Effects of Drilling Fluid Encapsulators on Well Cement Slurries
-
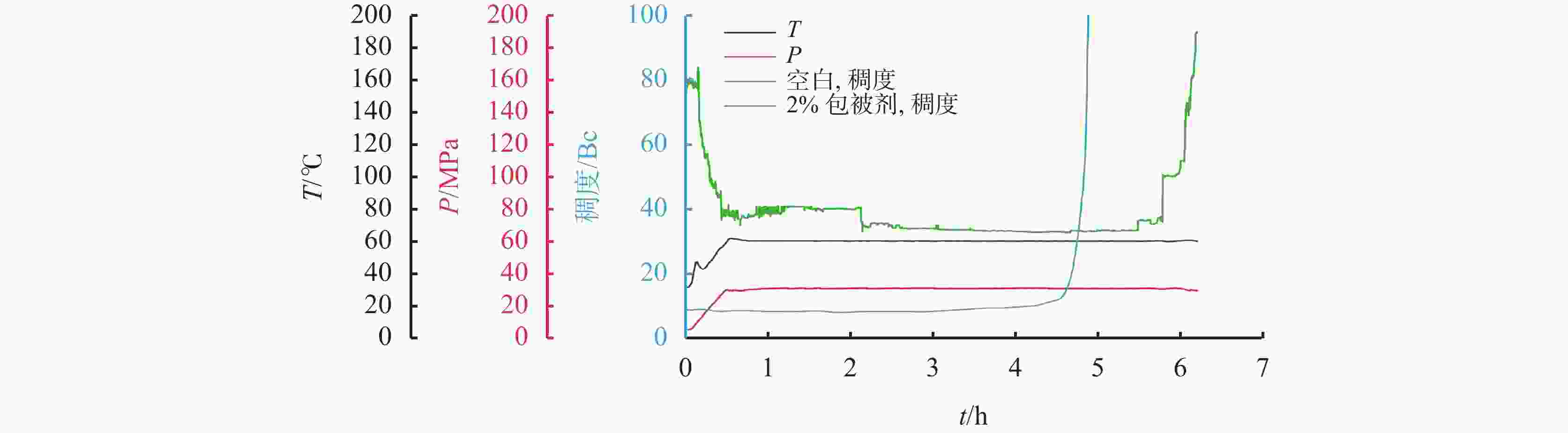
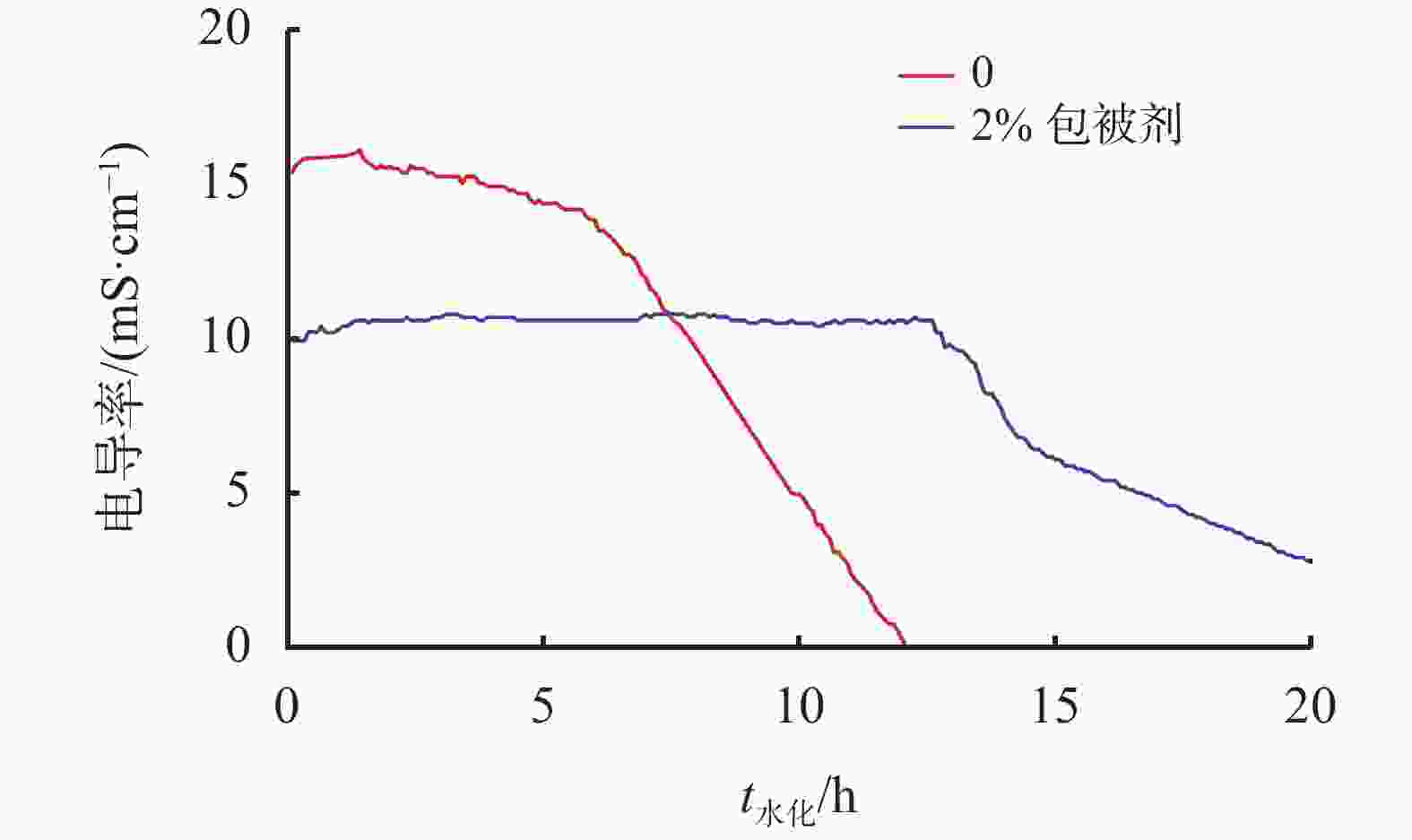
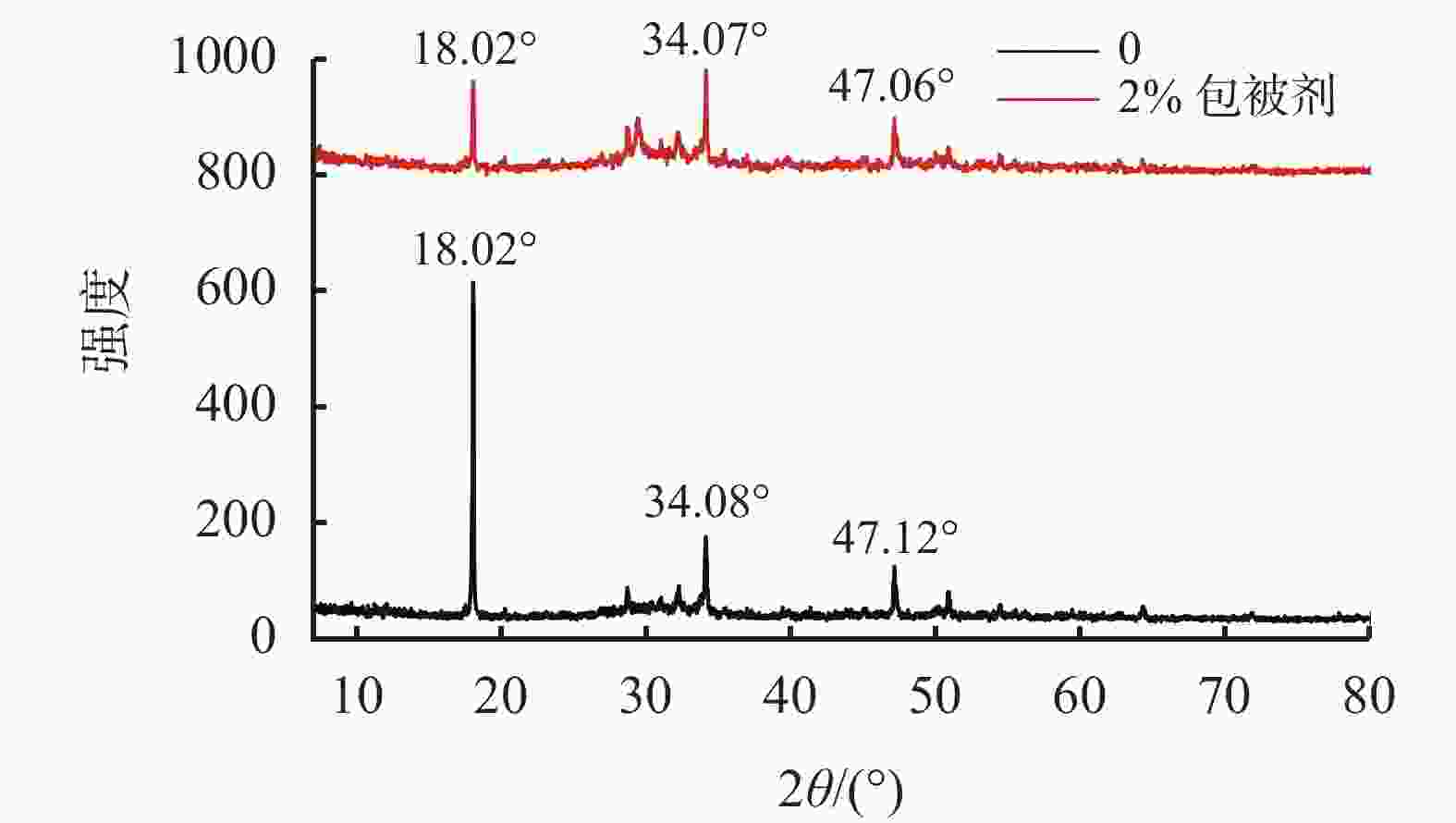
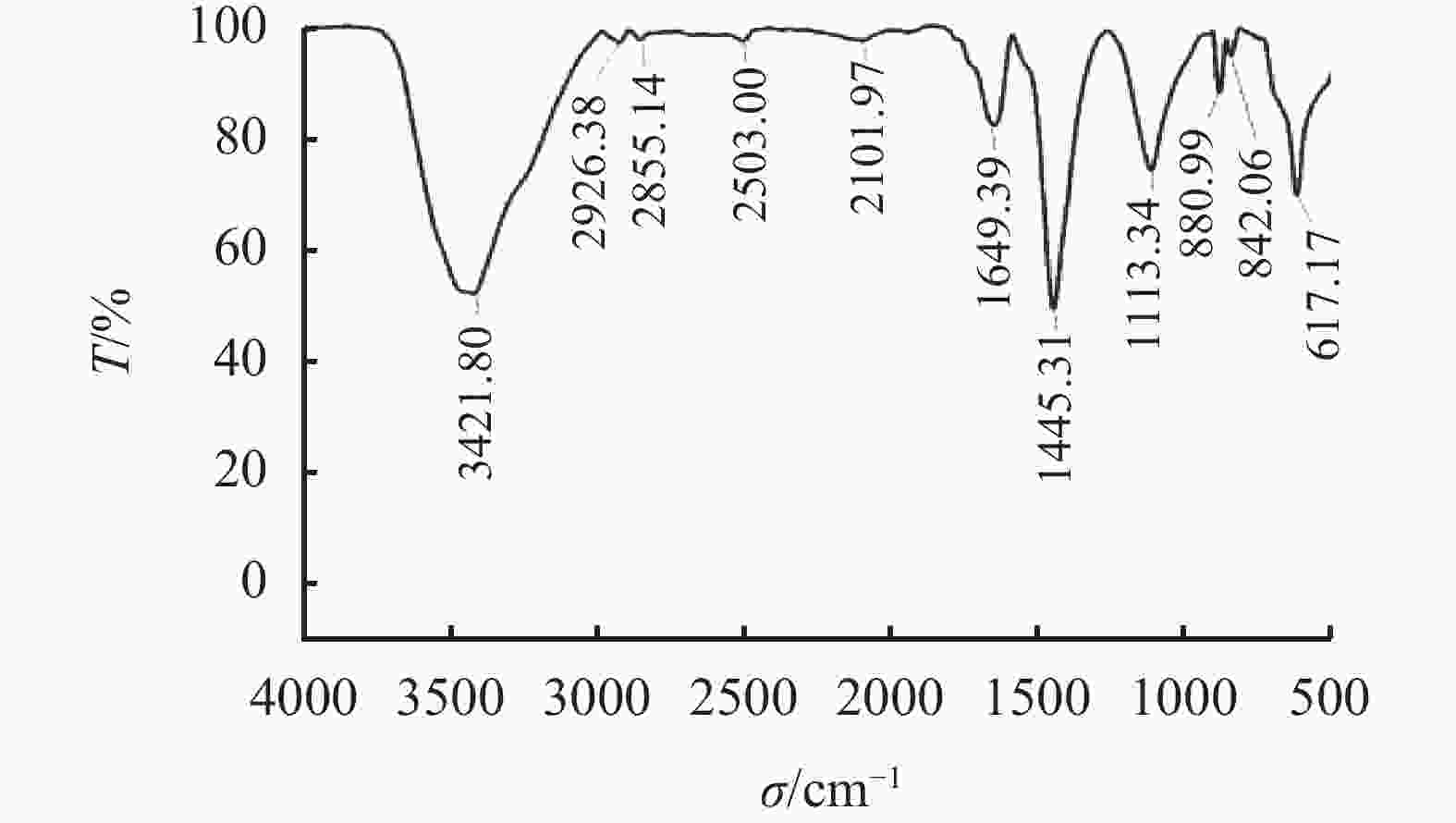
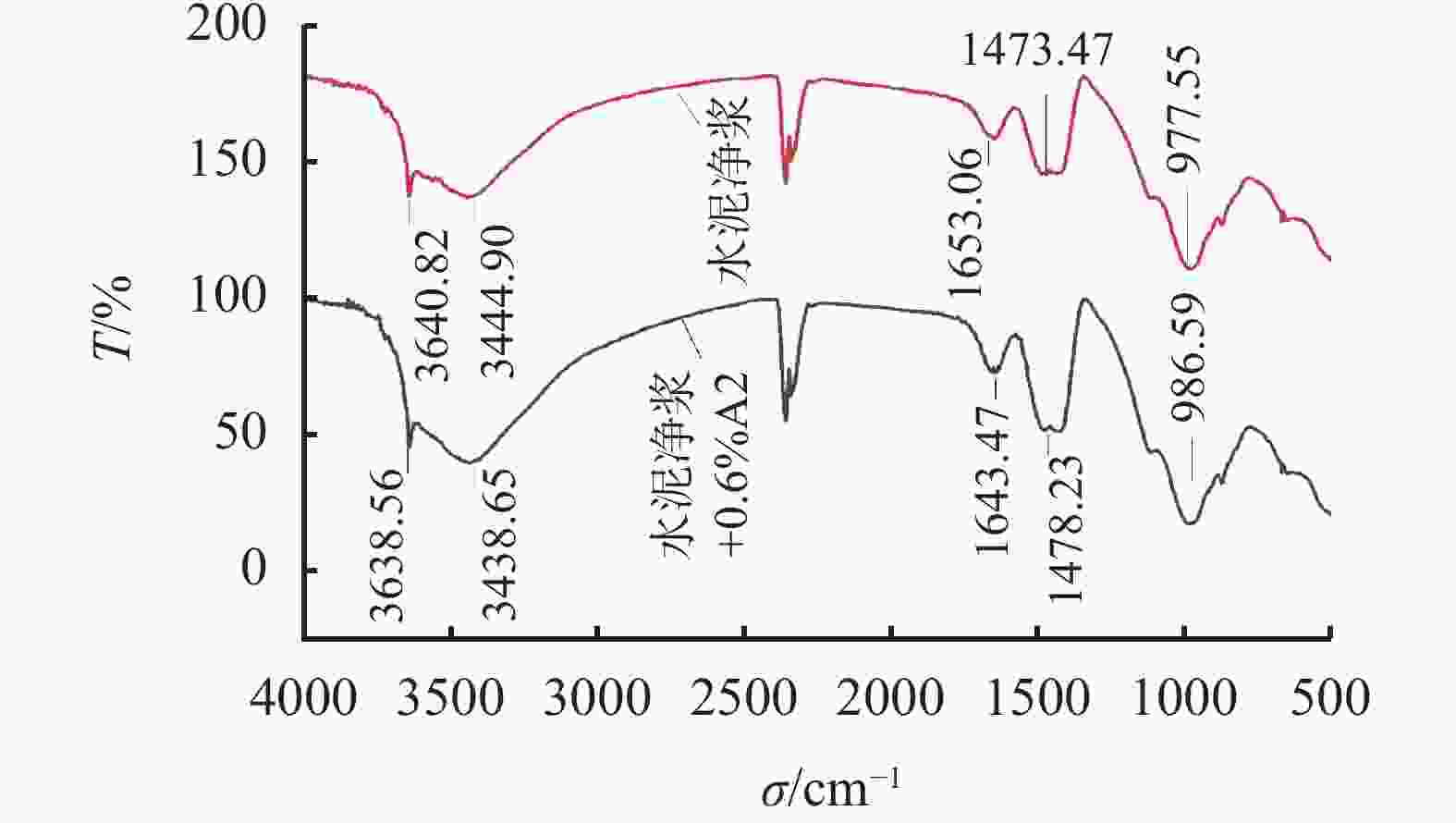
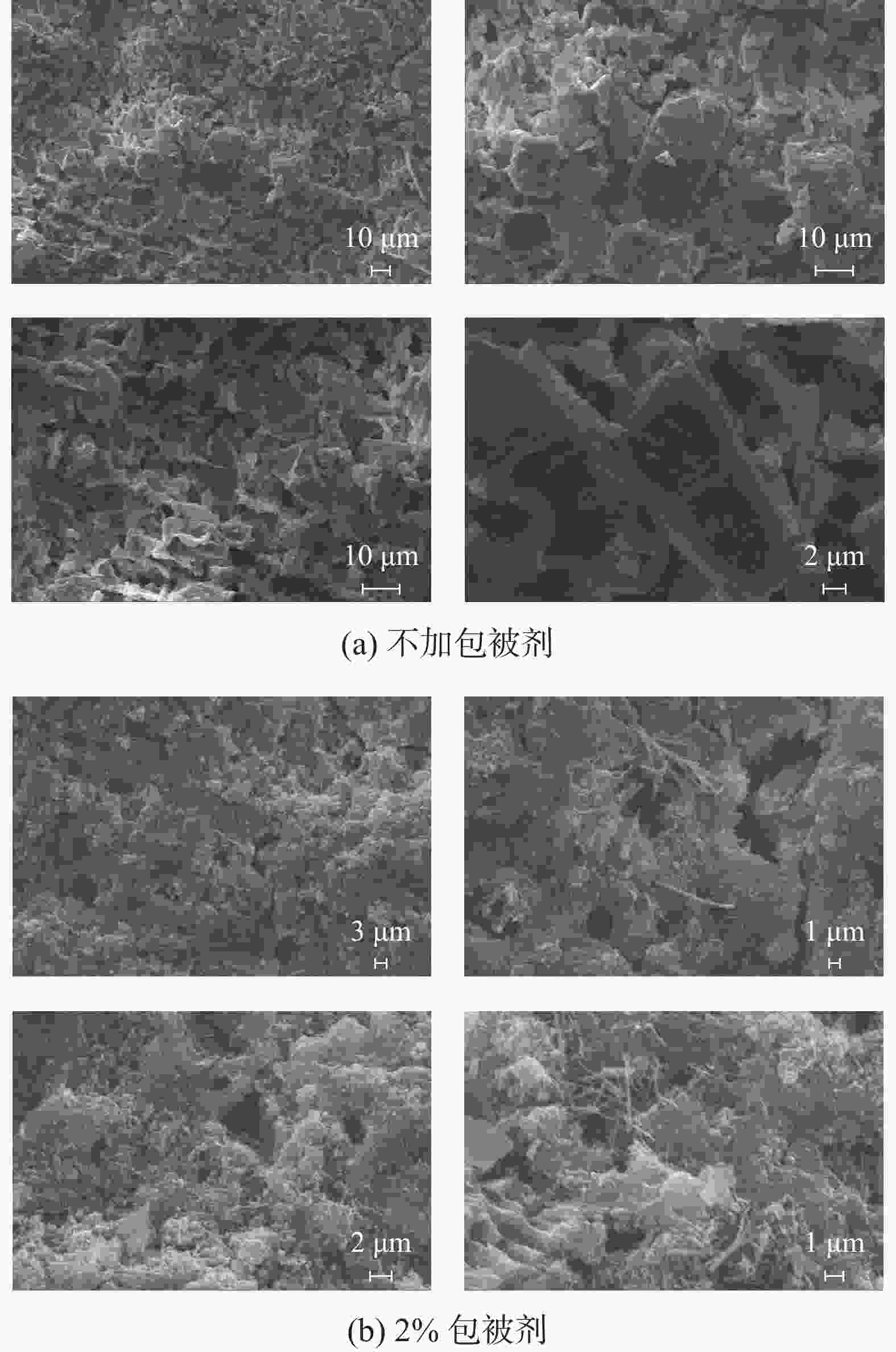
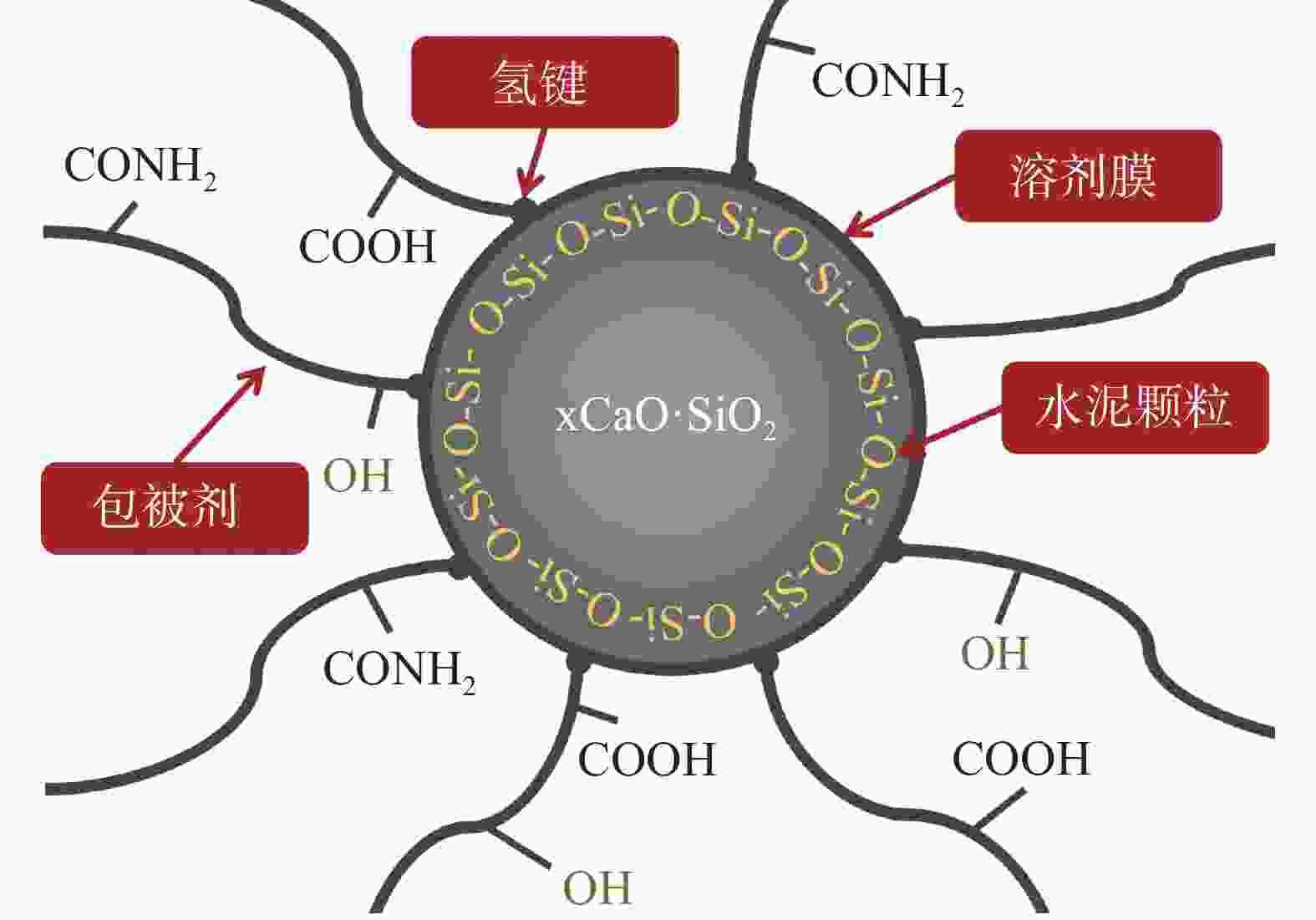
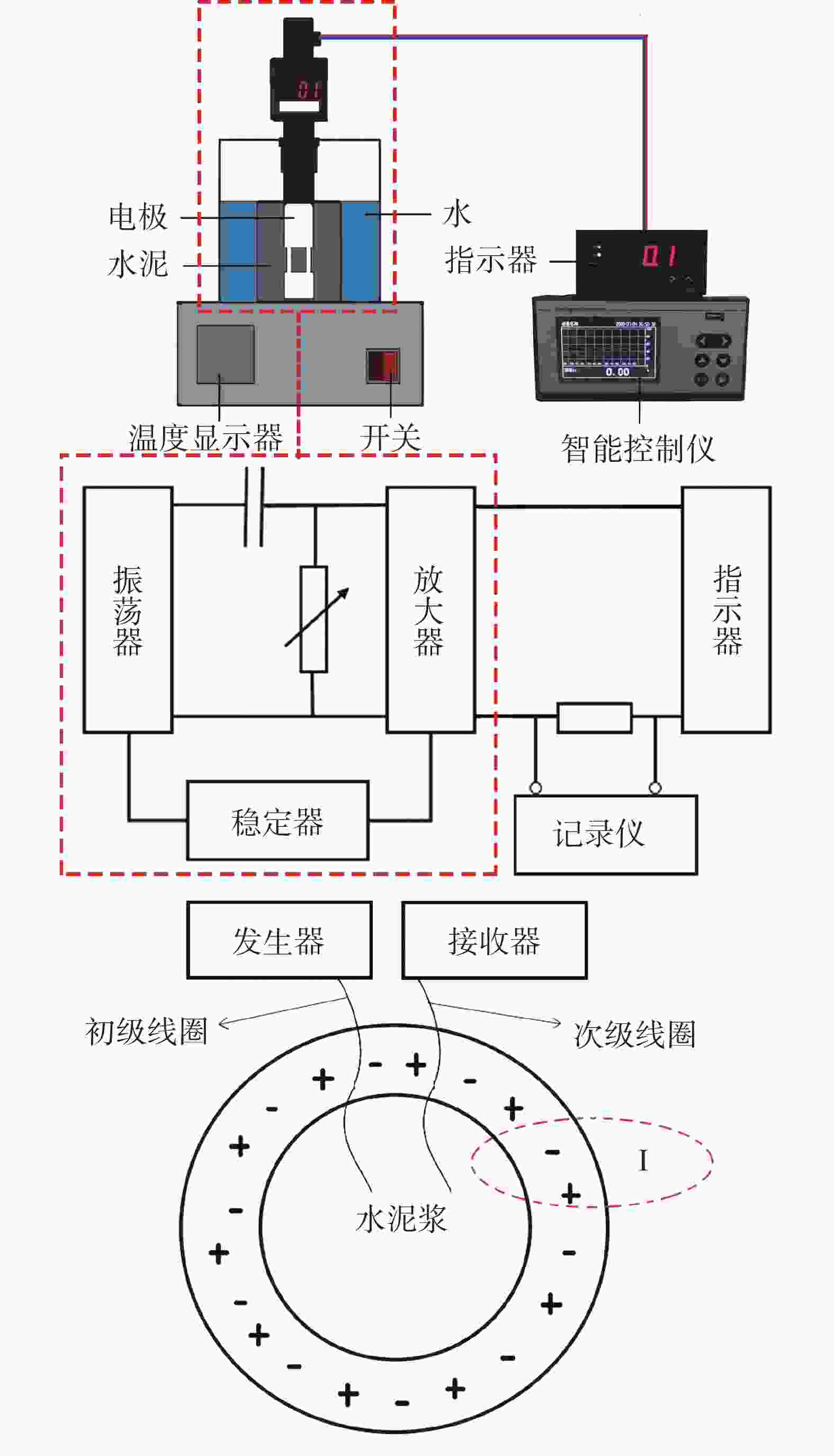
摘要: 针对钻井液与固井水泥浆相互接触时会使混浆流动性能变差的问题,实验研究了包被剂对固井水泥浆稠化时间、流变性能和抗压强度的影响。采用红外光谱、X射线衍射仪以及扫描电镜探究了包被剂对固井水泥浆的污染机理。同时利用电导率评价方法,比较了掺入包被剂前后固井水泥浆电导率的变化。研究结果表明,包被剂的掺入会降低水泥浆的流动度,当加量为0.6%时,水泥浆的流动度与纯水泥相比降低了52%;电导率实验分析表明,掺入包被剂后的水泥浆水化进行到12 h时,才进入加速期;包被剂的掺入降低了固井水泥浆水化的反应速率,延缓了其水化进程,从而导致固井水泥浆的抗压强度发展缓慢,在90 ℃养护条件下,掺量为0.2%时,其3 d强度与纯水泥相比降低了12.8%。包被剂中—OH、—CONH2、—COO-等具有吸附性能的官能团会吸附于水泥颗粒上,且包被剂中的亲水基团与固井水泥浆中的 Si—O 形成氢键,在水泥颗粒表面形成一层溶剂膜,阻碍了水与水泥颗粒的接触。Abstract: When a drilling fluid is mixed with a cement slurry, the flow of the mixture will become very poor. In a laboratory study, the effects of drilling fluid encapsulators on the thickening time, rheology and the compressive strength of cement slurries were investigated. Using IR, XRD and SEM, the mechanisms with which the cement slurries are contaminated by the drilling fluid encapsulators are studied. Electric conductivity method was also used to evaluate the changes of the electric conductivity of cement slurries before and after the cement slurries are mixed with drilling fluid encapsulators. The study results showed that the mobility of a cement slurry is reduced when an encapsulator is mixed with the cement slurry; a pure cement slurry contaminated with 0.6% encapsulator has its mobility reduced by 52%. Electric conductivity experiment showed that the hydration process of a cement slurry, which is contaminated with a drilling fluid encapsulator, begins accelerated only after 12 hours of hydration. The mixing of a drilling fluid encapsulator into a cement slurry will slow down the hydration process of the cement slurry, leading to a slow development of the compressive strength of the cement slurry. A cement slurry containing 0.2% drilling fluid encapsulator and cured at 90 ℃, has a 3 d strength that 12.8% lower than that of the pure cement slurry. The adsorption groups in the molecules of the encapsulator, such as —OH, —CONH2, —COO- etc., can be adsorbed onto the particles of the cement, and the hydrophilic groups of the encapsulator can form hydrogen bond with the Si—O bond in the cement molecules, thereby forming a solvent film on the surfaces of the cement particles, which in turn hinders the contact of water with the cement particles.
-
表 1 钻井液用包被剂对水泥浆性能的影响
包被剂/
%ρ/
g·cm−3流动度/
cm包被剂/
%ρ/
g·cm−3流动度/
cm0 1.89 25 0.4 1.89 16 0.2 1.89 18 0.6 1.89 12 表 2 包被剂对水泥石抗压强度的影响
包被剂/% p3 d/MPa p7 d/MPa 60 ℃ 90 ℃ 60 ℃ 90 ℃ 0 13.94 19.28 23.25 22.87 0.20 13.25 16.80 16.07 19.00 0.40 12.91 12.96 15.85 15.19 0.60 12.80 15.59 19.98 13.72 -
[1] 郑力会,鄢捷年,陈勉,等. 钻井液用仿磺化沥青防塌剂的性能与作用机理[J]. 油田化学,2005,22(2):97-100.ZHENG Lihui, YAN Jienian, CHEN Mian, et al. Performance properties and punctioning mechanisms of pseudo ssulfonated aasphalt as anticaving agent for water base drilling fluids[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2005, 22(2):97-100. [2] 郭丽梅,薛锦华,陈曦. 新型屏蔽暂堵剂ZDJ室内性能评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2016,33(1):37-41.GUO Limei, XUE Jinhua, CHEN Xi. Laboratory evaluation of a new temporary plugging agent ZDJ[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2016, 33(1):37-41. [3] WANG F, TAN X, WANG R, et al. High temperature and high pressure rheological properties of high-density water-based drilling fluids for deep wells[J]. PetroleumScience, 2012, 9(3):354-362. [4] 乔宁. 固井水泥浆与钻井液接触污染作用研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量,2019,39(10):115-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2019.10.054QIAO Ning. Study on contact pollution of cement slurry and drilling fluid[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2019, 39(10):115-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4076.2019.10.054 [5] 马勇,刘伟,唐庚,等. 川渝地区“三高”气田超深井固井隔离液应用实践[J]. 天然气工业,2010,30(6):77-79. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.06.021MA Yong, LIU Wei, TANG Geng, et al. Application of spacer fluid for cementing ultra-deep walls in Sichuan and Chongqing "three highs" gas fields[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(6):77-79. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.06.021 [6] 郑友志,佘朝毅,姚坤全,等. 钻井液处理剂对固井水泥浆的污染影响[J]. 天然气工业,2015,35(4):76-81. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.04.012ZHENG Youzhi, SHE Chaoyi, YAO Kunquan, et al. Contamination effects of drilling fluid additives on cement slurry[J]. Natural Gas Industr, 2015, 35(4):76-81. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.04.012 [7] 李明,王伟,郑友志,等. 单因素法分析钻井液处理剂对水泥浆性能的影响[J]. 石油与天然气化工,2014,43(3):297-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2014.03.017LI Ming, WANG Wei, ZHENG Youzhi, et al. Impact of drilling fluid additives on performance of the cement slurry by single-factor[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2014, 43(3):297-301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3426.2014.03.017 [8] 刘慧婷,付家文,丛谧,等. 高强度低密度水泥石的微观结构和力学性能[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2020,39(11):3432-3438.LIU Huiting, FU Jiawen, CONG Mi, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength low-density cement[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(11):3432-3438. [9] 艾丽,李早元,谢飞燕,等. 常见无机盐对油井水泥石抗压强度的影响机理[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2012,29(4):63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.04.018AI Li, LI Zaoyuan, XIE Feiyan, et al. State key laboratory of oil and gas reservoir geology and exploitation southwest petroleum university[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2012, 29(4):63-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.04.018 [10] MCCARTER W J, CHRISP T M, STARRS G, et al. Characterization of physio-chemical processes and hydration kinetics in concretes containing supplementary cementitious materials using electrical property measurements[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2013, 50(7):26-33. [11] MCCARTER W J, CHRISP T M, STARRS G. The early hydration of alkali-activated slag: developments in monitoring techniques[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 1999, 21(4):277-283. [12] 李明,杨雨佳,张冠华,等. 钻井液中生物增黏剂对固井水泥浆性能及结构的影响[J]. 天然气工业,2014,34(9):93-98. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.09.015LI Ming, YANG Yujia, ZHANG Guanhua, et al. Impact of a biological tackifier in a drilling fluid system on the performance and structure of a cement slurry[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(9):93-98. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2014.09.015 [13] 杨念,况守英,岳蕴辉. 几种常见无水碳酸盐矿物的红外吸收光谱特征分析[J]. 矿物岩石,2015,35(4):37-42.YANG Nian, KUANG Shouying, YUE Yunhui. Infrared spectra analysis of several common anhydrous carbonate minerals[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 35(4):37-42. [14] ZHANG Z D, SCHERER G W, GEORGE W, et al. Morphology of cementitious material during early hydration[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2018:85-100. [15] 张栋,吴文祥,任佳潍,等. Ca2+与Mg2+对聚合物黏度影响及其增黏方法[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2016,35(1):105-108. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2016.01.021ZHANG Dong, WU Wenxiang, REN Jiawei, et al. Influences of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the viscosity of the polymer solution and thickening method[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2016, 35(1):105-108. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2016.01.021 -




 下载:
下载: