Encapsulation of Energy-storage Microspheres
-
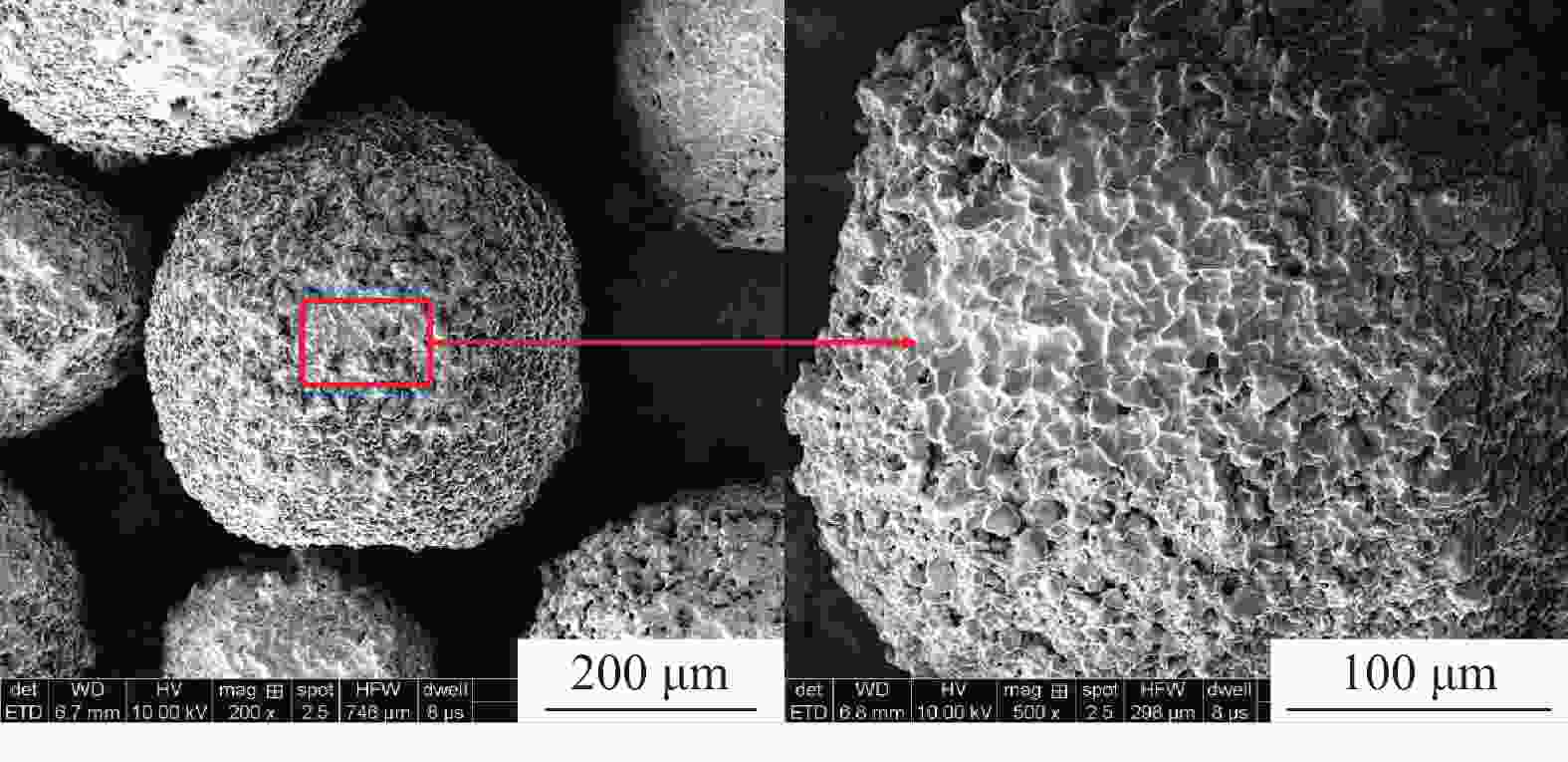
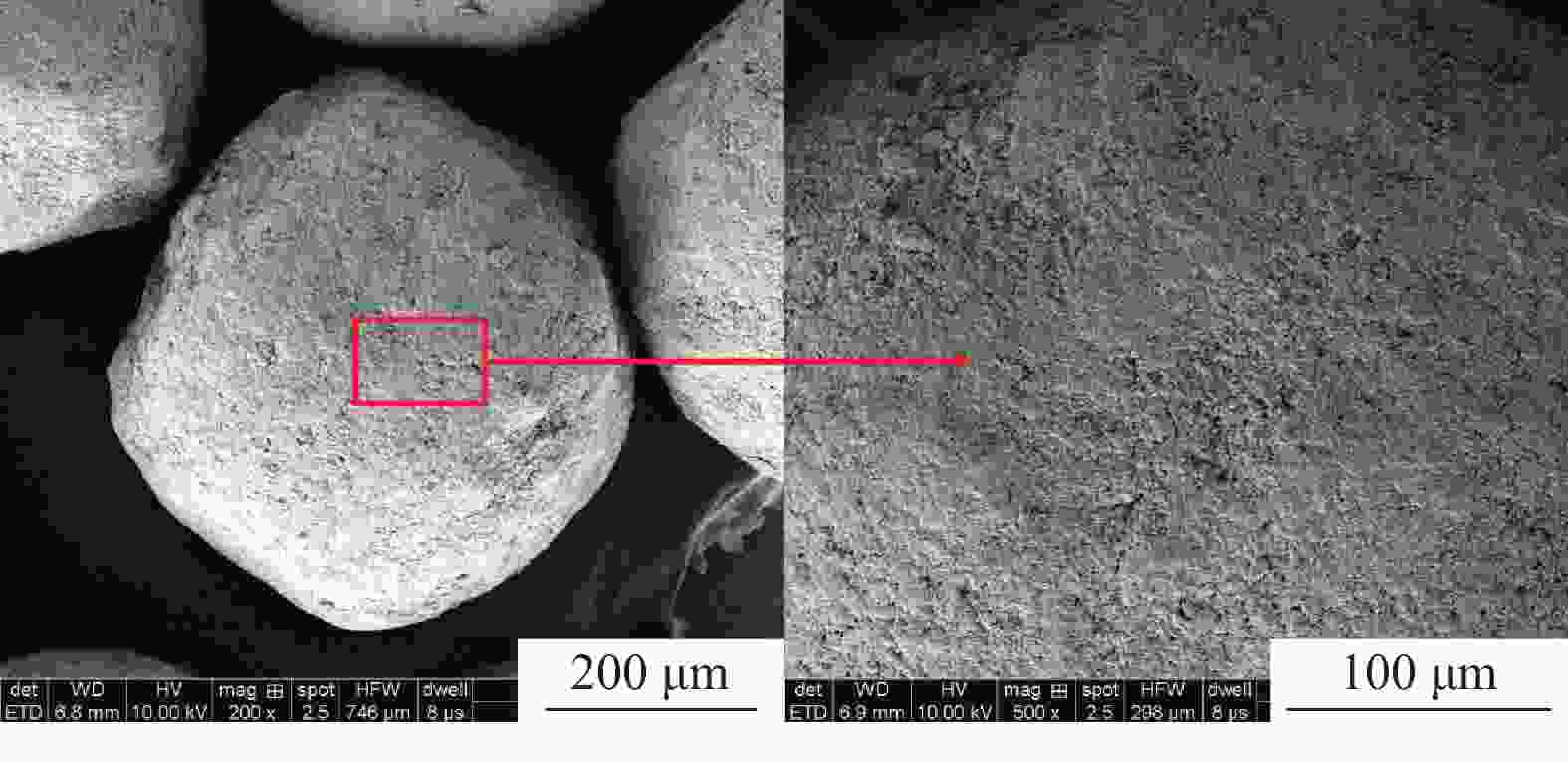
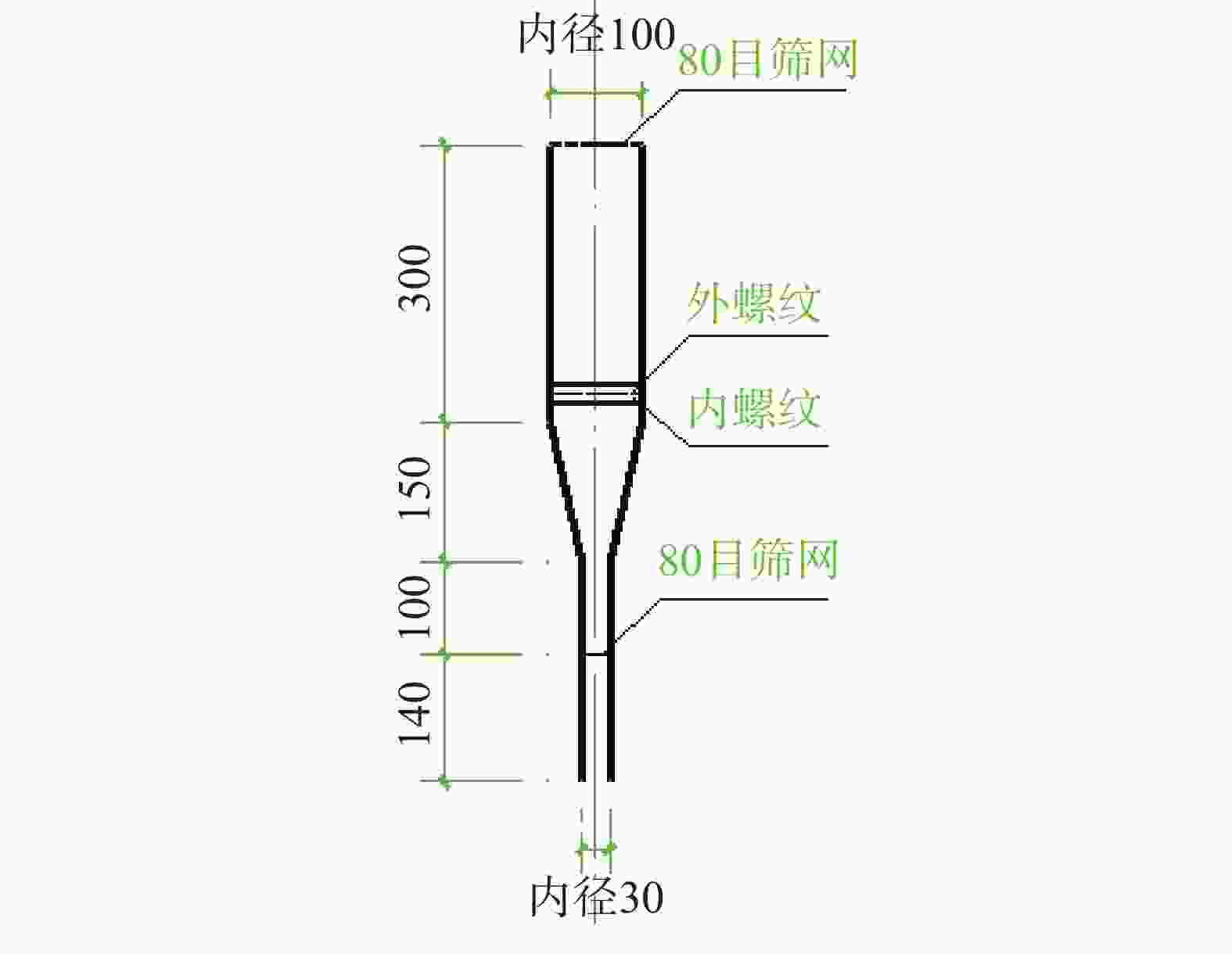
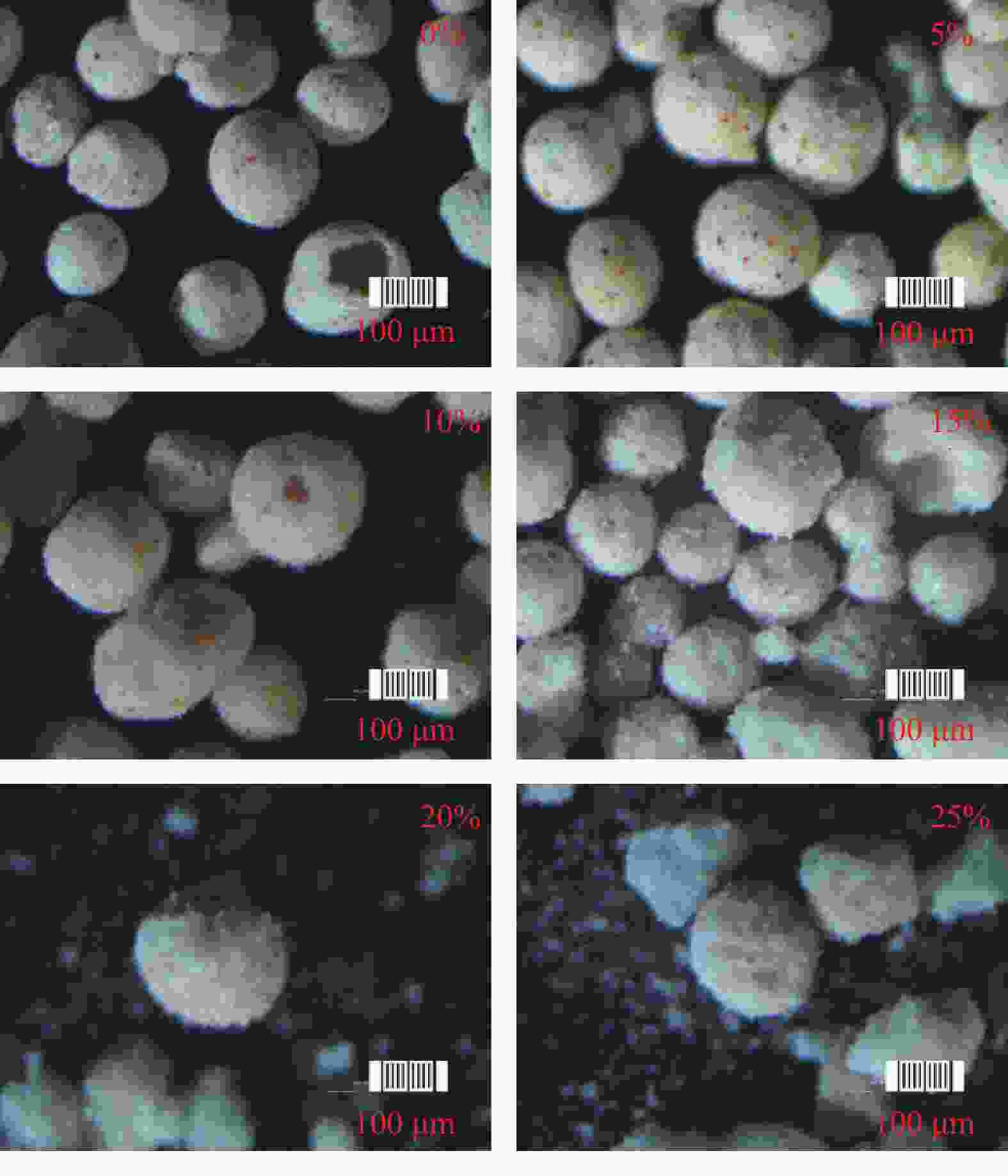
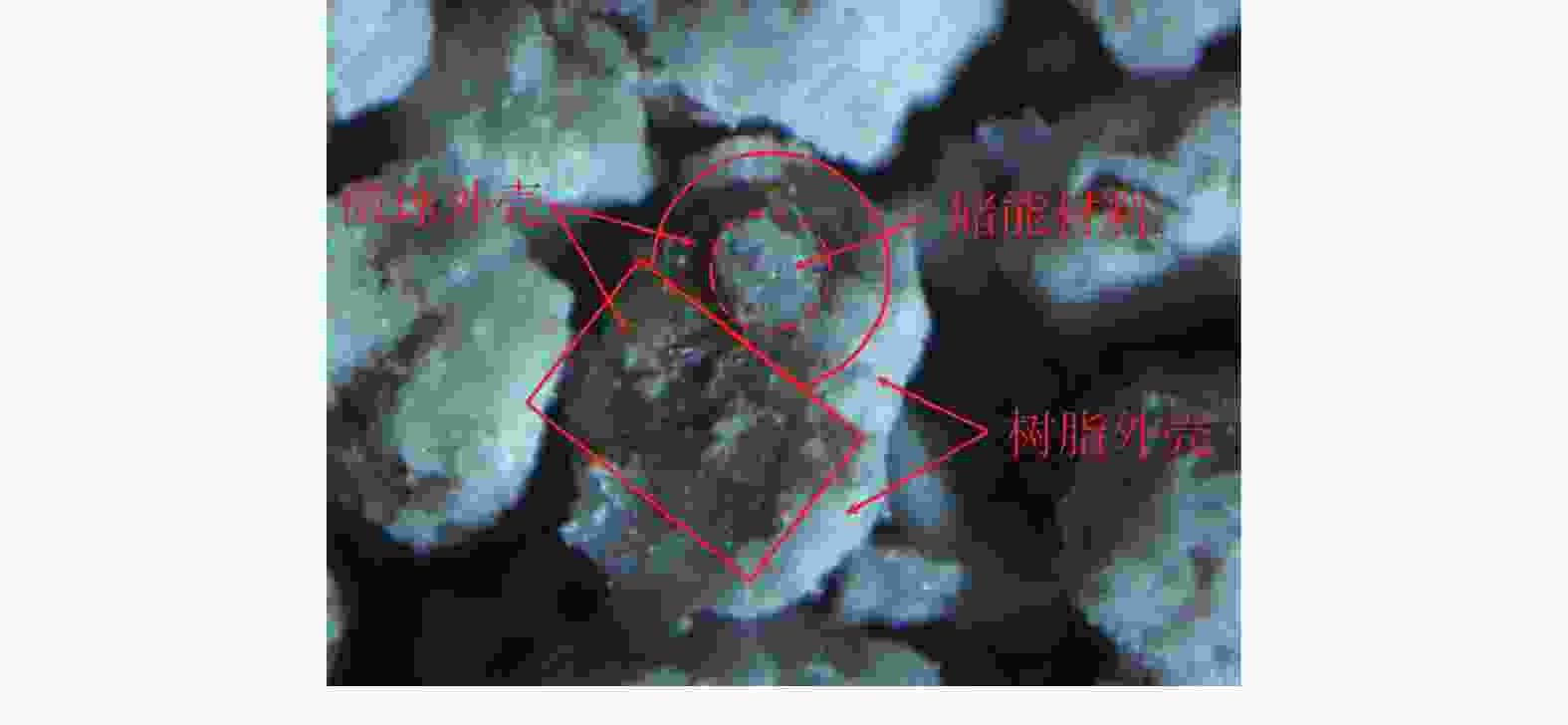
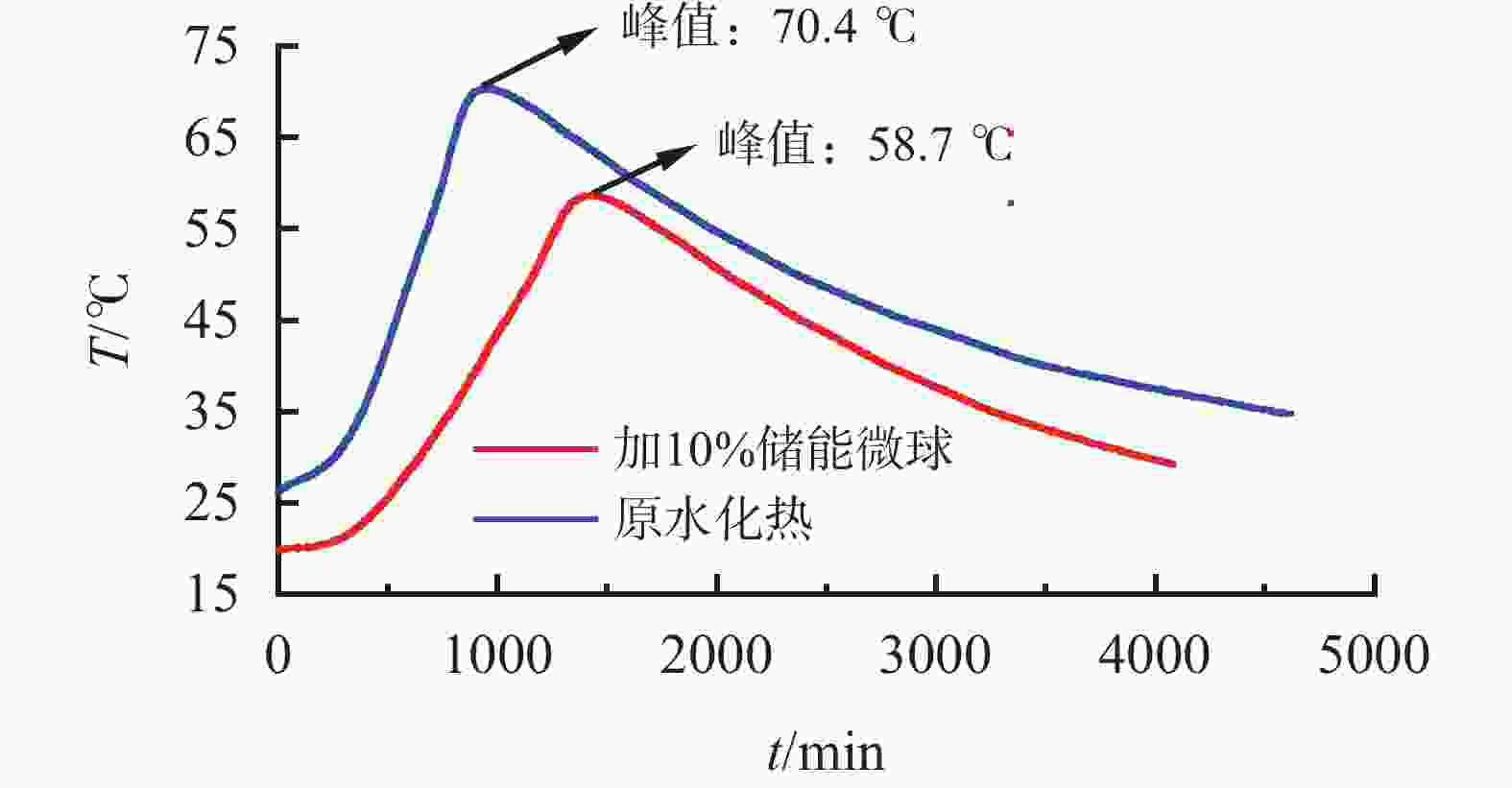
摘要: 为了保证在海洋深水油气井固井时水合物的稳定,需要在固井时使用低水化热水泥浆。目前的方法是在油井水泥中加入热能存储剂,但是将热能存储剂直接在水泥浆体系中应用,会出现配伍性差的问题。将热能存储剂吸收进入高强度载体微球内形成储能微球,可避免热能存储剂与水泥浆直接接触,是解决热能存储剂对固井水泥浆不利影响的有效措施。但是由于载体微球球壁开孔,热能存储剂仍然会从载体微球中泄漏,因此需要对储能微球进行封装。针对现有封装技术存在成本高、耗时长等问题,建立了以丙烯酸树脂为封装材料,利用喷涂法对载体微球进行封装的工艺,并对储能微球的封装效果进行评价优化,得到最合适的丙烯酸树脂的质量分数为20%,最终形成了一套简单高效的储能微球封装方法。封装的储能微球具有很好的抗压、耐温、耐碱性能,能够在海水环境中长时间稳定存在,为解决热能存储剂与水泥浆不配伍难题开辟一条新的途径,对有效封隔天然气水合物层具有重要的意义,同时也可为其他油井水泥外加剂载体研发提供借鉴。Abstract: To maintain the gas hydrate in stable conditions during deep offshore well cementing, a cement slurry with low heat of hydration should be used. Presently this is realized by adding heat energy storage agents in the oil well cement. The problem with this method is that the heat energy storage agent directly added into the cement slurry has poor compatibility. If the heat energy storage agent is absorbed into a high strength carrier microsphere to form an energy storage microsphere, the direct contact of the heat energy storage agent with the cement slurry can be avoided, and this should be an effective measure to solve the negative effects of heat energy storage agents on cement slurries. Opening of carrier microsphere walls will cause the leaking of the heat energy storage agent from the carrier microspheres, encapsulation of the microspheres is thus necessary. A new encapsulation methos is required to solve the problems existed with the existing encapsulation technology such as high cost and time consuming. In laboratory experiment, acrylic acid resin was chosen as the encapsulation material, and the carrier microspheres were encapsulated with spray method. Evaluation of the encapsulation showed that the best encapsulation can be achieved at a acrylic acid resin mass fraction of 20%. A simple efficient encapsulation method was thus developed. The energy storage microspheres thus encapsulated have good compressive strength, good high temperature stability and good resistance to alkaline environment. They can stay in marine environment for a long time. The development of this encapsulation technology and the energy storage microspheres has opened a new way of solving the incompatibility between heat energy storage agent and cement slurry, and is important to the effective isolation of natural gas hydrate. It has also provided a clue for the development of additive carriers for oil well cement.
-
Key words:
- Energy storage microsphere /
- Oil well cement /
- Acrylic acid resin /
- Encapsulation method
-
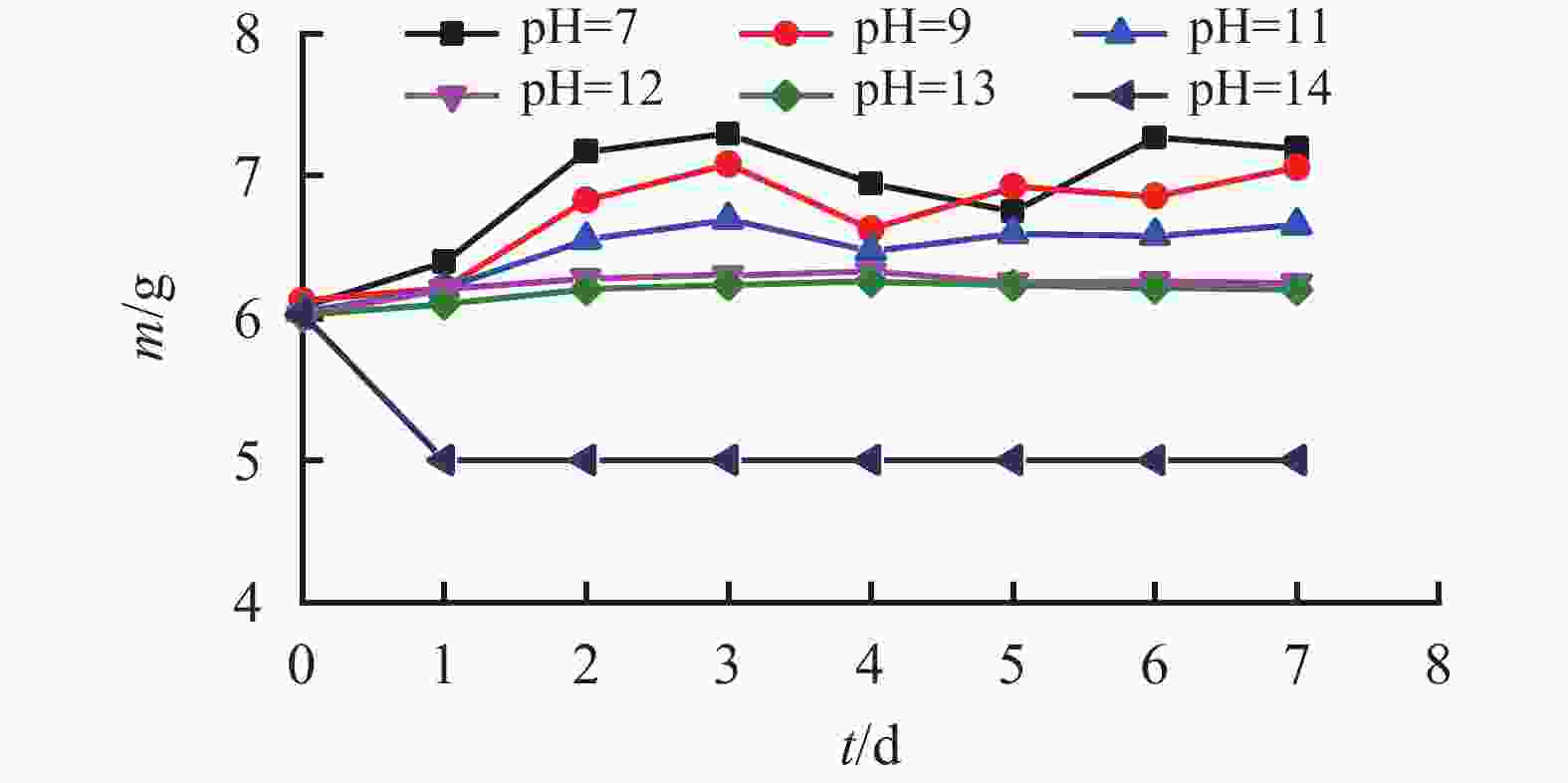
表 1 储能微球封装后在同温度下的质量变化情况
t/h 不同温度下的质量/g 20 ℃ 40 ℃ 60 ℃ 80 ℃ 95 ℃ 0 5 5 5 5 5 0.5 5 5 5 5 5 1.0 5 5 5 5 5 1.5 5 5 5 5 5 2.0 5 5 5 5 5 表 2 储能微球的耐矿化度性能测试
t/d m/g t/d m/g 0 5.936 4 6.230 1 6.178 5 6.304 2 6.206 6 6.240 3 6.260 7 6.271 -
[1] 王瑞和,齐志刚,步玉环. 深水水合物层固井存在问题和解决方法[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2009,26(1):78-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2009.01.027WANG Ruihe, QI Zhigang, BU Yuhuan. Problems and solutions in deep water hydrate layer cementing[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2009, 26(1):78-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2009.01.027 [2] ARMSTRONG L J, JEAN P, PUZ G. Deepwater development environmental issues and challenges[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 2002, 55(4):522-528. [3] 王斌斌,王瑞和. 固井水泥浆的水化规律[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2010,34(3):57-60.WANG Binbin, WANG Ruihe. The hydration law of cement slurry[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) , 2010, 34(3):57-60. [4] 许明标,王晓亮,周建良,等. 天然气水合物层固井低热水泥浆研究[J]. 石油天然气学报,2014(11):134-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2014.11.028XU Mingbiao, WANG Xiaoliang, ZHOU Jianliang, et al. Research on low heat cement slurry for natural gas hydrate layer cementing[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2014(11):134-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2014.11.028 [5] 席方柱,屈建省,吕光明,等. 深水低温固井水泥浆的研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2010,32(1):40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2010.01.010XI Fangzhu, QU Jiansheng, LYU Guangming, et al. Research on deep-water low-temperature cementing slurry[J]. Petroleum Drilling & Production Technology, 2010, 32(1):40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2010.01.010 [6] 蒋世全, 许明标, 周建良, 等. 一种防止天然气水合物分解的低热水泥浆: CN104559981A[P]. 2015.JIANG Shiquan, XU Mingbiao, ZHOU Jianliang, et al. A low-heat cement slurry for preventing the decomposition of natural gas hydrate: CN104559981A[P]. 2015. [7] LIU H J, BU Y H, SANJAYAN J G, et al. The application of coated superabsorbent polymer in well cement for plugging the microcrack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 104:72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.058 [8] LIU H J, BU Y H, GUO Q Q, et al. Converting hydration heat to achieve cement mixture with early strength and low hydrating-thermal dissipation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 151:113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.098 [9] LIU H J, BU Y H, SANJAYAN J G, et al. Suitability of polyacrylamide superabsorbent polymers as the internal curing agent of well cement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 112:253-260. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.217 [10] BU Y H, MA R, LIU H J, et al. Low hydration exothermic well cement system: The application of energy storage microspheres prepared by high-strength hollow microspheres carrying phase change materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 117:103907. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103907 [11] 方玉堂,匡胜严,张正国,等. 纳米胶囊相变材料的制备[J]. 化工学报,2007,58(3):771-775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2007.03.041FANG Yutang, KUANG Shengyan, ZHANG Zhengguo, et al. Preparation of nano-encapsulated phase change materials[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China) , 2007, 58(3):771-775. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-1157.2007.03.041 [12] 郝红,梁国正. 微胶囊技术及其应用[J]. 现代化工,2002,22(3):60-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4320.2002.03.015HAO Hong, LIANG Guozheng. Microencapsulation Technology and Its Application[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2002, 22(3):60-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4320.2002.03.015 [13] 绀户朝治. 微胶囊化工艺学 [M]. 阎世翔, 译. 北京: 轻工业出版社, 1989.KONTO Chaozhi. Microencapsulation technology [M]. YAN Shixiang, translate. Beijing: Light Industry Press, 1989. [14] 张兴祥, 王馨, 吴文健. 相变材料胶囊制备与应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009.ZHANG Xingxiang, WANG Xin, WU Wenjian. Preparation and application of phase change material capsules[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. [15] 刘硕,张东. 纳米胶囊相变材料研究进展[J]. 化学通报,2008,71(12):906-911.LIU Shuo, ZHANG Dong. Research progress of nanocapsule phase change materials[J]. Chemistry Bulletin, 2008, 71(12):906-911. [16] TSENG Y H, FANG M H, TSAI P S, et al. Preparation of microencapsulated phase-change materials (MCPCMs) by means of interfacial polycondensation[J]. Journal of microencapsulation, 2005, 22(1):37-46. doi: 10.1080/02652040400026558 [17] 杨超,张东,李秀强. 相变材料微胶囊研究现状及应用[J]. 储能科学与技术,2014,3(3):203-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4239.2014.03.004YANG Chao, ZHANG Dong, LI Xiuqiang. Research status and application of phase change material microcapsules[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2014, 3(3):203-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4239.2014.03.004 [18] 柳华杰, 步玉环, 马睿, 等. 一种相变储能微球及其制备方法: CN107500591B[P]. 2019.LIU Huajie, BU Yuhuan, MA Rui, et al. A phase change energy storage microsphere and its preparation method: CN107500591B[P]. 2019. [19] 马敬昆, 蒋庆哲, 王永宁, 等. 交联聚合物微球的制备及岩心封堵性能研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2010, 32(2): 84-88.MA Jingkun, JIANG Qingzhe, WANG Yongning, et al. Preparation of crosslinked polymer microsphere and plugging performance study[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2010, 32(2): 84-88. [20] 郭永宾, 李中, 刘和兴, 等. 低温早强低水化放热水泥浆体系开发[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2019, 36(4): 500-505.GUO Yongbin, LI Zhong, LIU Hexing, et al. Development of a low temperature early strength cement slurry with low exothermic heat of hydration[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(4): 500-505. -




 下载:
下载: