The Effects of Particle Size of Silica Flour on the Performance of Oil Well Cement at High Temperature and High Pressure
-
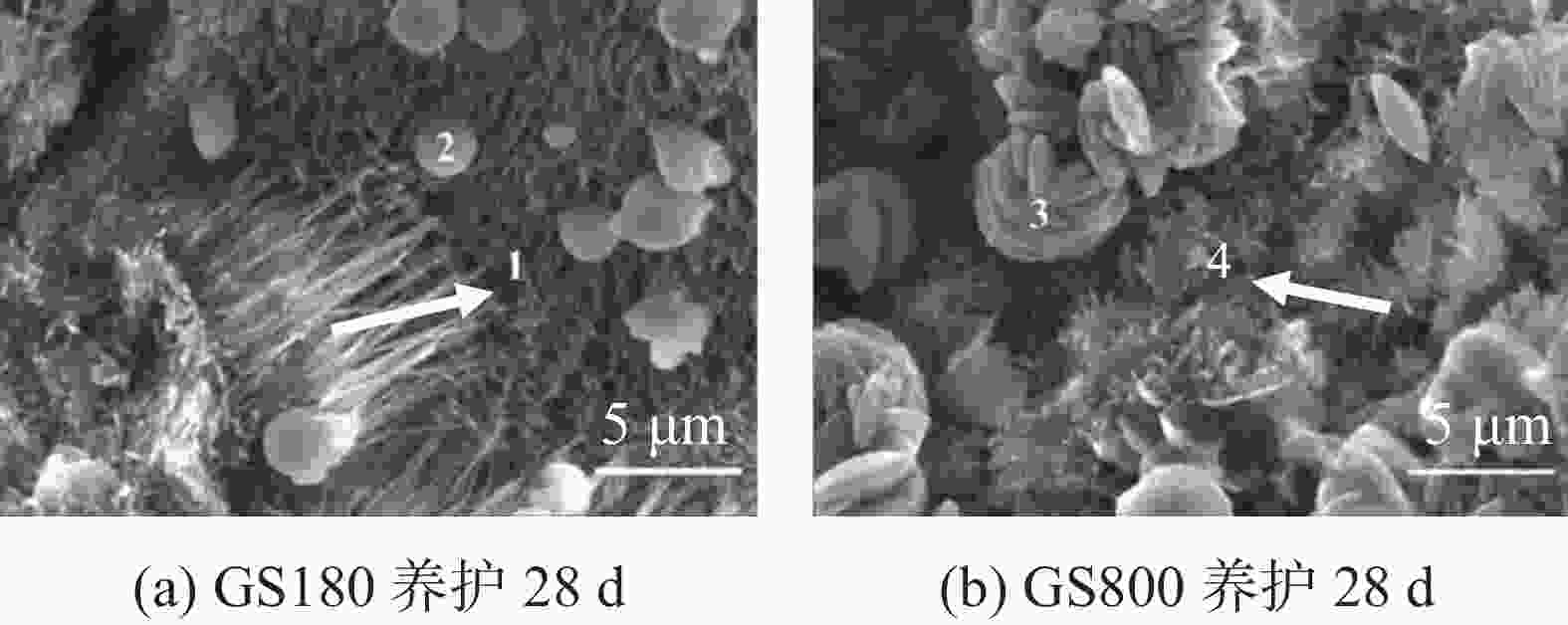
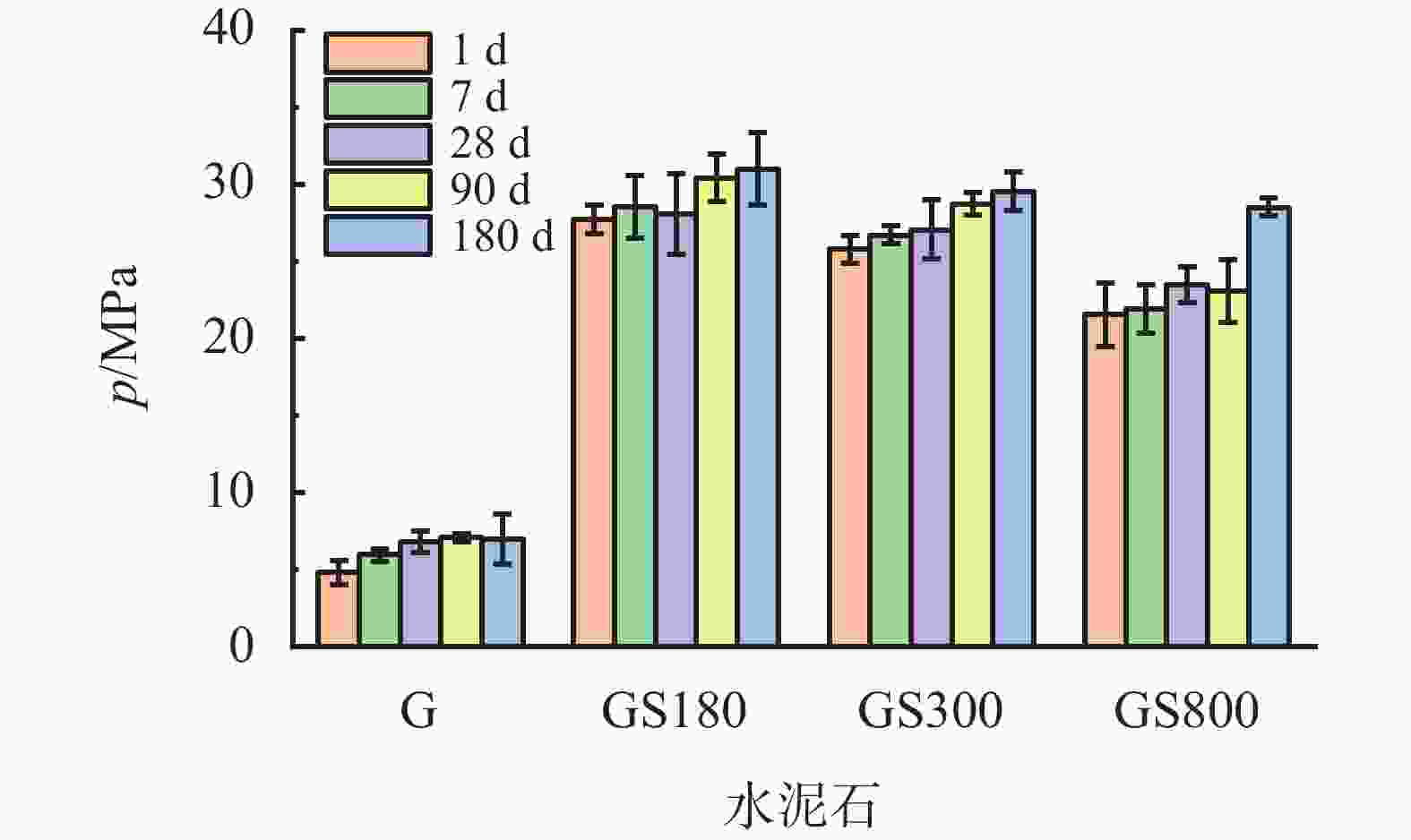
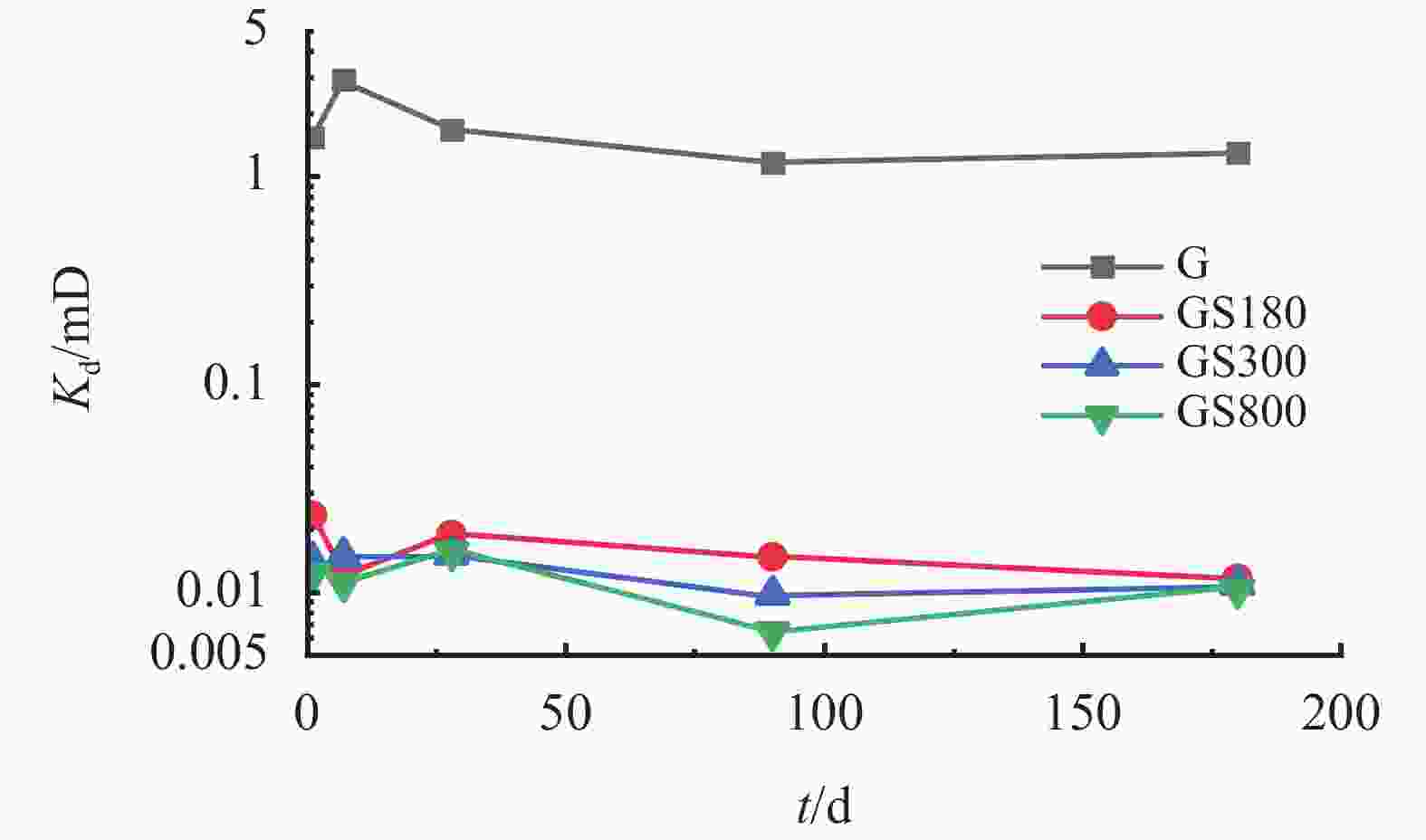
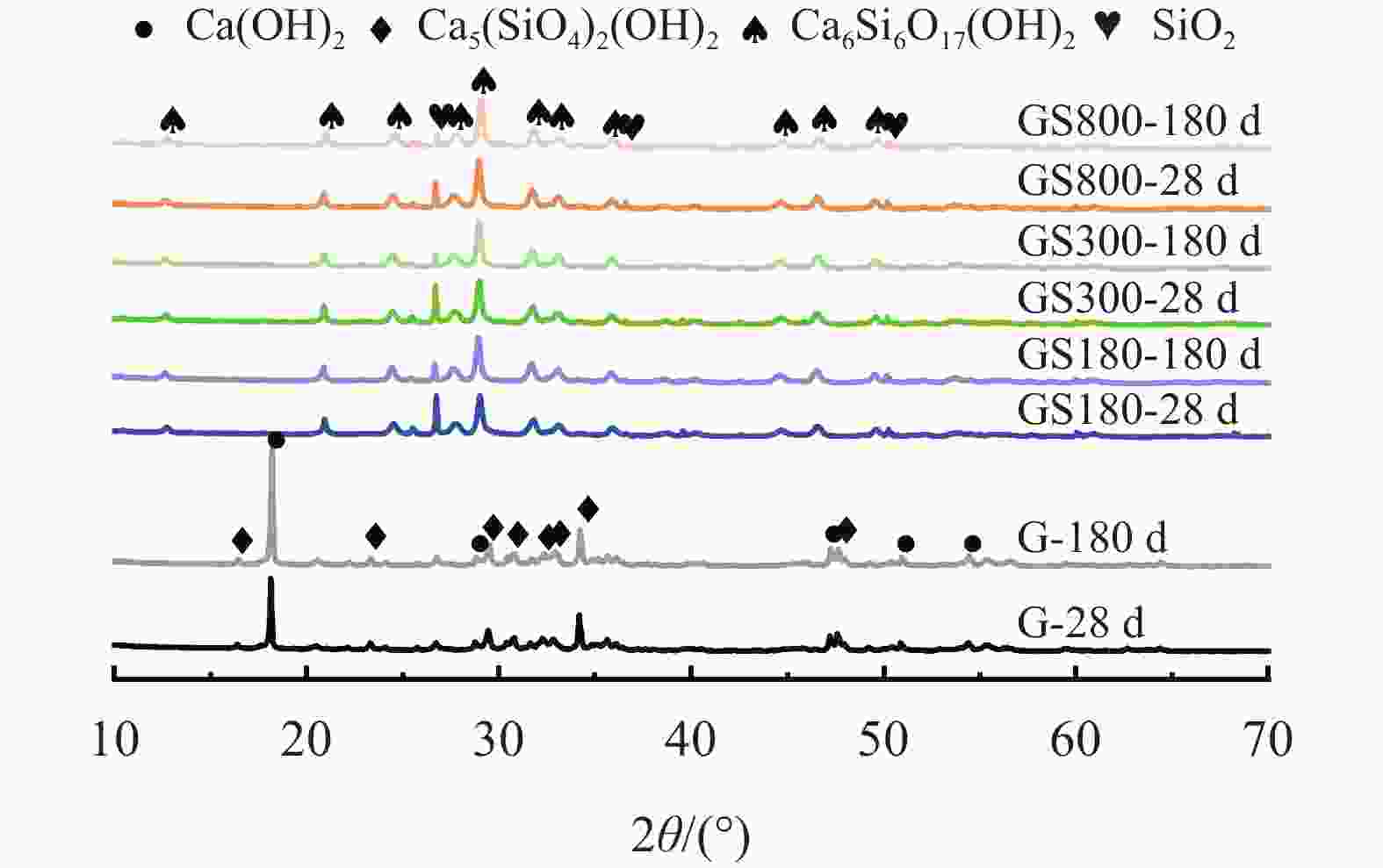
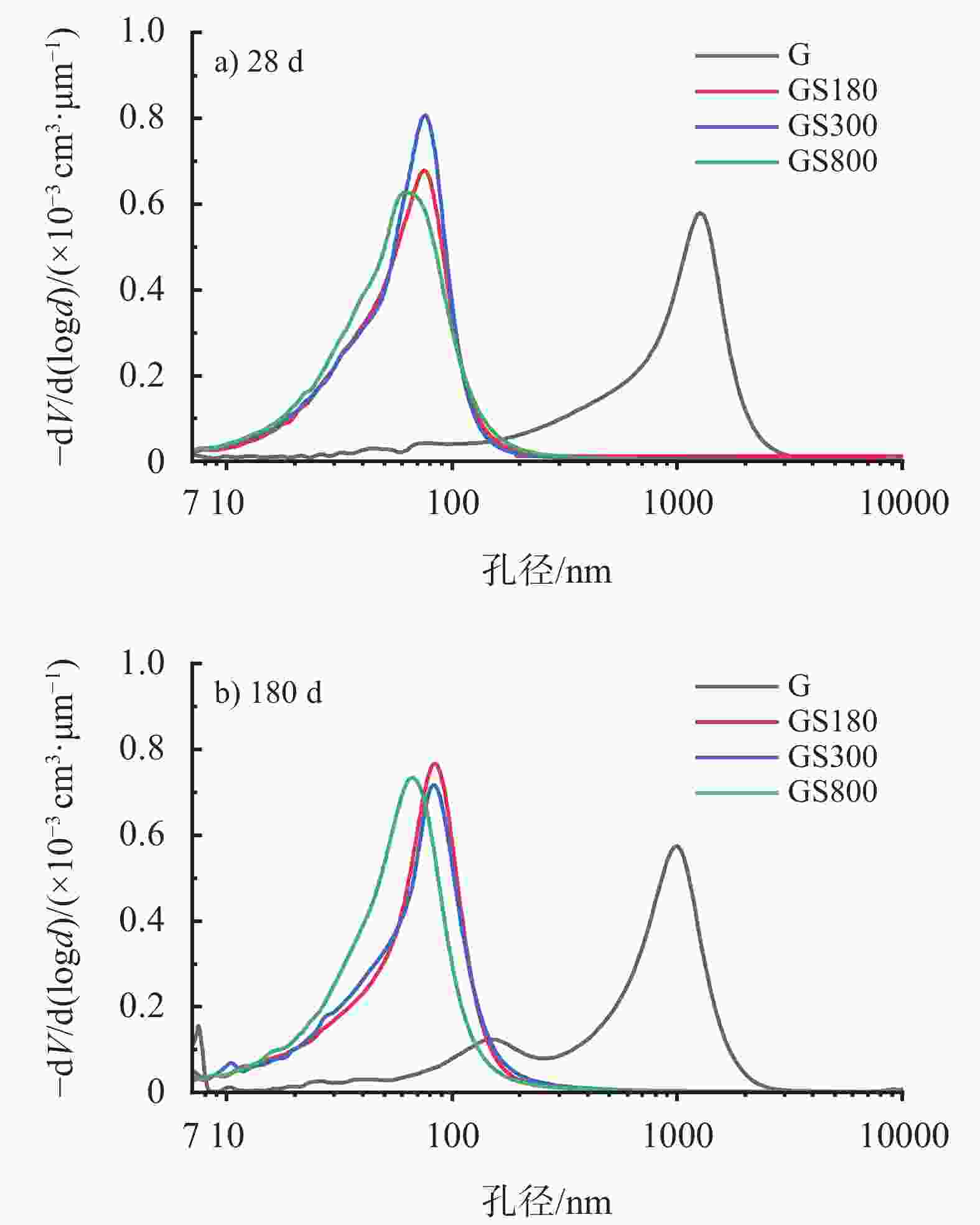
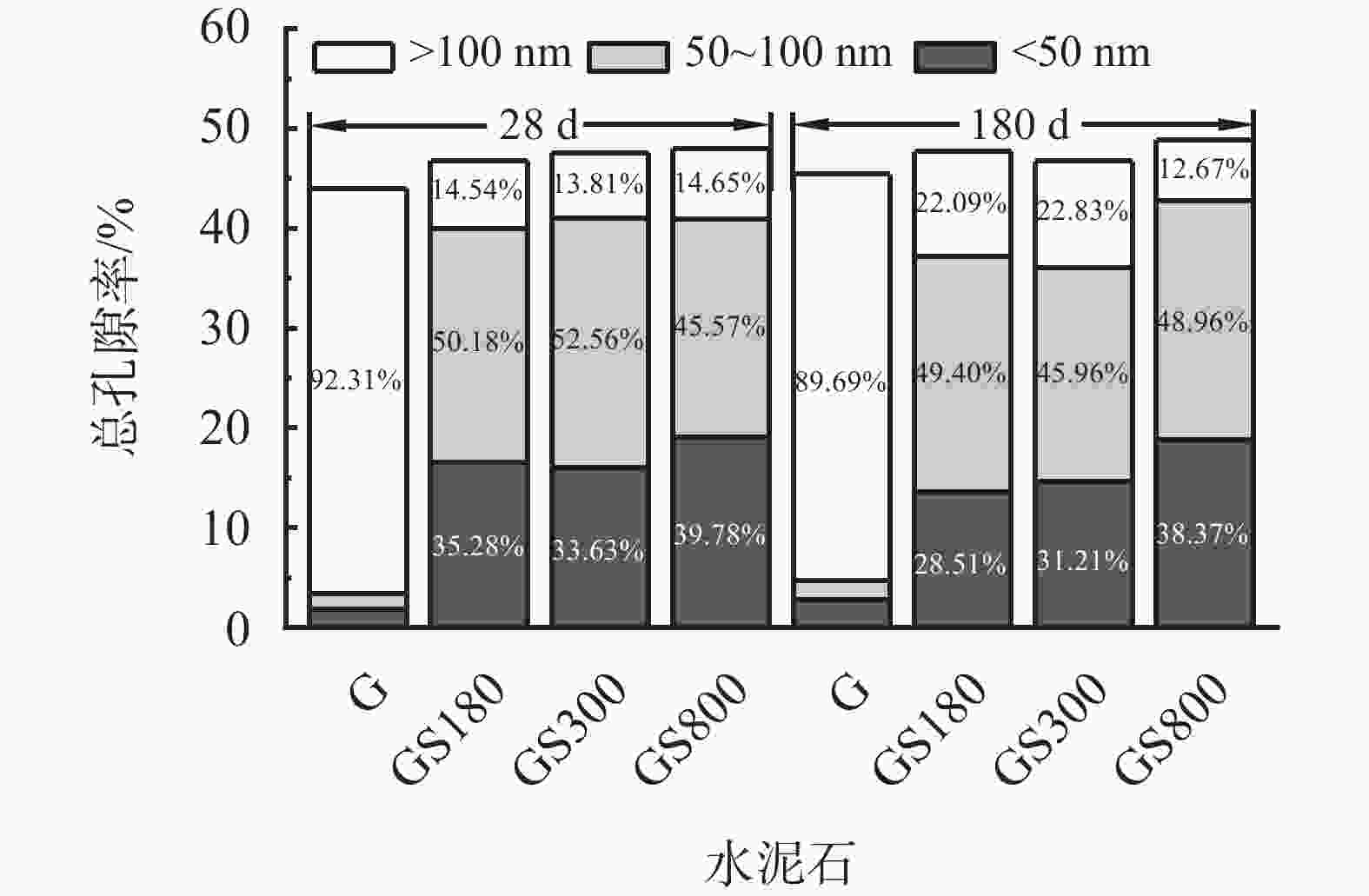
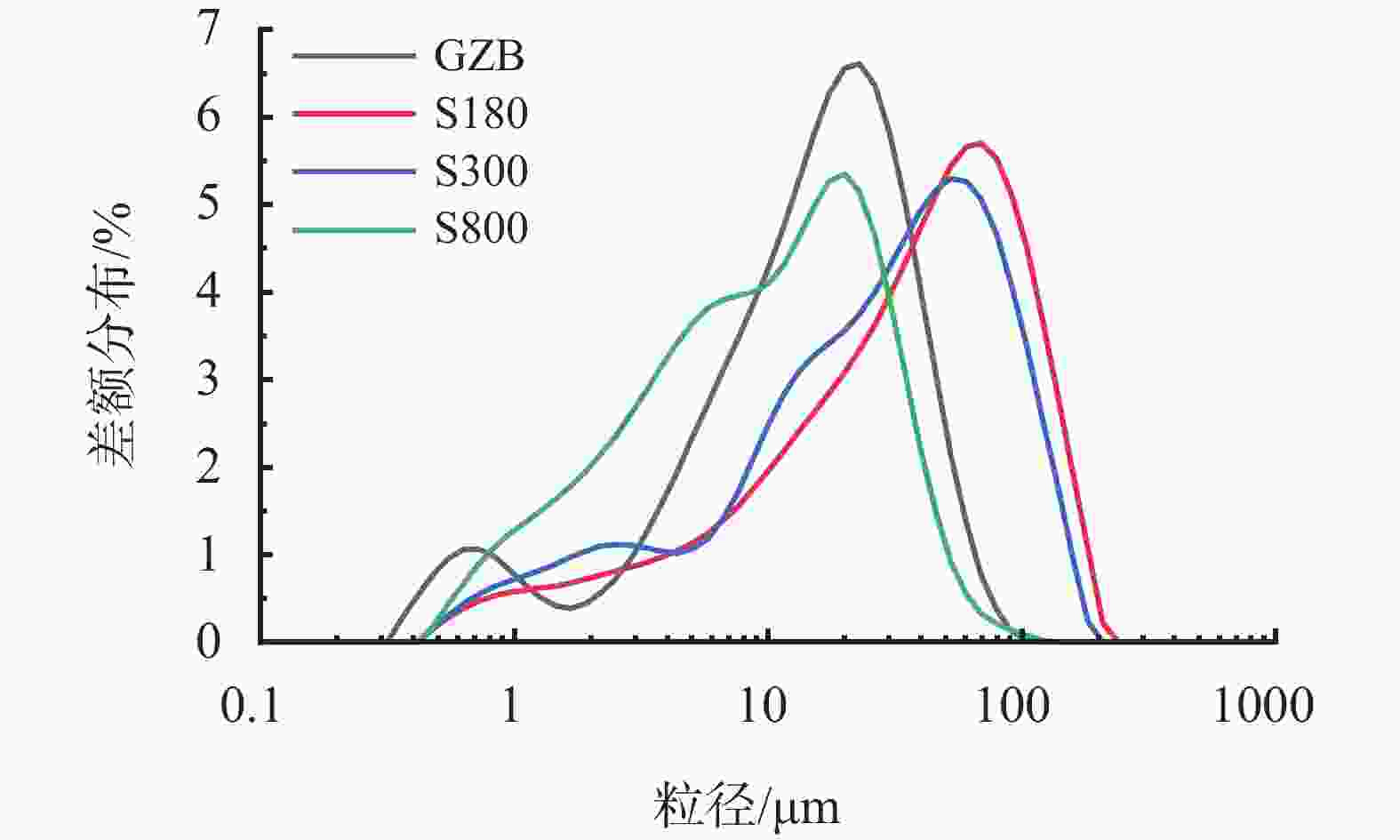
摘要: 在油井水泥中掺入石英砂是防止水泥石在高温高压下强度衰退的常用手段,通过在G级油井水泥中内掺35%不同粒径的石英砂,并在高温高压(240 ℃×21 MPa)下养护至180 d,来探究石英砂粒径对油井水泥石高温力学性能的影响。实验测试了加入不同粒径石英砂的水泥石的抗压强度和渗透率,分析了水泥石的水化产物和孔隙结构。结果表明,石英砂能够防止水泥石在高温下强度衰退,但是水泥石的抗压强度随石英砂粒径的减小而降低;掺入石英砂可降低水泥石的渗透率,石英砂的粒径越小,水泥石的渗透率越低。掺入较大粒径石英砂的水泥石中,生成的针状硬硅钙石较长,是水泥石具有较高抗压强度的主要原因。以300目35%加砂水泥为基础,复配其他外加剂形成高温高压水泥浆配方,在南海DX-11-2井应用,现场固井施工顺利,24 h时CBL和VDL测井显示固井质量优良。Abstract: Silica flour is commonly used in oil well cement to prevent the strength retrogression of hardened cement paste at high temperature and high pressure. In this study, a class G cement slurry was mixed with 35% silica flour of different sizes and cured at high temperature and high pressure (240 ℃ and 21 MPa) for 180 d to study the effects of the silica flour particle size on the high temperature mechanical properties of the hardened cement paste. The compressive strength and permeability of the hardened cement paste containing silica flour of different particle sizes were measured, and the hydration products and pore structure were analyzed. It was found that silica flour prevented the strength retrogression of the hardened cement paste at high temperature, and the compressive strength of the hardened cement paste decreased with the decrease of silica flour particle size. Silica flour reduced the permeability of the hardened cement paste. The smaller the particle size of the silica flour, the lower the permeability. The cement slurry mixed with larger particle size silica flour produced longer needle-like xonotlite, which was the main reason why the hardened cemlent paste had high compressive strength. A high temperature and high pressure cement slurry containing 35% 300-mesh silica flour and other additives was used to cement the well DX-11-2 in the Nanhai oilfield. The well cementing operation was smoothly performed, and the 24 h CBL and VDL wireline logging showed that the cementing quality was excellent.
-
Key words:
- Hardened cement paste /
- Silica flour /
- Particle size /
- High temperature /
- High pressure /
- Well cementing /
- Cementing quality
-
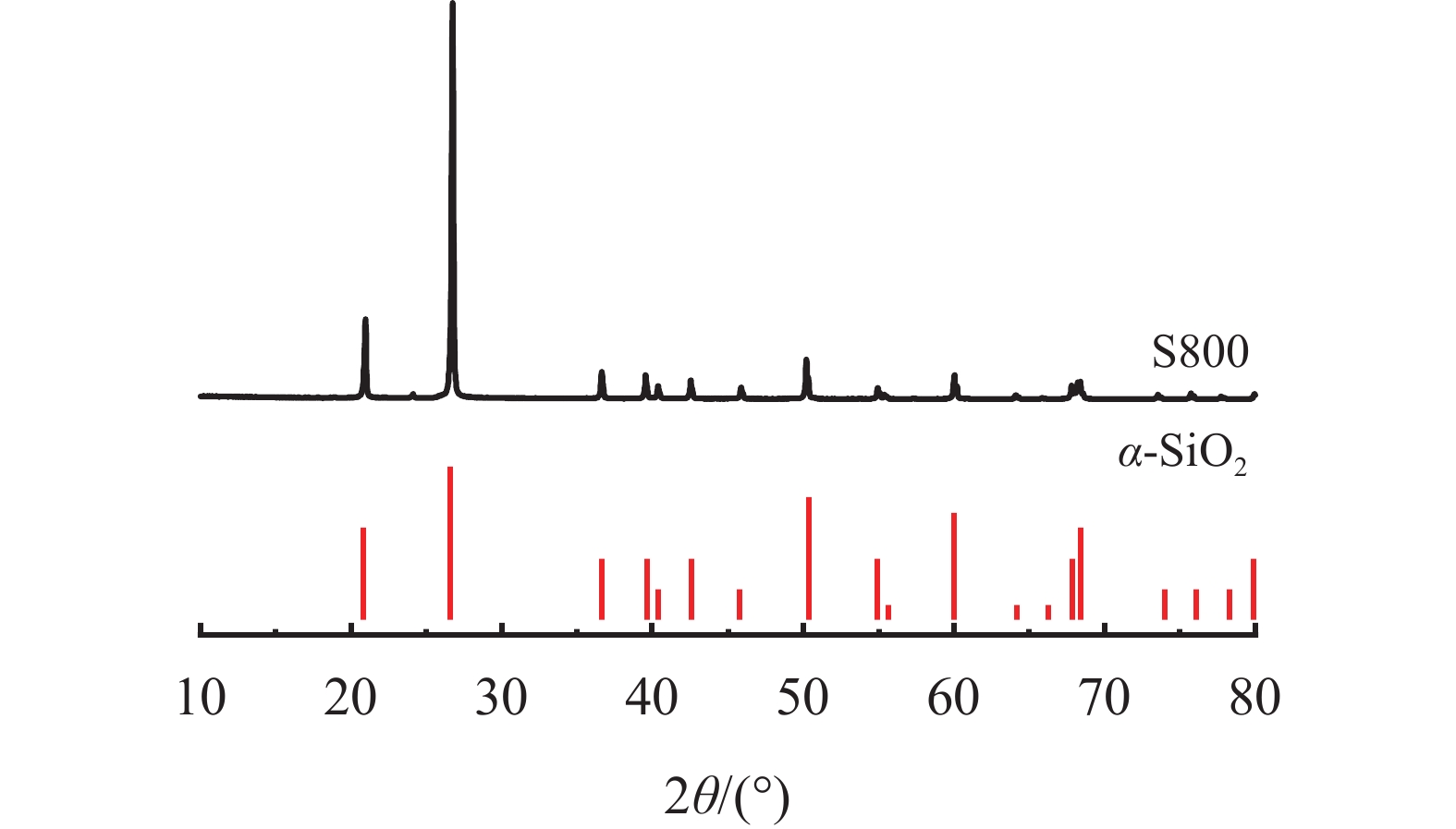
表 1 实验材料的化学成分和油井水泥矿物组成
氧化物 化学成分组成/% 油井水泥
物相矿物组成/% GZB S180 S300 S800 Rietveld法 SiO2 22.29 98.31 97.48 98.17 C3S 60.7 Al2O3 4.25 0.57 1.15 0.91 C2S 16.6 CaO 61.70 0.03 0.18 0.06 C3A 2.3 MgO 1.63 0.01 0.14 0.06 C4AF 17.2 SO3 1.93 0.03 CaSO4 2.7 TiO2 0.31 0.04 0.04 0.03 Fe2O3 5.68 0.03 0.21 0.09 K2O 0.38 0.14 0.25 0.18 Na2O 0.15 0.01 0.03 0.04 MnO 0.28 LOI 0.48 0.12 0.22 0.18 表 2 净浆及加砂35%水泥浆的基本性能
水泥浆 ρ/(g·cm−3) 流动度/cm G 1.90 19.2 GS180 1.85 22.1 GS300 1.84 21.3 GS800 1.84 17.7 -
[1] 苏义脑,路保平,刘岩生,等. 中国陆上深井超深井钻完井技术现状及攻关建议[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2020,42(5):527-542. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.001SU Yinao, LU Baoping, LIU Yansheng, et al. Status and research suggestions on the drilling and completion technologies for onshore deep and ultra deep wells in China[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5):527-542. doi: 10.13639/j.odpt.2020.05.001 [2] 徐新丽. 累积工况下常规加砂水泥石的耐温性[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(6):754-759.XU Xinli. High temperature resistance of conventional set sand cement under cumulative working conditions[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(6):754-759. [3] YANG T, WU Q, ZHU H, et al. Geopolymer with improved thermal stability by incorporating high-magnesium nickel slag[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 155:475-484. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.081 [4] KRAKOWIAK K J, THOMAS J J, MUSSO S, et al. Nano-chemo-mechanical signature of conventional oil-well cement systems: Effects of elevated temperature and curing time[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2015, 67:103-121. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2014.08.008 [5] NELSON E B, GUILLOT D. Well cementing [M]. Second ed. , Schlumberger, 2006. [6] DE SENA COSTA B L, DE SOUZA G G, DE OLIVEIRA FREITAS J C, et al. Silica content influence on cement compressive strength in wells subjected to steam injection[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 158:626-633. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.09.006 [7] GE Z, YAO X, WANG X, et al. Thermal performance and microstructure of oil well cement paste containing subsphaeroidal konilite flour in HTHP conditions[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 172:787-794. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.268 [8] PERNITES R B, SANTRA A K. Portland cement solutions for ultra-high temperature wellbore applications[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2016, 72:89-103. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.05.018 [9] OMOSEBI O, MAHESHWARI H, AHMED R, et al. Investigating temperature effect on degradation of well cement in HPHT carbonic acid environment[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 26:1344-1362. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.08.018 [10] Recommended practice for testing well cements [S]. API RP 10B-2, 2013. [11] YANAGISAWA K, HU X, ONDA A, et al. Hydration of β-dicalcium silicate at high temperatures under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2006, 36(5):810-816. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.12.009 [12] PANG X, QIN J, SUN L, et al. Long-term strength retrogression of silica-enriched oil well cement: A comprehensive multi-approach analysis[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2021, 144:106424. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2021.106424 [13] HUA S, WANG K, YAO X. Developing high performance phosphogypsum-based cementitious materials for oil-well cementing through a step-by-step optimization method[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2016, 72:299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.05.017 [14] 耿晨梓,姚晓,代丹,等. SiO2晶态物性对高温水泥石力学性能的影响[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(6):777-783.GENG Chenzi, YAO Xiao, DAI Dan, et al. Effects of physical properties of SiO2 crystalline state on mechanical properties of high temperature set cement[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(6):777-783. -




 下载:
下载: