Damage of Sandy Conglomerate Reservoirs in Dzungar Basin by Fracturing Fluids and Measures for Protection of the Reservoir Damage
-
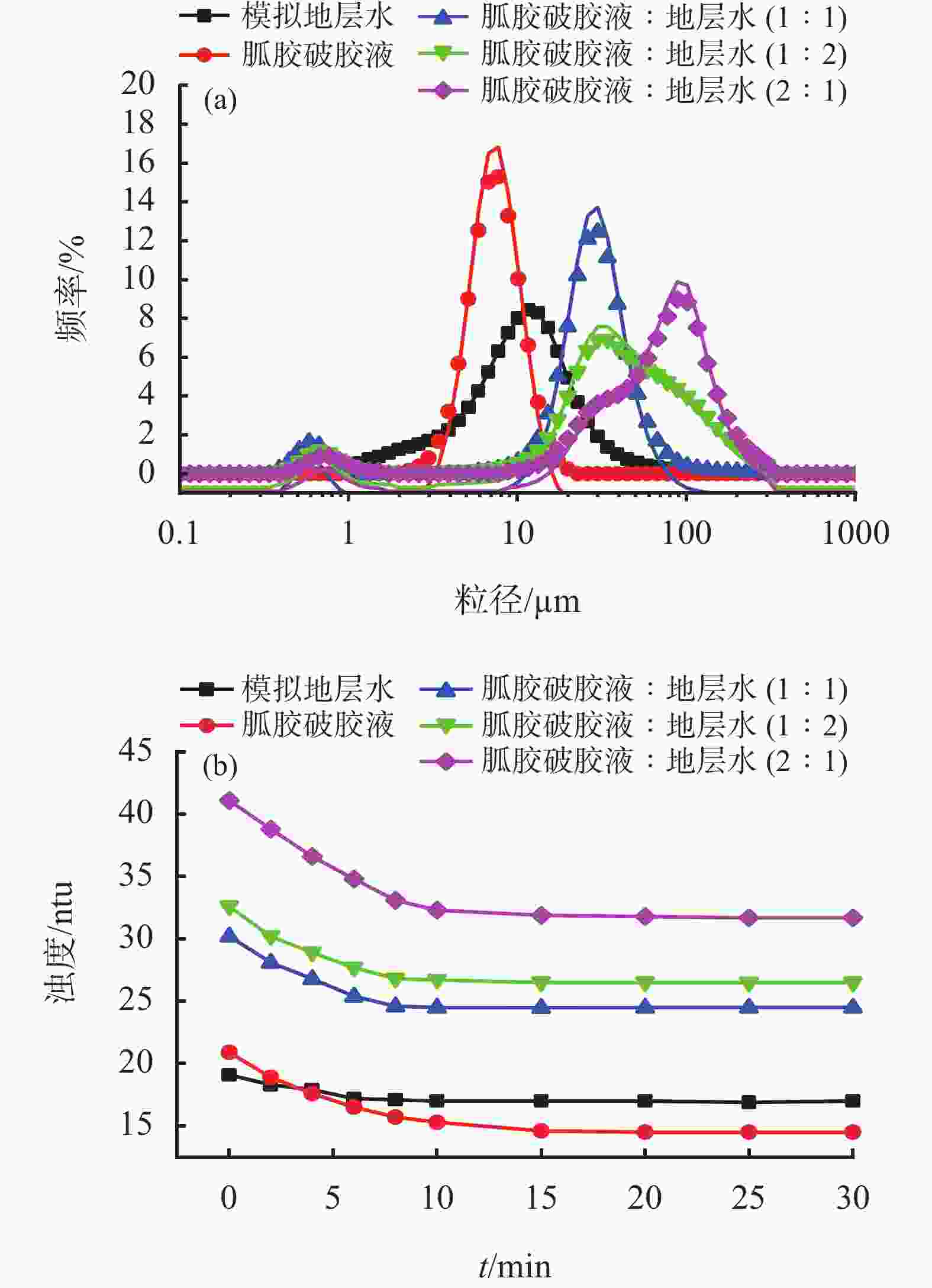
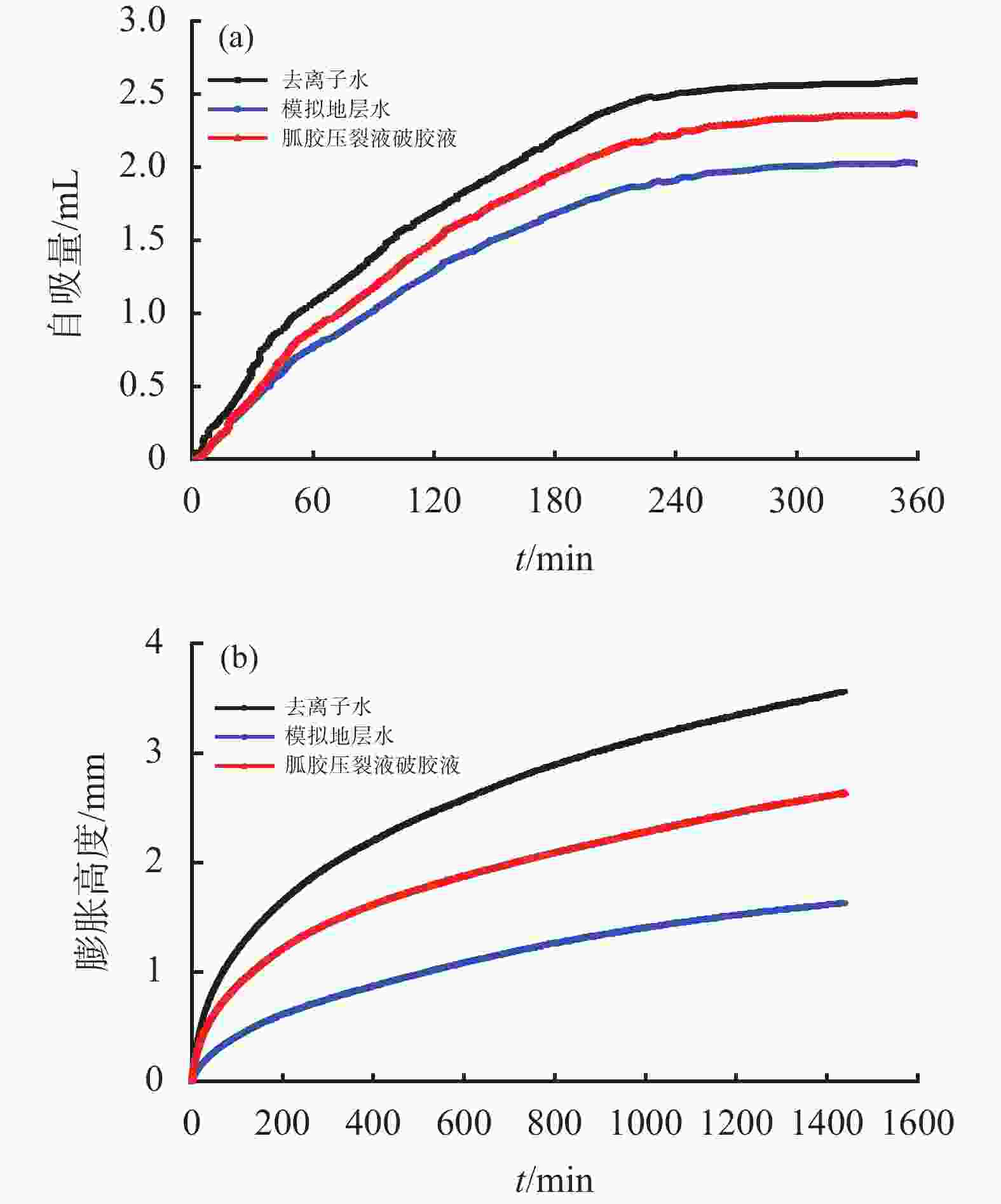
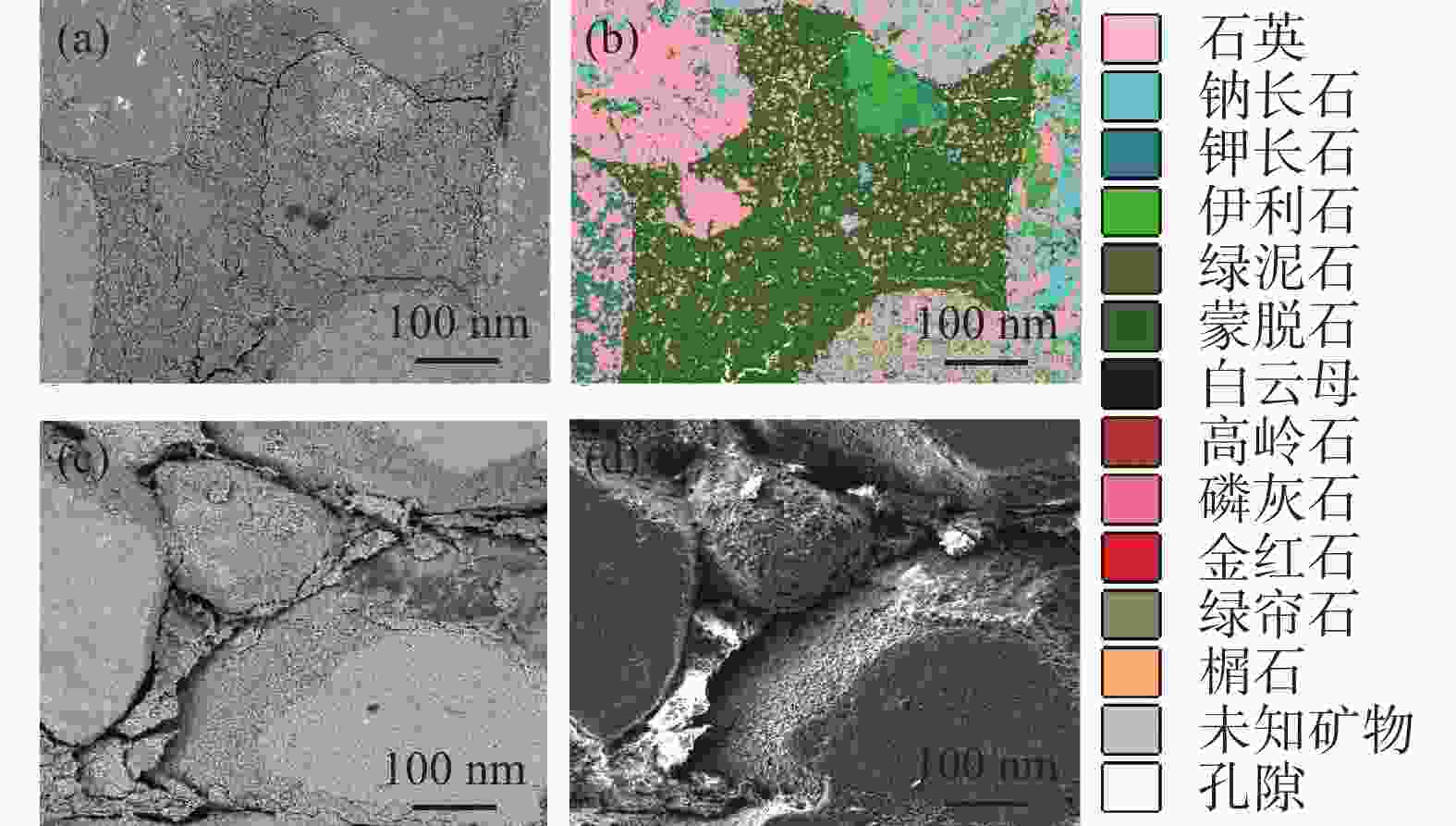
摘要: 针对准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷区上乌尔禾组砾岩储集层压裂开采过程中储层损害等问题,在分析准噶尔盆地砂砾岩上乌尔禾组玛湖1井区储集层基本特征的基础上,开展了压裂液破胶液与地层水流体配伍性及固相颗粒堵塞评价、储层敏感性评价、毛细管自吸及黏土矿物水化膨胀评价实验,分析了储层损害的主要因素;对防膨抑制剂,仿生双疏压裂液助排剂进行了优选;此外,还建立了储层敏感性损害智能化定量预测技术。研究结果表明,准噶尔盆地砂砾岩上乌尔禾组玛湖1井区储层损害主要因素是蒙脱石吸水膨胀损害、强毛细管自吸损害、固相颗粒堵塞损害、水敏和弱酸敏性损害。优选出的4%聚醚胺抑制剂膨胀量在1.28 mm,2%仿生双疏助排剂的助排效率在88.54%以上; 2%聚醚胺和2%双疏压裂液体系的岩心自吸量为1.38 mL,膨胀量为1.42 mm,返排率达到86.2%;建立的储层敏感性损害智能化定量预测技术的预测精度在85%以上,形成了一套适合准噶尔盆地玛湖砾岩储集层保护体系。Abstract: Formation damage has long been a problem existed in producing through fracturing the conglomerate reservoir in the upper Wuerhe formation in Mahu sag, Dzungar basin. Based on the analysis of the basic characteristics of the upper Wuerhe conglomerate reservoirs in the Mahu-1 block in Dzungar basin, laboratory experiments were performed to evaluate 1) the compatibility between the fluid from fracturing fluid after gel breaking and the formation water, as well as the plugging of reservoir formations by solid particles; 2) the sensitivity of the reservoir to various damaging factors; and 3) capillary imbibition and the swelling of clay minerals though hydration. Main factors contributing to the reservoir damage were analyzed. In the laboratory evaluation experiments, the clay swelling inhibitor and the biomimetic amphiphobic fracturing fluid cleanup additives were selected. In addition, an intelligent quantitative prediction technology for reservoir sensitivity damage was also established. The study results showed that the main factors contributing to the damage of the sandy conglomerate upper Wuerhe formation in the Mahu-1 block in Dzungar basin include swelling of the montmorillonite caused by water absorption, strong capillary imbibition, solid particle blocking, water sensitivity and weak acid sensitivity. In laboratory swelling test with 4% polyetheramine solution, the cores only swelled by 1.28 mm, the cleanup efficiency of the biomimetic amphiphobic cleanup additive was at least 88.54%. The amount of the fluid (2% polyetheramine plus 2% amphiphobic fracturing fluid) absorbed by the cores was 1.38 mL, resulting in a length of swelling of 1.42 mm, and the ratio of the back flowed fracturing fluid was 86.2%. Using the intelligent quantitative prediction technology, the precision of the sensitivity prediction can be as high as more than 85%. All these study results together formed a set of technology for protecting the conglomerate reservoirs in the Mahu block in Dzungar basin.
-
表 1 克206井储层岩心敏感性评价
井深/
m储层敏感性程度/% 速敏 水敏 酸敏 碱敏 应力敏 3597.02 81.83 56.55 17.97 12.21 71.43 3638.93 79.16 68.18 31.76 20.62 87.54 3618.70 67.94 43.05 23.81 27.31 79.38 3599.75 74.63 53.47 24.93 14.73 78.51 表 2 抑制剂优选评价
抑制剂 加量
/%24 h浸
泡结果自吸
量/mL膨胀高
度/mm去离子水 完全泡散 2.68 2.41 模拟地层水 完全泡散 2.01 1.24 胍胶破胶压裂液 完全泡散 2.48 1.51 聚醚 4 部分泡散 2.12 1.04 聚胺 4 部分泡散 1.55 0.89 聚醚胺 4 未泡散 1.07 0.88 固壁剂 4 完全泡散 1.27 1.03 聚乙烯亚胺 4 完全泡散 1.46 0.93 硅酸镁锂 4 完全泡散 1.59 1.13 聚合物微球 4 完全泡散 1.61 1.19 表 3 仿生双疏压裂液助排剂的性能评价
助排剂 表面张力/
mN·m−1界面张力/
mN·m−180 ℃表面张力改变量/
mN·m−180 ℃界面张力改变量/
mN·m−1接触角/
(°)返排率/
%胍胶破胶液 30.56 16.32 降低1.7 降低1.2 27.89 36.40 1%双疏助排剂 26.70 13.98 降低2.2 降低2.7 71.34 67.54 2%双疏助排剂 17.74 6.47 降低1.5 降低1.6 94.37 88.54 表 4 添加2%聚醚胺和2%双疏助排剂的破胶液储层保护性能
体系 自吸量/
mL膨胀高
度/mm返排
率/%去离子水 2.68 2.41 模拟地层水 2.01 1.24 胍胶压裂液破胶液 2.48 1.51 36.4 添加2%聚醚胺和2%双疏破胶的破胶液 1.38 1.42 86.2 表 5 储层敏感性损害定量预测技术对玛湖1井区储层岩心的预测结果
敏感性类型 预测参数 实测 预测 准确率/% 速敏 速敏指数/% 78.7 81.7 95.4 临界流速/cm·s-1 11 600 12 400 93.5 水敏 水敏指数/% 53.2 49.4 92.8 临界矿化度/mg·L-1 30 200 31 600 95.5 酸敏 酸敏指数/% 12.9 14.3 90.0 -
[1] 陈磊,杨镱婷,汪飞,等. 准噶尔盆地勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质,2020,41(5):505-518.CHEN Lei, YANG Yiting, WANG Fei, et al. Exploration history and enlightenment of Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(5):505-518. [2] 张辉,岳欣欣,朱颜,等. 准噶尔盆地春光油田油藏特征及成藏模式[J]. 新疆石油地质,2020,41(4):379-387.ZHANG Hui, YUE Xinxin, ZHU Yan, et al. Reservoir characteristics and accumulation model of Chunguang Oilfield, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(4):379-387. [3] 关新,潘树新,曲永强,等. 准噶尔盆地沙湾凹陷滩坝砂的发现及油气勘探潜力[J]. 岩性油气藏,2021,33(1):90-98. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210109GUAN Xin, PAN Shuxin, QU Yongqiang, et al. Discovery and oil and gas exploration potential of beach-bar sands in Shawan sag, Junggar basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1):90-98. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210109 [4] 常天全,赵彬,刘凯,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖1井区下乌尔禾组油层识别标准研究[J]. 新疆地质,2021,39(2):270-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2021.02.011CHANG Tianquan, ZHAO Bin, LIU Kai, et al. Research on the identification criteria of the lower Wuerhe Formation in the Mahu 1 well block, Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2021, 39(2):270-274. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2021.02.011 [5] 李琼,吴建邦,周伟,等. 玛湖1井区乌尔禾组致密砂砾岩储层物性特征研究[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(14):5777-5783. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.14.019LI Qiong, WU Jianbang, ZHOU Wei, et al. Study on physical properties of tight glutenite reservoirs in Wuerhe Formation in Mahu 1 well block[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(14):5777-5783. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.14.019 [6] 霍进,支东明,郑孟林,等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油藏特征与形成主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质,2020,42(4):506-512. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004506HUO Jin, ZHI Dongming, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of formation of Lucaogou Formation shale reservoir in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Experimental Geology, 2020, 42(4):506-512. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004506 [7] 李兆丰,唐相路,黄立良,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组页岩岩相发育特征[J]. 能源与环保,2021,43(4):108-114.LI Zhaofeng, TANG Xianglu, HUANG Liliang, et al. Lithofacies development characteristics of Fengcheng formation shale in Mahu sag, Junggar basin[J]. Energy and Environmental Protection, 2021, 43(4):108-114. [8] 付瑜,柳益群,蒋宜勤,等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘玛湖凹陷三叠系百口泉组砂砾岩储层孔隙结构及渗流特征[J]. 西北地质,2020,53(2):223-234.FU Yu, LIU Yiqun, JIANG Yiqin, et al. Pore structure and seepage characteristics of glutenite reservoirs in Triassic Baikouquan formation in Mahu sag, northwestern margin of Junggar basin[J]. Northwest Geology, 2020, 53(2):223-234. [9] 王然, 杨森, 万敏, 等. 玛南上斜坡区上乌尔禾组弱胶结砂砾岩储集层特征及控制因素[J/OL]. 特种油气藏: 1-10[2021-11-04].WANG Ran, YANG Sen, WAN Min, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of weakly cemented glutenite reservoirs in the upper Wuerhe Formation in the upper Manan slope area [J/OL]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs: 1-10[2021-11-04 ]. [10] 卞保力,吴和源,李娜,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷东斜坡中二叠统扇三角洲储层特征与成因[J]. 新疆地质,2017,35(3):306-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2017.03.014BIAN Baoli, WU Heyuan, LI Na, et al. Characteristics and genesis of middle permian fan delta reservoirs in the eastern slope of Mahu sag, Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2017, 35(3):306-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2017.03.014 [11] 靳军,康逊,胡文瑄,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷西斜坡百口泉组砂砾岩储层成岩作用及对储集性能的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2017,38(2):323-333. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170212JIN Jun, KANG Xun, HU Wenxuan, et al. Diagenesis of the glutenite reservoir in Baikouquan formation in the west slope of Mahu sag, Junggar basin and its influence on reservoir performance[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2017, 38(2):323-333. doi: 10.11743/ogg20170212 [12] 单祥,徐洋,郭华军,等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷北斜坡玛131井区块三叠系百口泉组储层敏感性评价[J]. 地质科技情报,2017,36(1):176-182.SHAN Xiang, XU Yang, GUO Huajun, et al. Reservoir sensitivity evaluation of Triassic Baikouquan formation in block Ma 131, north slope of Mahu sag, Junggar basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(1):176-182. [13] 高天然,屈海瑜,常程. 低渗砂岩气藏压裂液伤害机理及评价[J]. 辽宁化工,2021,50(6):901-903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2021.06.045GAO Tianran, QU Haiyu, CHANG Cheng. Damage mechanism and evaluation of fracturing fluid in low permeability sandstone gas reservoirs[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(6):901-903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2021.06.045 [14] 汪洋. 压裂液体系残渣含量影响因素分析[J]. 当代化工,2020,49(7):1420-1423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.07.038WANG Yang. Analysis of Influencing factors on residue content in fracturing fluid system[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(7):1420-1423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2020.07.038 [15] 袁媛,孟英峰,李皋,等. 致密砂岩储层毛管自吸微观分布特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率,2020,27(5):71-78.YUAN Yuan, MENG Yingfeng, LI Gao, et al. Microscopic distribution characteristics of capillary self-absorption in tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Oil and Gas Geology and Recovery, 2020, 27(5):71-78. [16] 王俊杰,胡勇,刘义成,等. 致密砂岩气层毛细管自吸水锁损害及控制因素[J]. 断块油气田,2019,26(5):626-631.WANG Junjie, HU Yong, LIU Yicheng, et al. Capillary self-absorption water lock damage and control factors in tight sandstone gas layers[J]. Fault Block Oil and Gas Fields, 2019, 26(5):626-631. [17] 彭小强,武俊学,赵玉,等. 致密岩心压裂液伤害评价实验方法初探[J]. 新疆石油天然气,2018,14(3):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2018.03.015PENG Xiaoqiang, WU Junxue, ZHAO Yu, et al. Preliminary study on the experimental method for damage evaluation of fracturing fluid in tight cores[J]. Xinjiang Oil and Gas, 2018, 14(3):67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2018.03.015 [18] 马爱青,何绍群,宋丹,等. 黏土矿物膨胀防治体系SLAS-3的应用与机理研究[J]. 油田化学,2007(4):320-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4092.2007.04.008MA Aiqing, HE Shaoqun, SONG Dan, et al. Application and mechanism of clay mineral swelling prevention system SLAS-3[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2007(4):320-323. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4092.2007.04.008 [19] YESUFU-RUFAI S, MARCELIS F, GEORGIADIS A, et al. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) study of redox conditions in sandstones: Impact on wettability modification and mineral morphology[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020:597:124765. [20] 中华人民共和国能源局. 储层敏感性流动试验评价方法: SY/T 5358—2010[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.Energy Administration of the People's Republic of China. Evaluation method of reservoir sensitivity flow test: SY/T 5358—2010[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [21] 蒋官澄,倪晓骁,李武泉,等. 超双疏强自洁高效能水基钻井液[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2020,47(2):390-398. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.02.18JIANG Guancheng, NI Xiaoxiao, LI Wuquan, et al. Super-amphiphobic strong self-cleaning high-efficiency water-based drilling fluid[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2):390-398. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.02.18 [22] NI X, JIANG G, LI Y, et al. Synthesis of superhydrophobic nanofluids as shale inhibitor and study of the inhibition mechanism[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 484: 957-965. [23] 中华人民共和国能源局. 压裂酸化用助排剂性能评价方法: SY/T5755—2016[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2016.Energy Administration of the People's Republic of China. Performance evaluation method of drainage aid for fracturing and acidizing: SY/T 5755—2016[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2016. -





 下载:
下载: