Response Surface Optimization of Biosafety Disposal of Waste Water Based Drilling Fluids for Deep Drilling
-
摘要: 针对大庆油田深层致密气废弃水基钻井液固液分离难、泥饼含水率高(>80%)、存在二次污染的问题,开展了废弃水基钻井液无害化处理技术研究,在分析废弃水基钻井液特性与处理难点基础上,应用Box-Behnken中心组合实验和响应面分析法,通过考察破胶剂、助凝剂与絮凝剂的最佳配比对废弃钻井液固液分离效果的影响,创新建立了固液分离泥饼含水率与处理配方参数间的数学模型,研发出了以脱稳絮凝为核心的废弃水基钻井液无害化处理技术,形成了脱稳-絮凝-固液分离处理工艺。现场实验结果表明,废弃水基钻井液经该项技术处理后,泥饼含水率为47%,泥饼浸出液悬浮物含量为63 mg/L,泥饼浸出液中石油类、COD等9项主要污染指标符合GB 8978—1998《污水综合排放标准》、DB23/T 693—2000《黑龙江省废弃钻井液处理规范》相关要求,该技术成果解决了大庆油田深层水基钻井液破胶脱稳效果差等难题,具有较好的推广应用价值。Abstract: Water based drilling fluids have been used to drill deep tight gas wells in Daqing Oilfield. In the treatment of the waste drilling fluids, it was found that the solids and the liquids were difficult to be separated from each other, the mud cakes had water-cut of greater than 80%, and secondary contamination existed in future operations. A study on the bio-safety disposal of waste water based drilling fluids was conducted to solve these problems. Based on the analyses of the characteristics of and difficulties in the treatment of the water drilling fluids, the Box-Behnken Central Composite Experiment and Response Surface Method were chosen as a means of study. By exploring the effects of the optimum ratio of gel breaker, coagulant aid and flocculant on the solid-liquid separation efficiency of the waste water based drilling fluids, a new mathematical model was established describing the relationship between the water-cut of mud cakes for solids-liquid separation and the treatment recipe parameters. A method for the biosafety disposal of waste water based drilling fluids was developed, with destabilization and flocculation as the core technique. Using the mathematical model and the biosafety disposal method, a destabilization-flocculation-solid-liquid separation technique was established. Field test results have shown that a waste water based drilling fluid, after treatment with the technique, formed a mud cake with water-cut of 47%, the suspension content in the mud cake leachate was 63 mg/L. Nine major pollution indices such as COD etc. of the waste drilling fluid conform to the requirements of the national standard GB 8978—1998 and the local standard DB23/T 693—2000, namely, “Waste Drilling Fluid Treatment Specification of Heilongjiang Province”. This technology provides an effective solution to the poor gel breaking and destabilization efficiency of the water based drilling fluids for deep hole drilling in Daqing Oilfield and has good promotion and application values.
-
Key words:
- Drilling fluid /
- Waste /
- Biosafety disposal /
- Chemical destabilization /
- Response surface method
-
表 1 滤液基本指标参数
滤液批次 COD/
mg·L−1总铬/
mg·L−1Cr6+/
mg·L−1总铅/
mg·L−1砷/
mg·L−1全盐量/
mg·L−1石油类/
mg·L−1悬浮物/
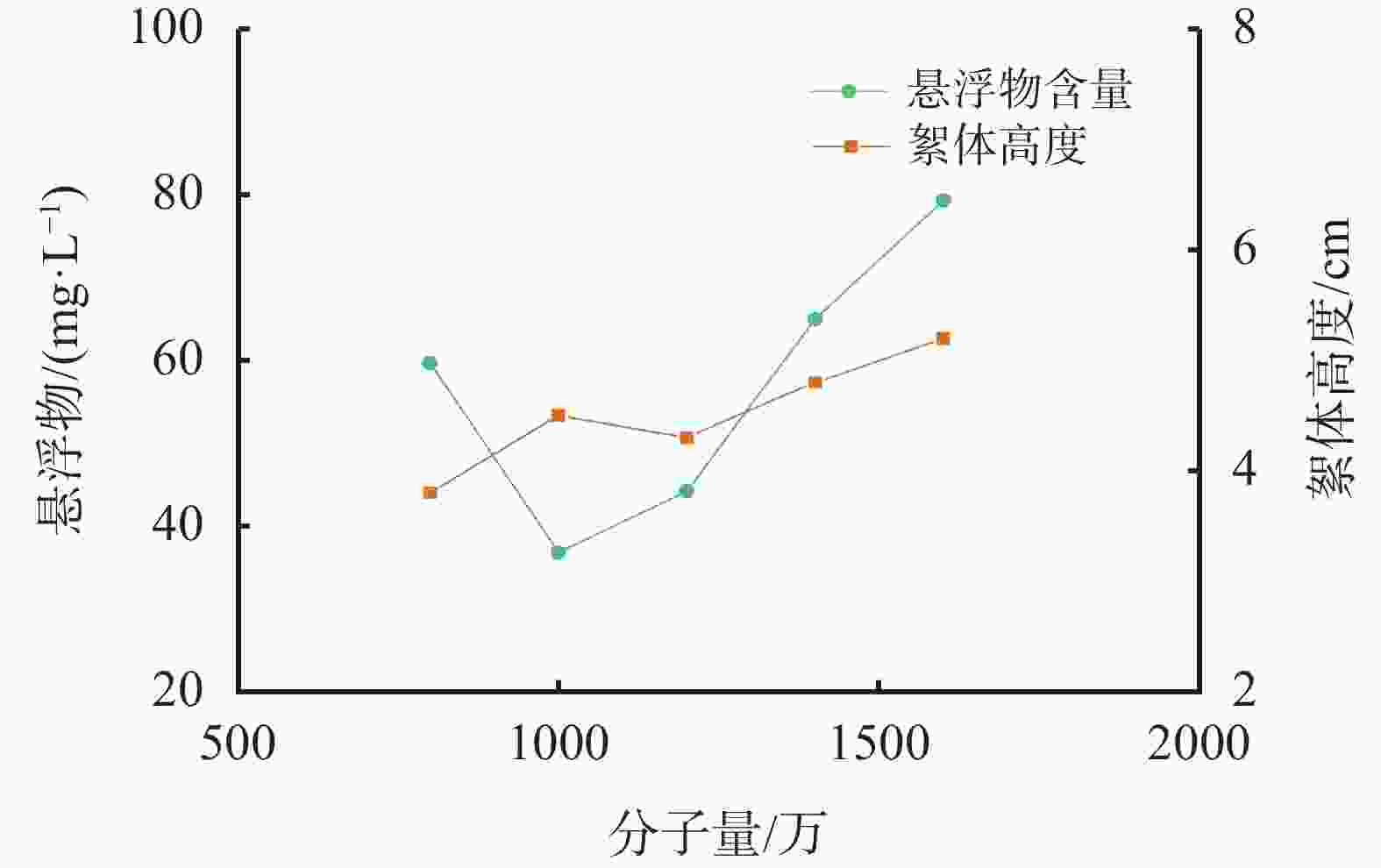
mg·L−1pH 1 7950 0.004 0.004 1.000 0.095 6570 2.45 4600 10 2 8040 0.004 0.004 0.733 0.007 8410 2.19 5350 10 3 9530 0.004 0.004 0.922 0.032 7650 2.33 4050 10 标准 100 1.500 0.100 1.000 0.500 2000 10.00 300 6~9 表 2 不同离子度絮凝剂处理深层水基钻井液
离子
度/%ν5/
mL·min-1析出液
V/mL悬浮物/
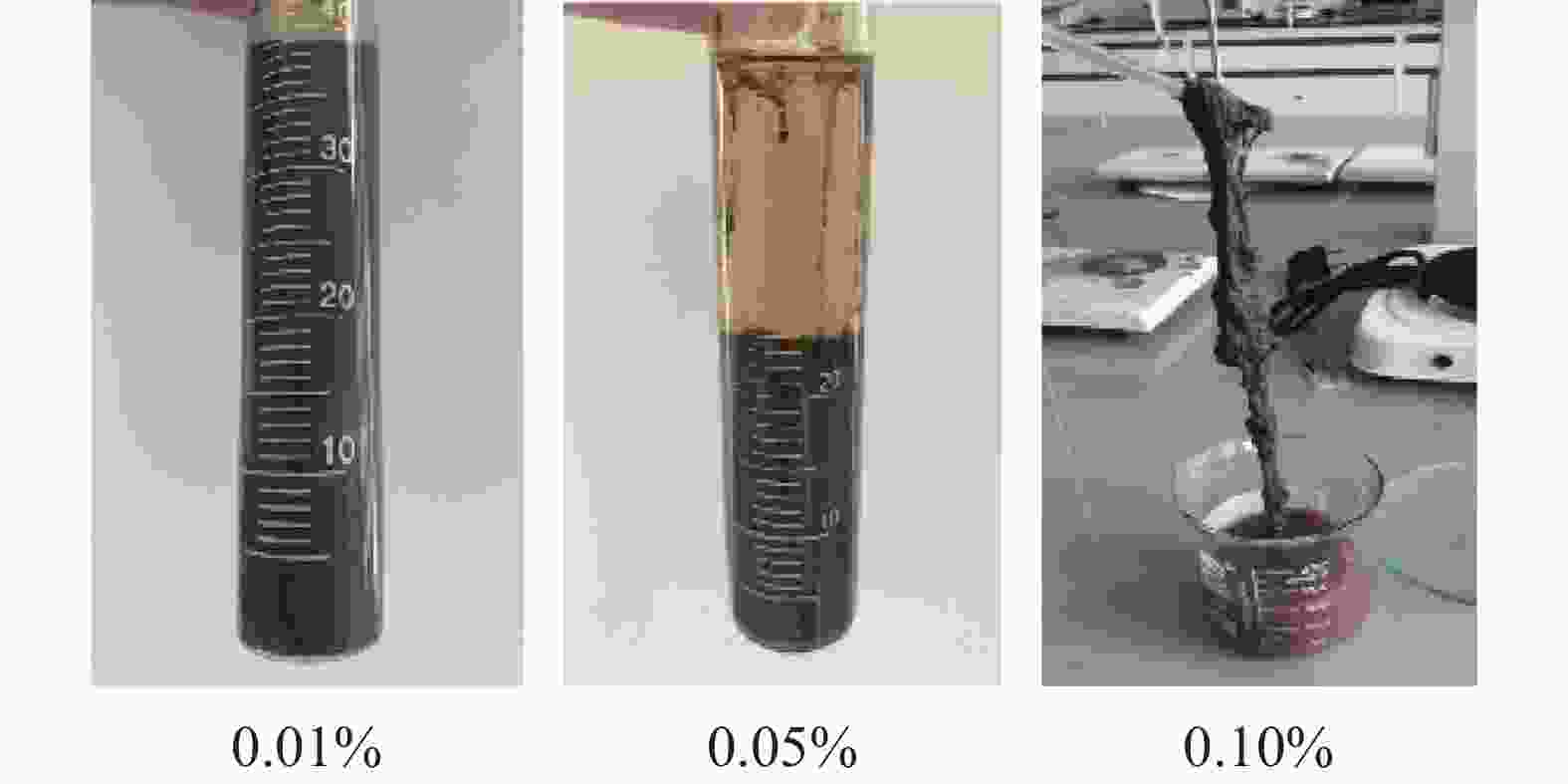
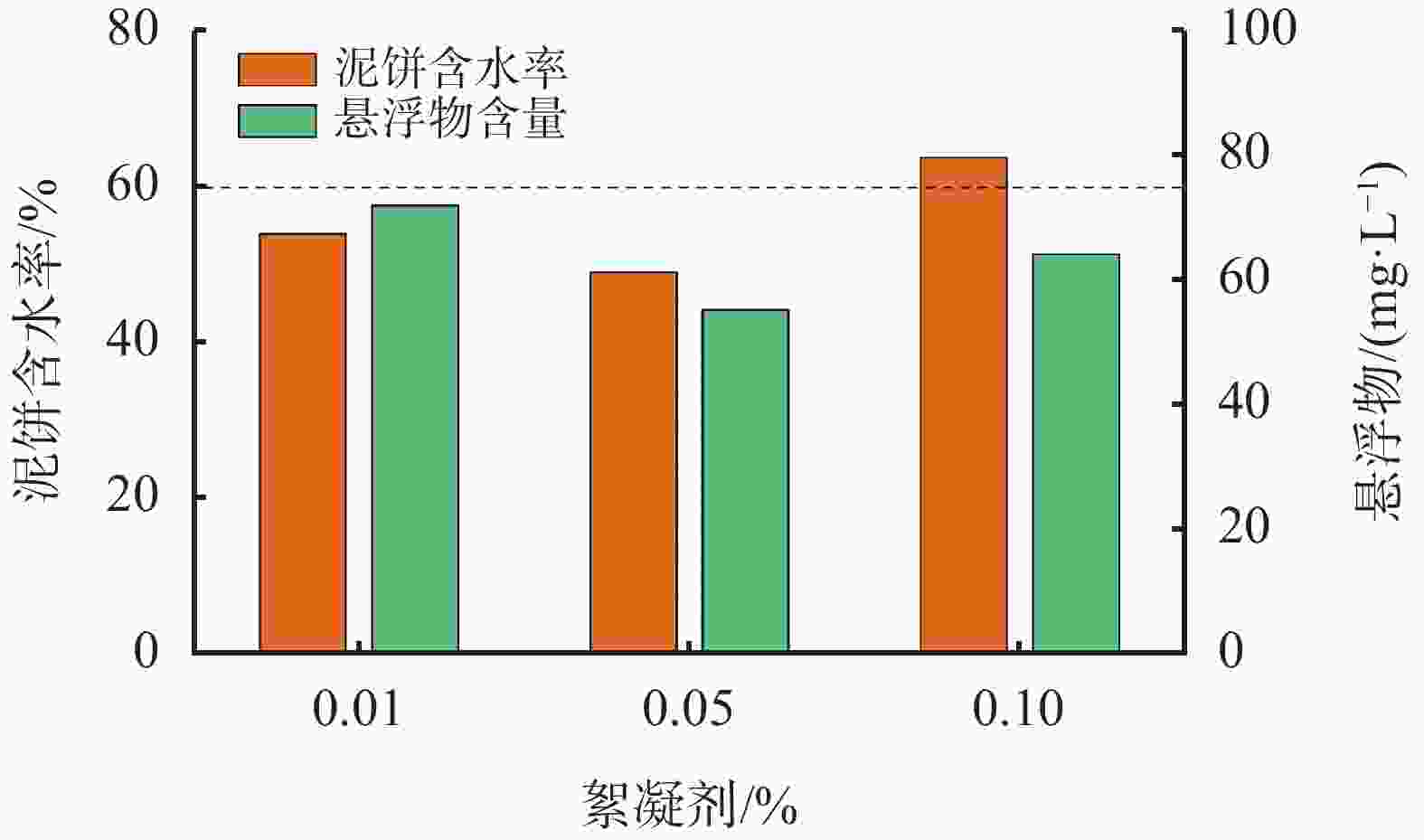
mg·L-1絮体状态 5 8.60 42.5 317.7 絮体过小、松散 10 8.30 41.0 87.6 絮体较大 20 8.24 41.2 32.1 颗粒适中、较紧密 30 8.76 43.8 338.2 絮体过小、疏松 40 8.60 43.0 262.5 絮体过小、疏松 表 3 助凝剂CJ与破胶剂PAJ和絮凝剂CPJ 复配对深层水基钻井液破胶效果对比
破胶剂
PAJt/
min不同复配结果处理后的析出液体积/mL 0.5%CJ+
0.01%CPJ1.0%CJ+
0.01%CPJ1.5%CJ+
0.01%CPJ7% 10 7.0 9.0 11.0 20 10.0 12.0 13.5 30 11.5 13.5 15.5 40 13.0 15.0 16.5 9% 10 12.0 12.0 10.0 20 14.5 15.0 13.0 30 15.5 15.0 15.0 40 15.5 15.0 15.0 表 4 响应面因素水平
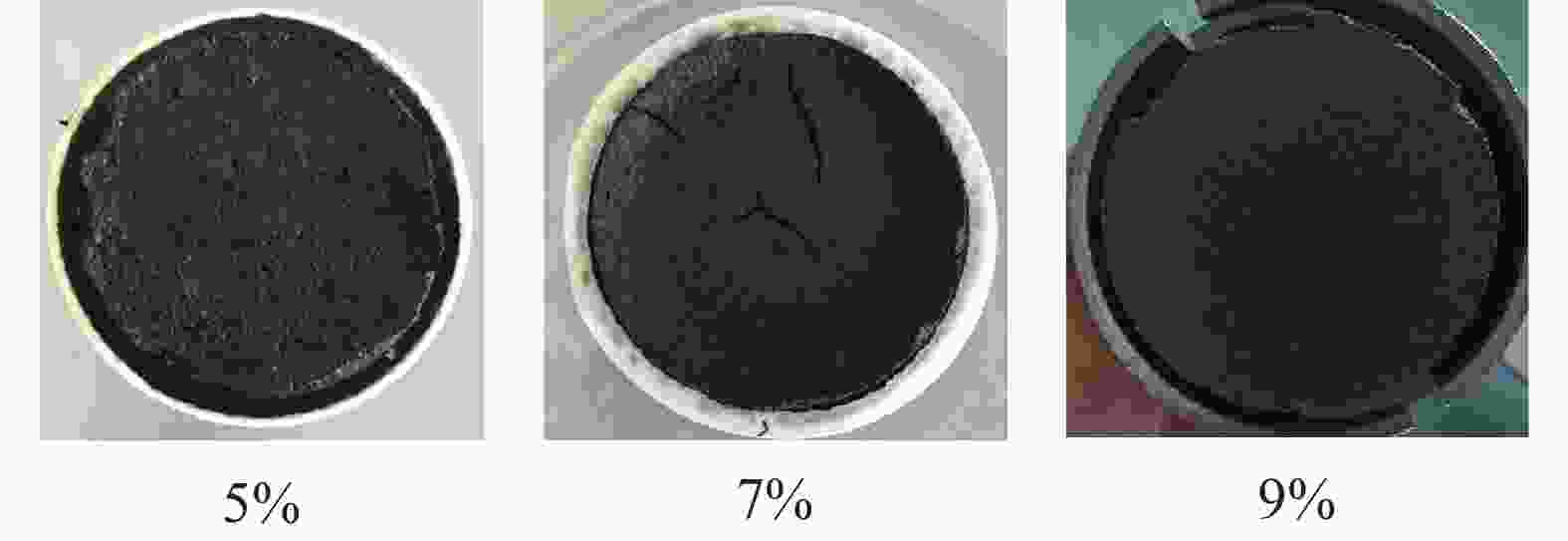
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A(X1/%) 7 8 9 B(X2/万) 800 1000 1200 C(X3/%) 10 15 20 D(X4/%) 0.5 1.0 1.5 表 5 响应面设计与结果
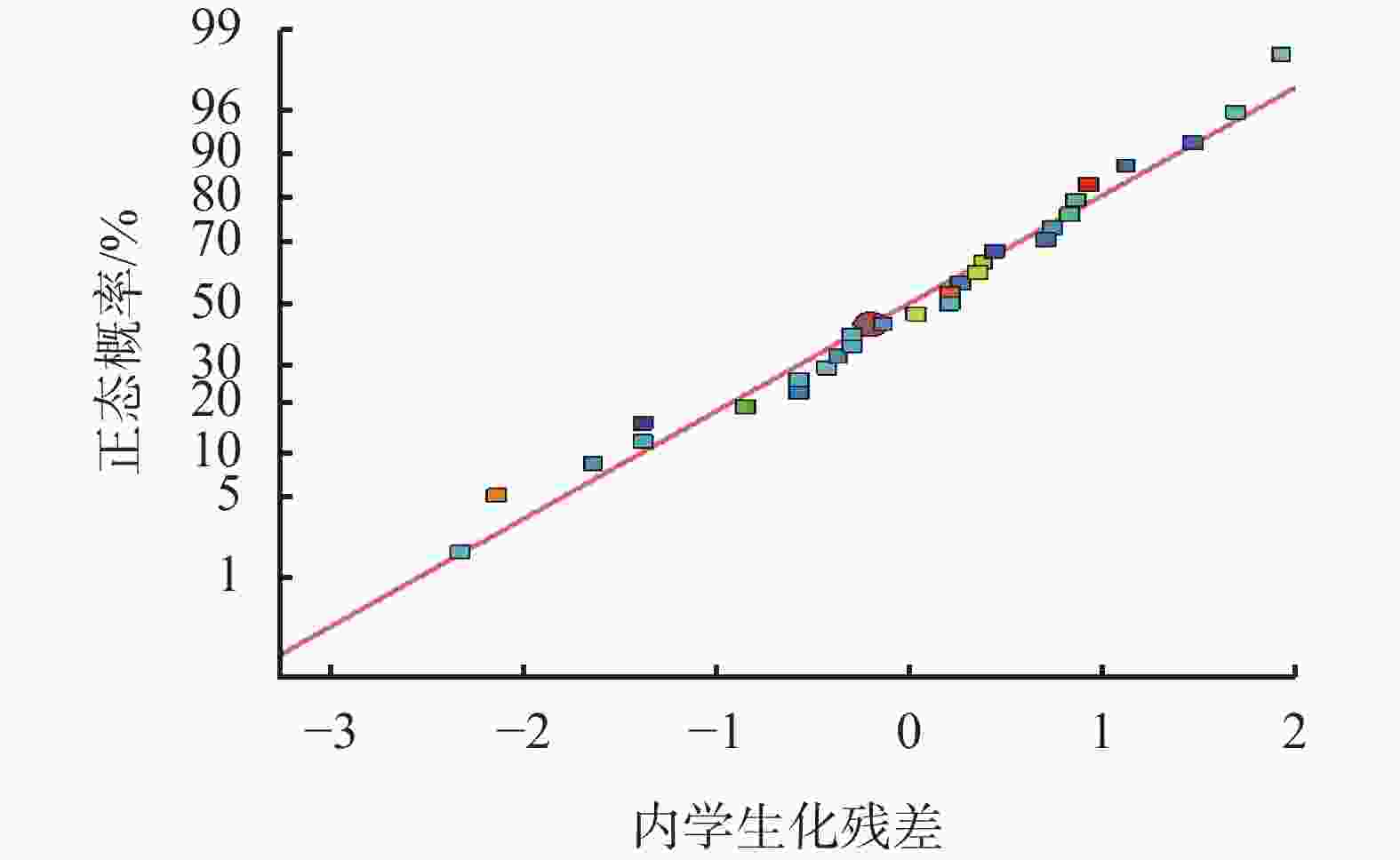
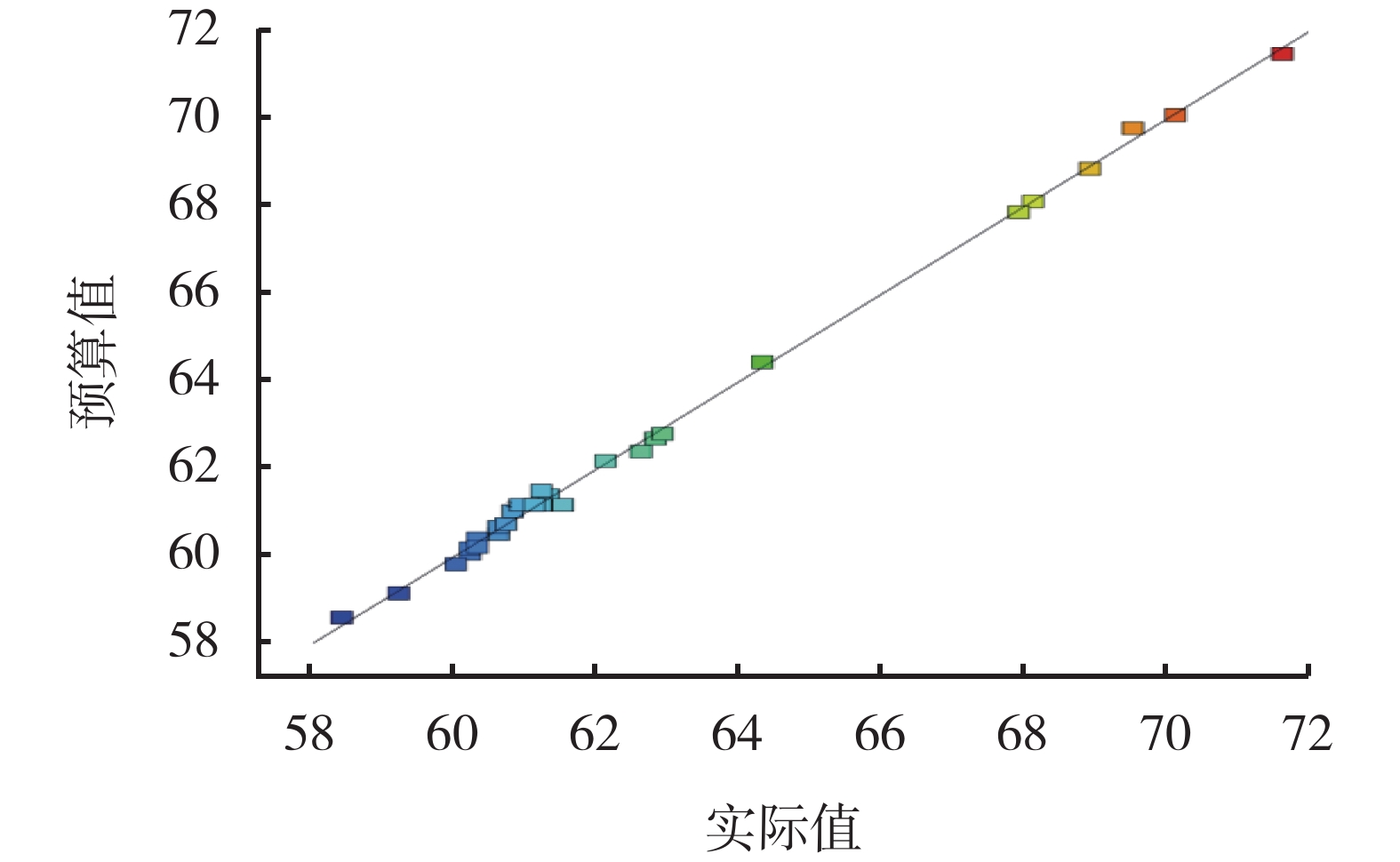
序号 A B C D Y/% 1 7 800 15 1.0 63.2 2 9 800 15 1.0 67.5 3 7 1200 15 1.0 59.5 4 9 1200 15 1.0 60.6 5 8 1000 10 0.5 60.1 6 8 1000 20 0.5 62.3 7 8 1000 10 1.5 62.1 8 8 1000 20 1.5 60.6 9 7 1000 15 0.5 62.3 10 9 1000 15 0.5 59.6 11 7 1000 15 1.5 58.7 12 9 1000 15 1.5 59.2 13 8 800 10 1.0 65.6 14 8 1200 10 1.0 60.3 15 8 800 20 1.0 64.9 16 8 1200 20 1.0 60.5 17 7 1000 10 1.0 59.1 18 9 1000 10 1.0 60.1 19 7 1000 20 1.0 59.2 20 9 1000 20 1.0 60.0 21 8 800 15 0.5 66.6 22 8 1200 15 0.5 61.8 23 8 800 15 1.5 64.8 24 8 1200 15 1.5 59.9 25 8 1000 15 1.0 61.1 26 8 1000 15 1.0 60.9 27 8 1000 15 1.0 61.3 28 8 1000 15 1.0 61.5 29 8 1000 15 1.0 61.2 表 6 响应面设计与结果
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F 显著水平 模型 371.7700 14 26.5500 572.39 < 0.0001 A 0.0675 1 0.0675 1.45 0.2477 B 201.7200 1 201.7200 4348.08 < 0.0001 C 5.6000 1 5.6000 120.78 < 0.0001 D 3.9700 1 3.9700 85.52 < 0.0001 AB 0.3600 1 0.360 0 7.76 0.0146 AC 0.4900 1 0.4900 10.56 0.0058 AD 1.5600 1 1.5600 33.68 < 0.0001 BC 0.3025 1 0.3025 6.52 0.0230 BD 6.5000 1 6.5000 140.16 < 0.0001 CD 0.7225 1 0.722 5 15.57 0.0015 A² 6.1800 1 6.1800 133.14 < 0.0001 B² 113.7000 1 113.7000 2450.73 < 0.0001 C² 2.6400 1 2.6400 56.97 < 0.0001 D² 11.3700 1 11.3700 245.16 < 0.0001 残差 0.6495 14 0.0464 失拟误差 0.4575 10 0.0458 0.9531 0.5703 纯误差 0.1920 4 0.0480 总离差 372.4200 28 表 7 现场试验处理剂加量与工艺条件
压滤
次数处理量/
m3破胶
剂/t絮凝
剂/kg助凝
剂/tt进料/
mint压榨/
minP压榨/
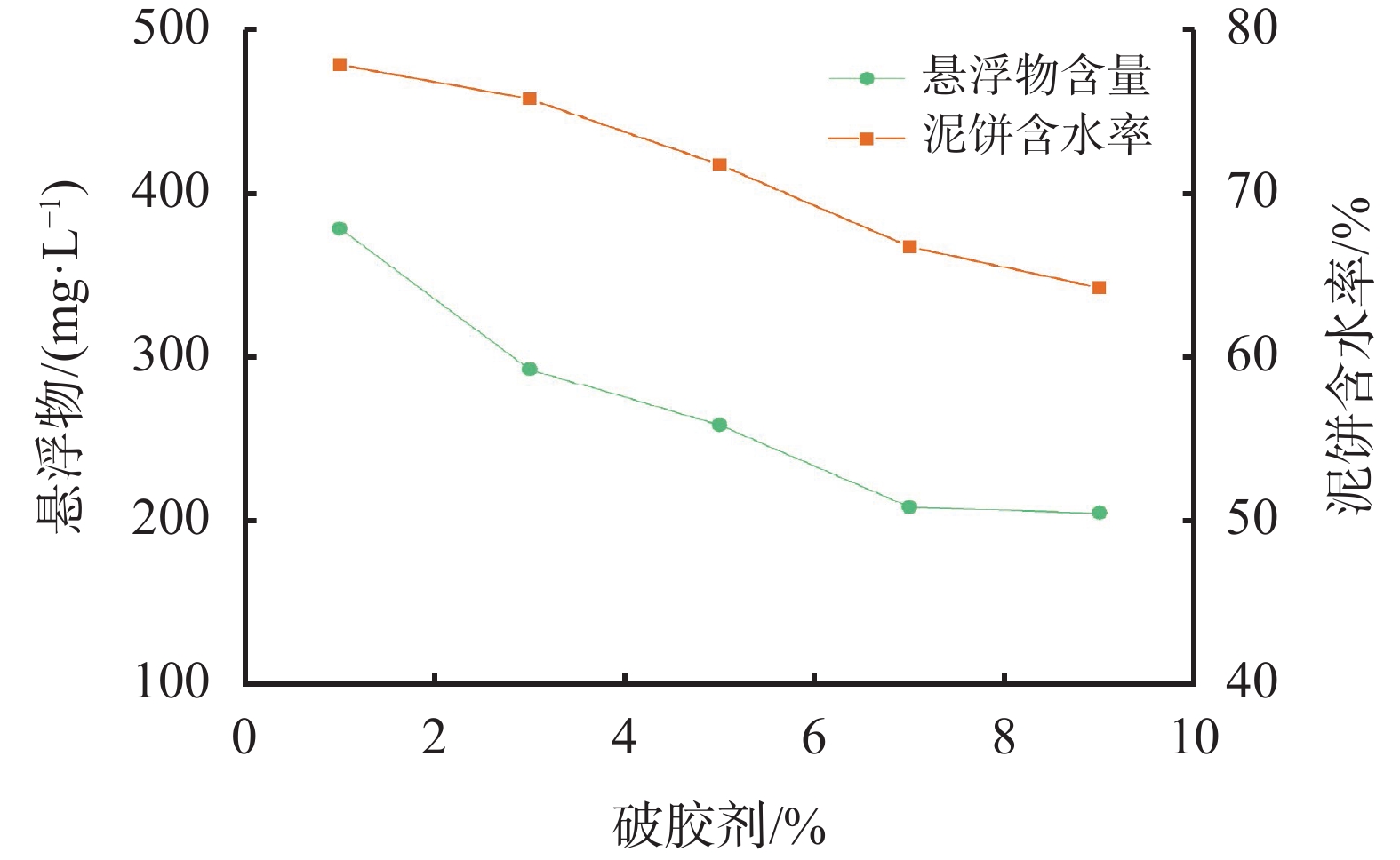
MPa一次 6 0.40 0.6 0.096 60 7 1.2 二次 4 0.27 0.4 0.064 50 20 1.2 三次 6 0.40 0.6 0.096 50 15 1.2 四次 7 0.47 0.7 0.112 60 10 1.2 表 8 滤液主要控制指标
滤液 悬浮物/(mg·L−1) 石油类/(mg·L−1) pH 标准值 300 10.00 6~9 处理前滤液 2380 3.32 9 一次压滤滤液 295 1.30 7 二次压滤滤液 270 1.10 7 三次压滤滤液 277 1.10 7 四次压滤滤液 278 1.30 7 表 9 泥饼及其浸出液主要控制指标
浸出液 泥饼含
水率/%CODCr/
mg·L−1总铬/
mg·L−1Cr6+/
mg·L−1总铅/
mg·L−1砷/
mg·L−1全盐量/
mg·L−1石油类/
mg·L−1悬浮物/
mg·L−1pH 标准值 60.0 100 1.500 0.100 1.0 0.50 2000 5.00 70.0 6~9 1#泥饼 48.2 84 0.004 0.004 0.1 0.16 1763 0.12 65.8 7 2#泥饼 45.8 91 0.004 0.004 0.1 0.18 1960 0.12 60.1 7 3#泥饼 47.0 88 0.004 0.004 0.1 0.12 1885 0.12 62.2 7 4#泥饼 46.9 78 0.004 0.004 0.1 0.10 1955 0.12 63.9 7 -
[1] 吴明霞. 废弃水基钻井液环境影响及固化处理技术研究[D]. 东北石油大学, 2012.WU Mingxia. Environmental impact and solidification of water-based drilling fluid[D]. Northeast Petroleum University, 2012. [2] 吴芳云, 陈进富, 赵朝成, 等. 石油环境工程[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 301.WU Fangyun, CHEN Jinfu, ZHAO Chaocheng, et al. Petroleum Environmental Engineering[M], 2002: 301. [3] 蒋淑英. 大庆油田废钻井液生物毒性及生物效应的研究[D]. 大庆石油学院, 2007.JIANG Shuying. The study of bio-toxicity and biological effects of the wastes drilling fluids from daqing oil field[D]. Daqing Petroleum University, 2007. [4] 王茂仁. 新疆油田钻井水基固液废弃物不落地处理技术研究[D]. 西南石油大学, 2017.WANG Maoren. Study on non-landing treatment technology of drilling water-based solid-liquid waste in Xinjiang Oilfield[D]. Southwest Petroleum University, 2017. [5] 王学川, 胡艳鑫, 郑书杰, 等. 国内外废弃钻井液处理技术研究现状[J]. 陕西科技大学学报, 2010, 28(6): 169-174.WANG Xuechuan, HU Yanxin, ZHENG Shujie, et al. Application status of waste drilling fluid treatment technology at home and abroad[J]. Journal of ShanXi University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 28(6): 169-174. [6] 郭敏辉. 化学调理改善活性污泥脱水性能的研究[D]. 浙江大学, 2014.GUO Minhui. Improvement of activated sludge dewaterability by chemical conditions[D]. Zhejiang University, 2014. [7] 董涛,钱秋兰,胡芝娟,等. 污泥化学调质及深度脱水[J]. 水泥技术,2013,2:22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6171.2013.02.002DONG Tao, QIAN Qiulan, HU Zhijuan, et al. Chemical conditioning and deep dewatering of sludge[J]. Cement Technology, 2013, 2:22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6171.2013.02.002 [8] 何纶, 樊世忠, 冉金成. 钻井完井液废弃物处理实用技术[M]. 中国矿业大学出版社, 2006.HE Lun, FAN Shizhong, RAN Jincheng. Practical treatment technology of drilling and completion fluid waste[M]. China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2006. [9] 周风山,曾光,何纶,等. 废弃钻井完井液固液分离技术研究进展[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2007(S1):59-64.ZHOU Fengshan, ZENG Guang, HE Lun, et al. Research progresses on the separation of solids and liquid in waste drilling and completion fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2007(S1):59-64. [10] 邱涌涛. 有机高分子絮凝剂的絮凝特征及絮凝机理初探[D]. 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.QIU Yongtao. Preliminary study on flocculation characteristics and flocculation mechanism of polymer flocculant [D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing, 2007. -




 下载:
下载: