Laboratory Research on Offshore Oil-Based Drill Cuttings Cleaning
-
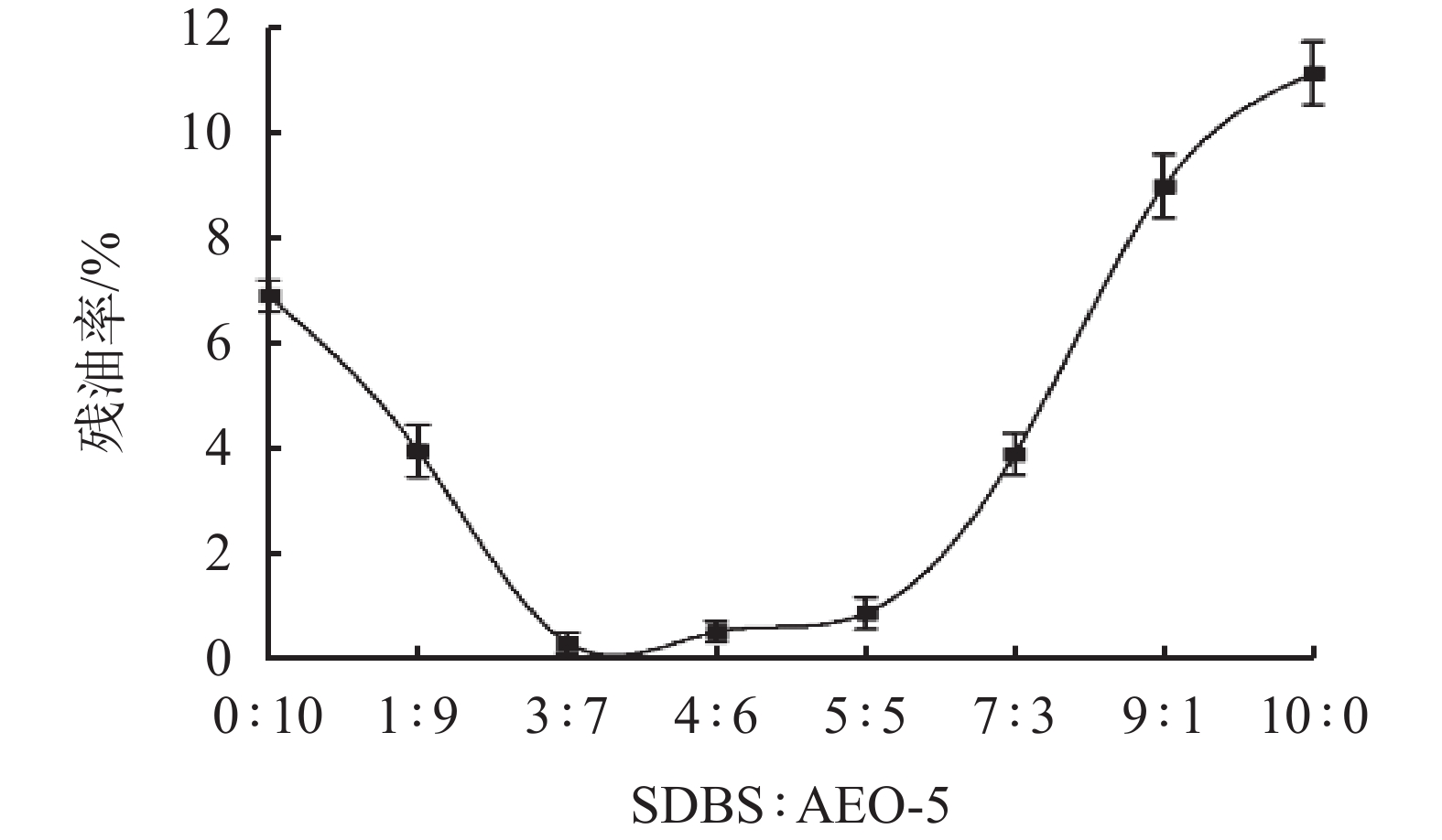
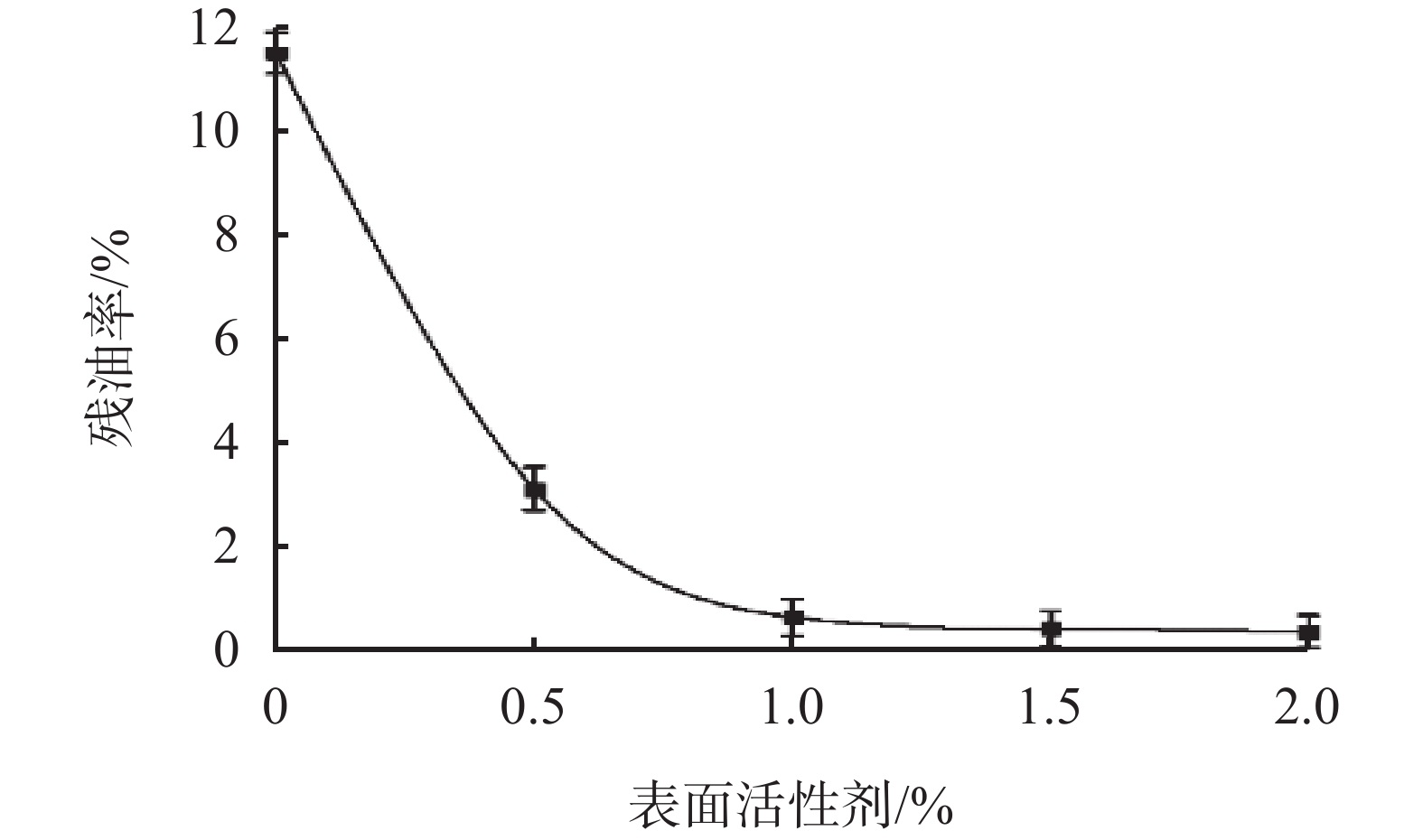
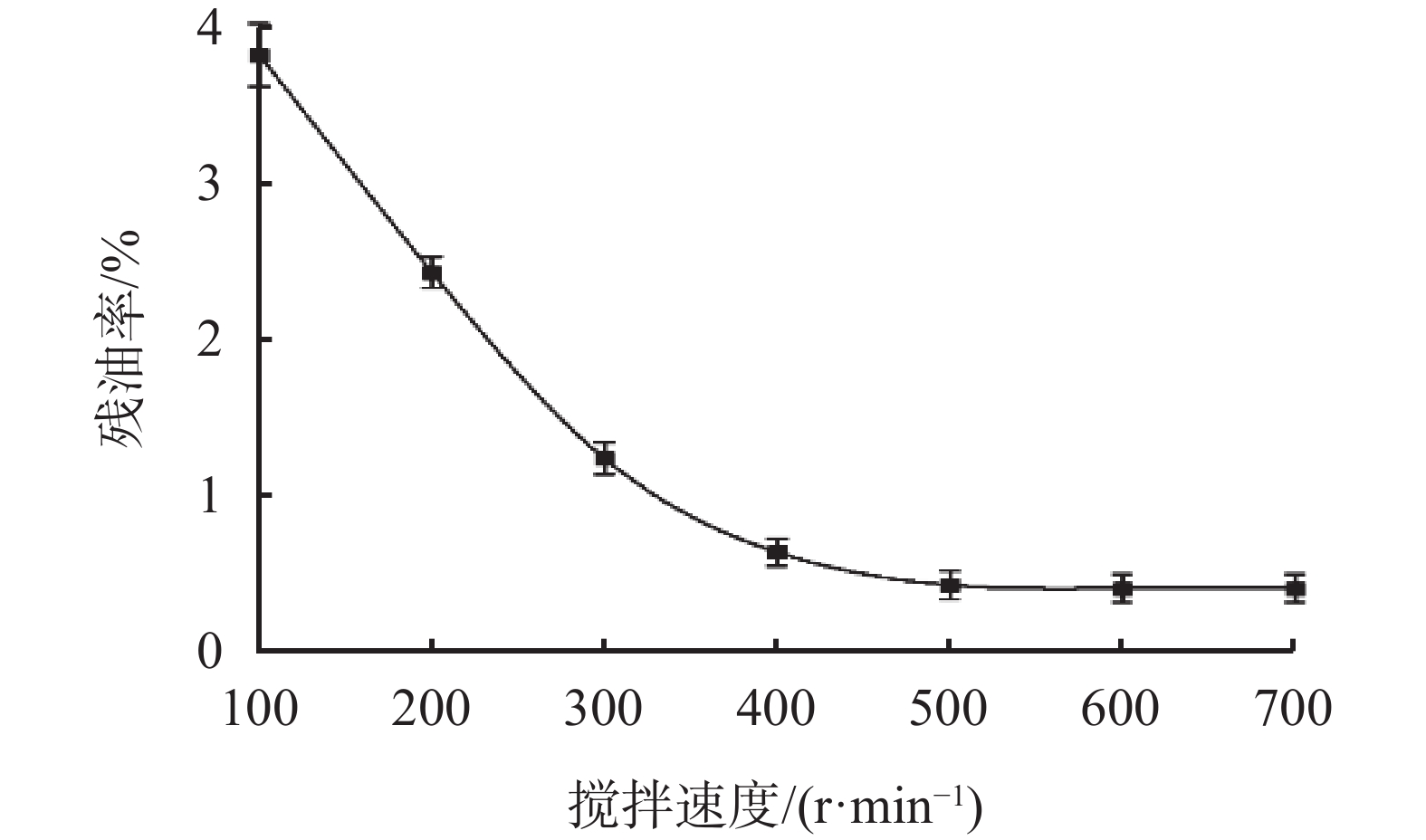
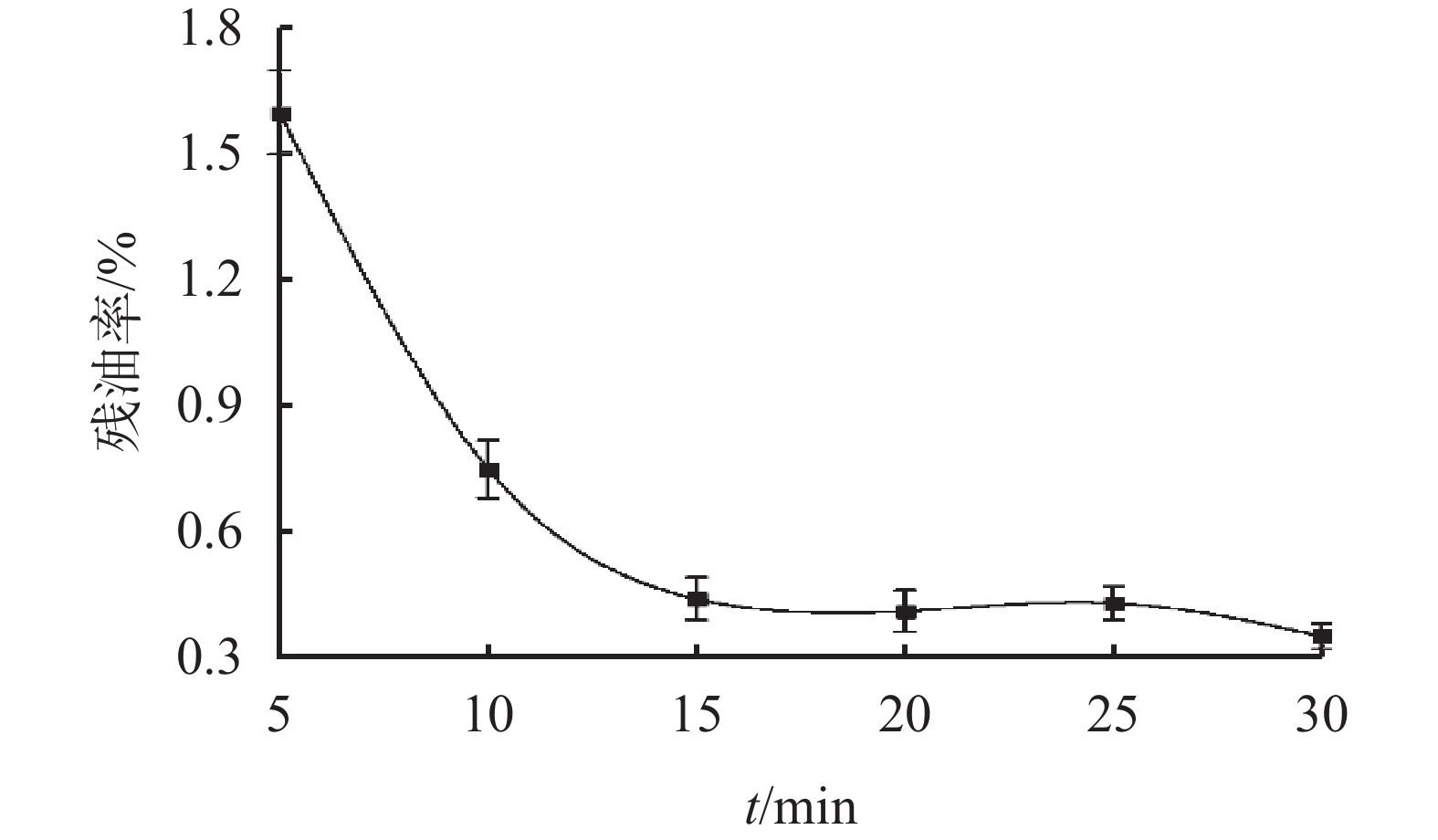
摘要: 使用油基钻井液进行钻井作业时,产生的油基钻屑含有基础油、钻井液处理剂等污染物,若其直接排放,会严重危害环境,也会造成大量油类资源的浪费。为此,使用表面活性剂水洗法处理海上钻井平台产生的油基钻屑,利用人工海水配制清洗液,得到清洗液配方为:0.7 %脂肪醇聚氧乙烯醚类非离子活性剂AEO-5+0.3%阴离子活性剂SDBS+0.15% Na5P3O10。通过室内清洗实验,探究了钻井液处理剂和钻屑矿物种类对残油率的影响。结果表明,钻井液处理剂会增大油相去除难度;钻屑矿物种类中,高岭石相比于云母石、长石、石英石清洗难度增加。最后确定最佳清洗工艺条件为:搅拌速率为500 r/min,固液比为1 ∶ 4,清洗时间为15 min,清洗温度为25 ℃。清洗结束后,钻屑残油率可降至1%以下,达到海上《海洋石油勘探开发排放限值》油基钻屑排放标准。Abstract: Drilled cuttings from wells drilled with oil based drilling fluids contain base oils and drilling fluid additives. These drilled cuttings, if discharged directly without proper disposal, will not only severely harm the environment, but also cause a huge waste of oils. To avoid this problem, the oily cuttings generated from offshore wells are generally cleaned with surfactant water solution. An oily cuttings cleaning fluid formulated with artificial seawater has this composition: 0.7% fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether AEO-5 + 0.3% anionic surfactant SDBS + 0.15% Na5P3O10. In laboratory experiment, the oily cuttings were cleaned with this solution and the effects of drilling fluid additives and the minerals of the drilled cuttings on the residue oils on cuttings were investigated. It was found that the presence of drilling fluid additives in the residue oil on cuttings makes the cleaning more difficult. Compared with mica, feldspar and quartz, kaolinite cuttings are more difficult to clean. Based on laboratory experiments, the optimum cuttings cleaning technique was determined as follows: mixing speed = 500 r/min, ratio of solid to liquid = 1:4, cleaning time = 15 min, temperature for the cleaning = 25 ℃. After the cuttings were cleaned, the residue oils on cuttings can be reduced to less than 1%, which satisfies the requirements of the standard “Effluent Limitations for Pollutants from Offshore Petroleum Exploration and Production”.
-
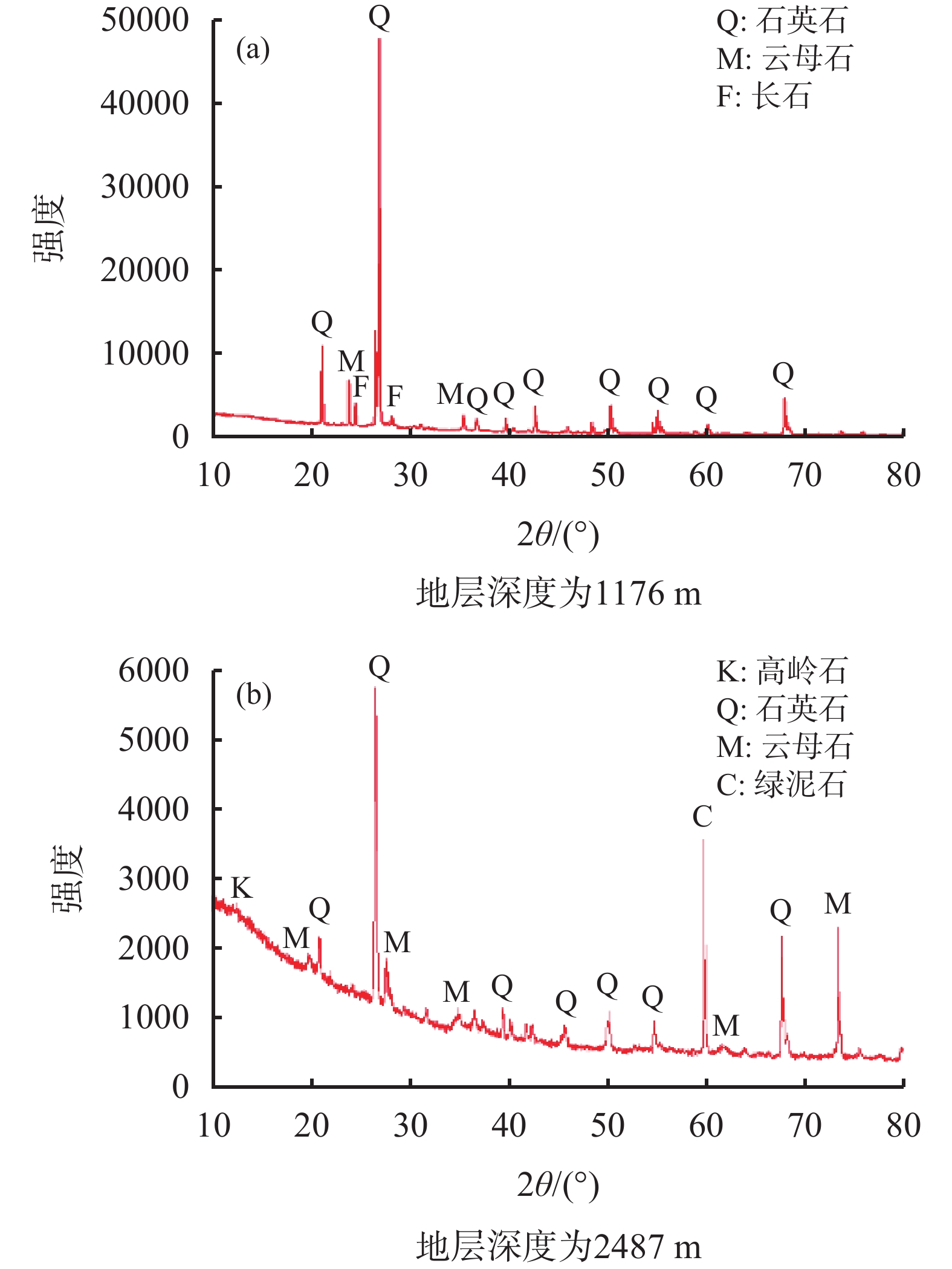
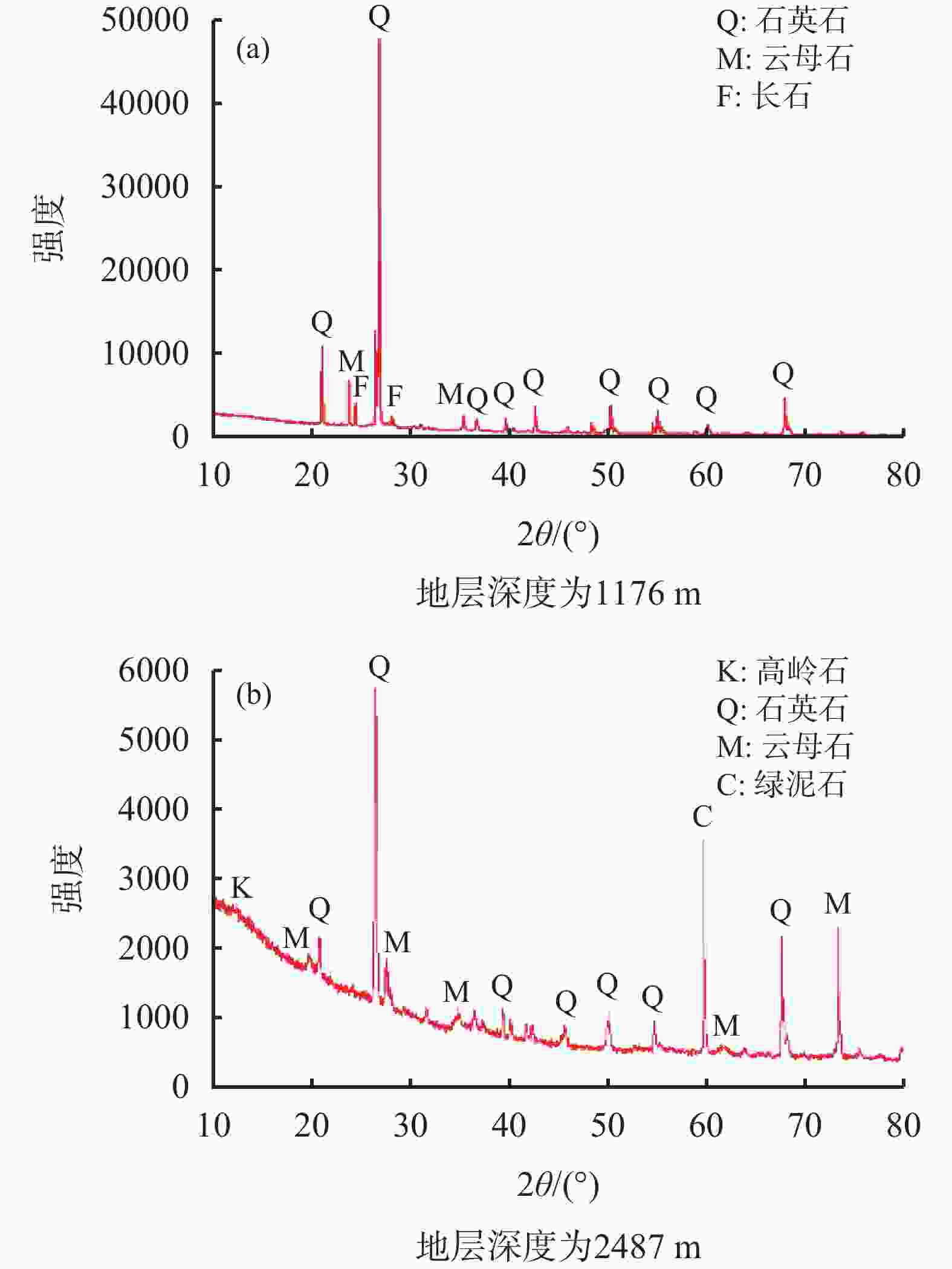
表 1 不同地层深度钻屑的矿物组成分析
地层深度/
m矿物
组成化学式 矿物含量/
%1176 石英石 SiO2 45.6 云母石 KAl2[Si3Al10](OH,F)2 28.4 长石 Na(AlSi3O8) 26.0 2487 高岭石 Al2SiO5(OH)4 31.9 石英石 SiO2 29.6 云母石 KAl2[Si3Al10](OH,F)2 24.7 绿泥石 (Mg0.99Al0.01)5(Al0.67Fe0.33)
(Si3.02Al0.98)O10(OH)813.8 -
[1] 杜坤. 油基钻井液新型高效乳化剂的研制与评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):555-560.DU Kun. Development and Evaluation of a New High Efficiency Emulsifier for Oil Base Drilling Fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5):555-560. [2] 王星媛,陆灯云,吴正良. 抗220℃高密度油基钻井液的研究与应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):550-554.WANG Xingyuan, LU Dengyun, WU Zhengliang. Study and Application of a High Density Oil Base Drilling Fluid with High Temperature Resistance of 220℃[J]. Drilling Fluid& Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5):550-554. [3] 赵国海. MEGADRIL油基钻井液在埕岛西合作区的应用[J]. 石化技术, 2021, 28(2): 160-161.ZHAO Guohai, Application of MEGADRIL oil-based drilling fluid in Chengdao West Cooperation Area [J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2021, 28(2): 160-161. [4] 刘宇程,袁丽娜,雍锐,等. 固体废物含油量测定方法与标准确立过程中的问题及建议: 以含油钻屑为例[J]. 环境工程学报,2020,14(9):2284-2290. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201912163LIU Yucheng, YUAN Lina, YONG Rui, et al. Problems and suggestions in establishing the determination method and standard of oil content of solid waste: an example using oil-based drill cuttings[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2020, 14(9):2284-2290. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201912163 [5] AYELE B A, LU J, CHEN Q Y. Optimization of aeration enhanced surfactant soil washing for remediation of diesel-contaminated soils using response surface methodology[J]. Peer J, 2020(8):8578-8603. [6] MOHEBBAN A, YAGHOOBZADEH P, GITIPOUR S, et al. Applicability of an anionic-nonionic surfactant in p-cresol contaminated soil washing: Finding the optimal mixing ratio[J]. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 2020(18):1207-1216. [7] 白羽,程远鹏,胡九江,等. 含油污泥热清洗处理技术研究现状与展望[J]. 应用化工,2020,49(6):1498-1501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.06.037BAI Yu, CHENG Yuanpeng, HU Jiujiang, et al. Progress and prospects of thermal cleaning and treatment of oily sludge[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(6):1498-1501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.06.037 [8] LI X, BAI Y, SUI H, et al. Understanding desorption of oil fractions from mineral surfaces[J]. Fuel, 2018(232):257-266. [9] MAO X, JIANG R, XIAO W, et al. Use of surfactants for the remediation of contaminated soils: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015(285):419-435. [10] 白鹤,武卫锋,翁良宇,等. 化学清洗处理高含油率油基钻屑的研究[J]. 天然气与石油,2018,36(3):76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2018.03.015BAI He, WU Weifeng, WENG Liangyu, et al. Study on chemical cleaning of oil-based cuttings with high oil content[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2018, 36(3):76-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2018.03.015 [11] 王曼琳,张衡,张梁,等. 声-化联合法清洗含油钻屑[J]. 化工环保,2018,38(2):222-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.02.018WANG Manlin, ZHANG Heng, ZHANG Liang, et al. Cleaning of oily cuttings by ultrasonic-chemical combination process[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2018, 38(2):222-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2018.02.018 -




 下载:
下载: