019, 51(7):693-707. doi: 10.1038/s41428-019-0178-3 [6] ZAREIE C, SEFTI M V, BAHRAMIAN A R, et al. A polyacrylamide hydrogel for application at high temperature and salinity tolerance in temporary well plugging[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal, 2018, 27(8):577-587. doi: 10.1007/s13726-018-0634-5 [7] WANG K, LIU G, GUO Y, et al. Preparation and properties of degradable hydrogels as a temporary plugging agent used for acidizing treatments to enhance oil recovery[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 637:128218. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128218 [8] LONG L, XIANGUANG X, JINSHENG S, et al. Vital role of nanomaterials in drilling fluid and reservoir protection applications[C]//Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition. OnePetro, 2012. [9] JIANXIANG S, LAIJU H, JIANGHONG J. Study on damage characteristics and formation protective drilling fluids in Dongying formation low permeability reservoir of Chengbei oilfield[J]. Advances in Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 10(1):38-43. [10] 戎克生,李建国,徐生江,等. 准噶尔盆地砂砾岩气层钻井中的储层保护技术[J]. 天然气工业,2012,32(2):63-66.RONG Kesheng, LI Jianguo, XU Shengjiang, et al. Reservoir protection technology in glutenite gas reservoir drilling in Junggar basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(2):63-66. [11] 韩韶朋. 大港枣园油田中高渗储层保护钻井液研究[D]. 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.HAN Shaopeng. Study on drilling fluid for medium-high permeability reservoir protection in Dagang Zaoyuan Oilfield [D]. China University of Petroleum ( Beijing ), 2019. [12] 王先兵,易炳刚,欧阳伟,等. 低渗透储层多级架桥暂堵储层保护技术[J]. 天然气工业,2013,33(7):85-89.WANG Xianbing, YI Binggang, OUYANG Wei, et al. Multistage bridging reservoir protection technology for low permeability reservoirs[J]. Gas Industry, 2013, 33(7):85-89. [13] 陈钢花,林雅平. 利用随钻资料对本布图油田本东油区进行岩性实时识别[J]. 勘探地球物理进展,2006(1):52-55.CHEN Ganghua, LIN Yaping. Real-time lithology identification of bendong oil region in benbutu oilfield using data while drilling[J]. Progress in geophysical exploration, 2006(1):52-55. [14] 杨园园,胡志方,罗涛,等. 本布图油田Y2井区断层封堵性分析[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报),2006(1):23-25.YANG Yuanyuan, HU Zhifang, LUO Tao, et al. Analysis of fault sealing in Y2 well area of Benbutu Oilfield[J]. Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas(Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute) , 2006(1):23-25. [15] 李中玲. 本布图油田保护油层钻井液技术研究[D]. 山东大学, 2007.LI Zhongling. Research on drilling fluid technology for reservoir protection in Benbutu oilfield [D]. Shandong University, 2007. [16] 刘永峰,张伟国,狄明利,等. 一种环保油基钻井液体系[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(4):449-455.LIU Yongfeng, ZHANG Weiguo, DI Mingli, et al. An environmentally friendly oil base mud[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(4):449-455. -





 下载:
下载: