Ammonolysis Modified Soybean Lecithin as a Drilling Fluid Lubricant
-
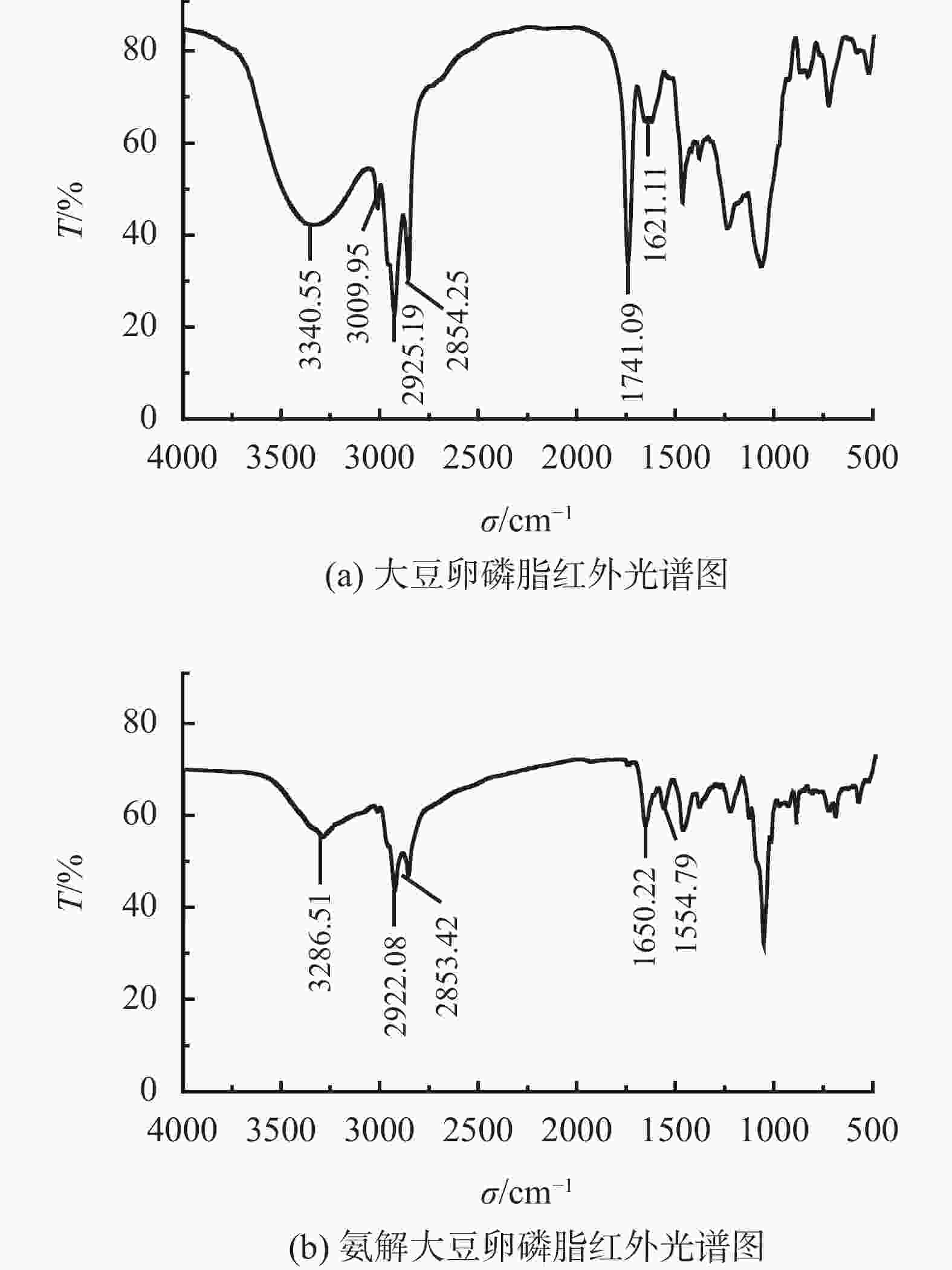
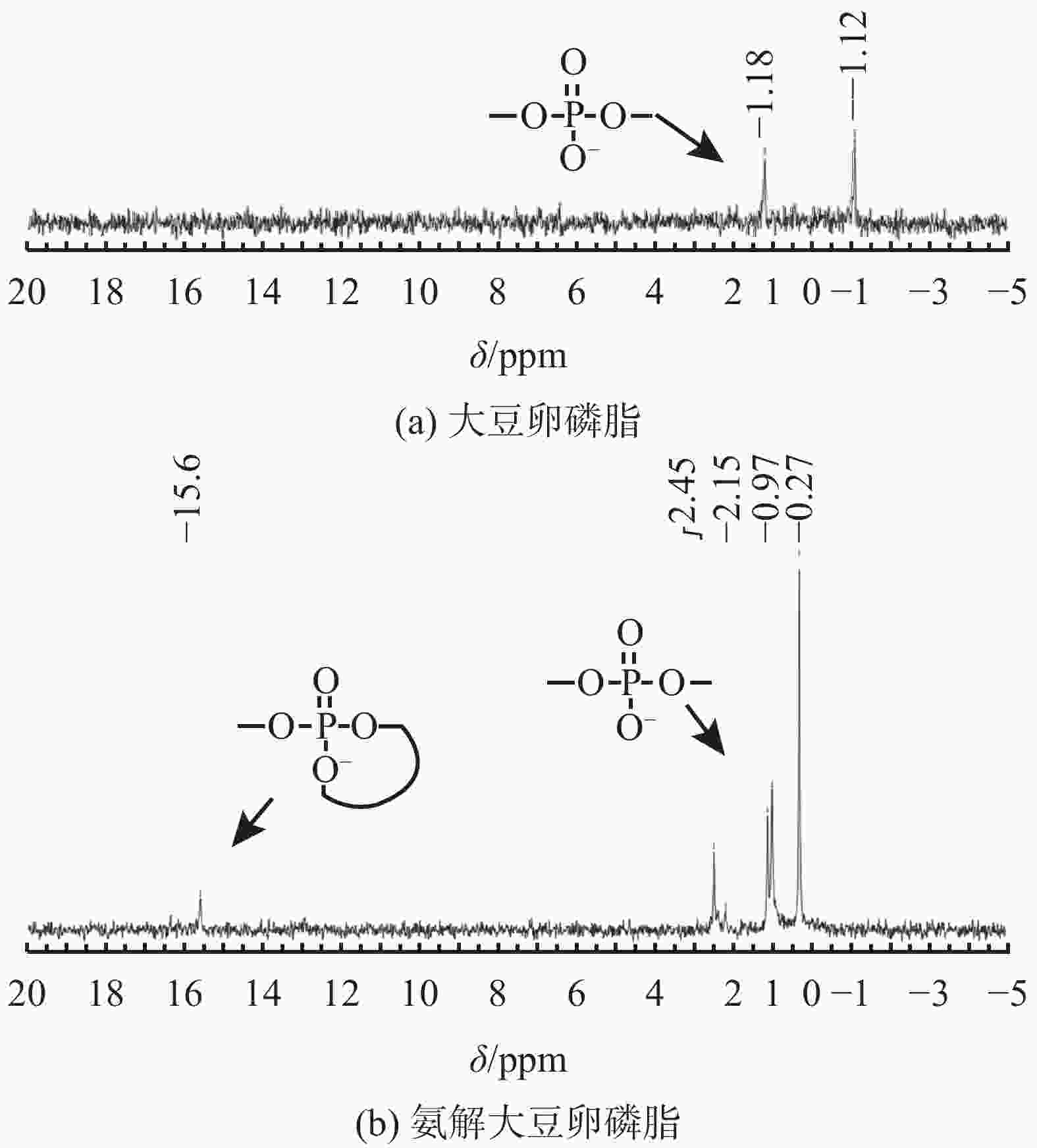
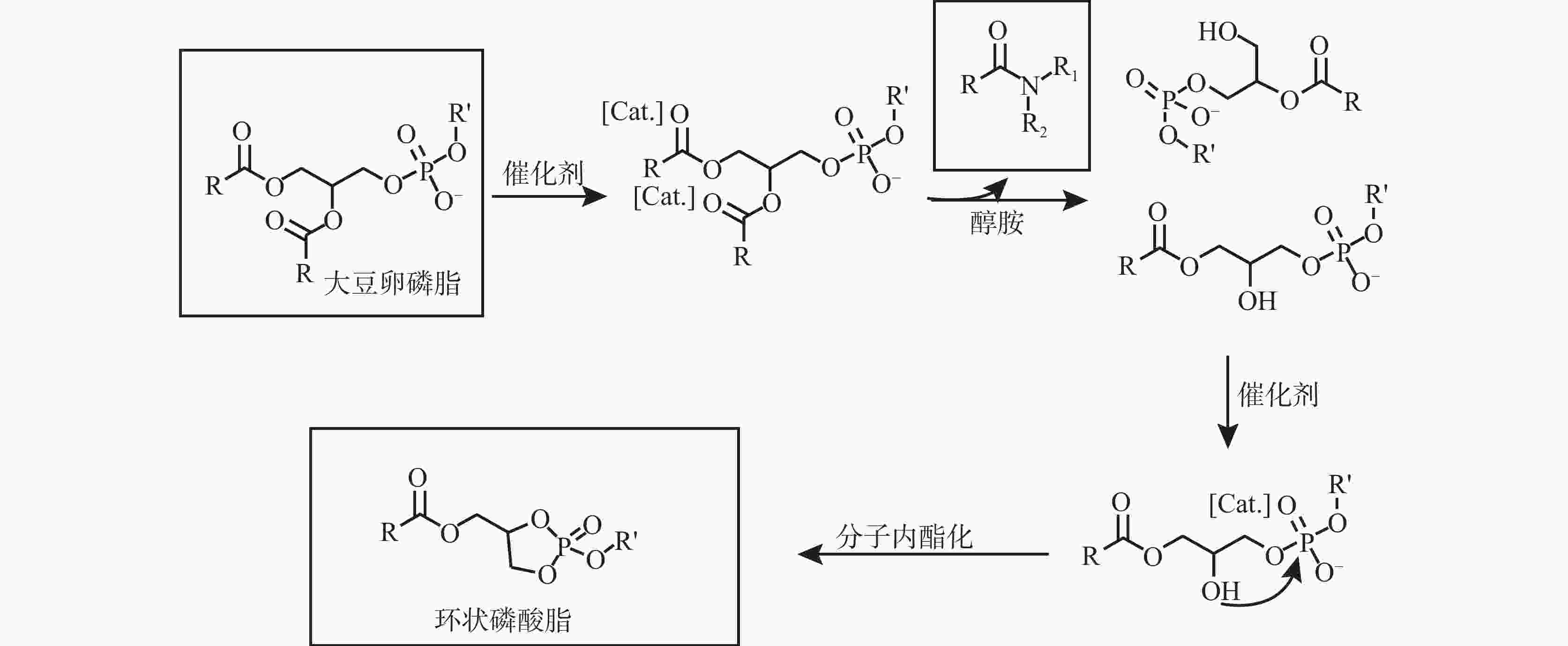
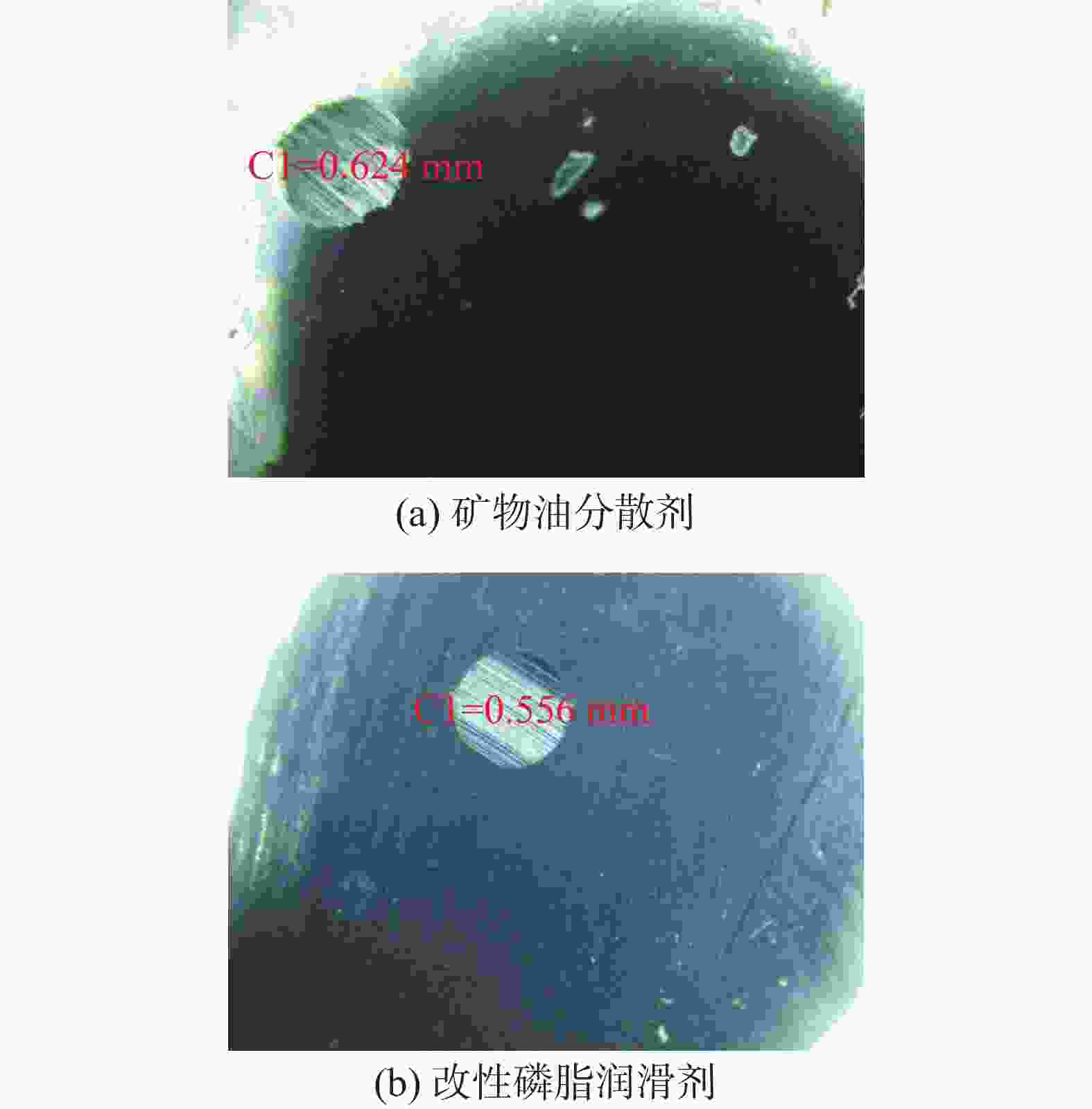
摘要: 大豆卵磷脂为双脂肪酸甘油磷脂衍生物,结构中富含磷酸酯基、羟基、氨基等润滑吸附基团,但是其结构中双脂肪酸甘油酯疏水性过强、分散性过低,无法直接作为钻井液润滑剂。将大豆卵磷脂、醇胺、催化剂、矿物油分散剂混合加热反应获得改性磷脂润滑剂,采用红外光谱与核磁共振磷谱分析了醇胺氨解大豆卵磷脂的机理。通过摩擦磨损实验确定了改性磷脂润滑剂的抗磨耐磨能力。对比其他市售润滑剂,分别测试了改性磷脂润滑剂的润滑性能、高温稳定性能、抗盐抗钙性能,最终测试了改性磷脂润滑剂对聚磺钻井液的配伍性能以及润滑提升能力。氨解改性工艺中醇胺的最佳加量为10%~25%,醇胺能够氨解大豆卵磷脂中脂肪酸酯形成脂肪酰胺,从而降低其结构中疏水脂肪链成分,提升其水分散性。氨解所形成的羟基进一步与磷酸酯阴离子发生分子内酯化反应形成五元环状磷酸酯,掩蔽磷酸酯阴离子。所形成的改性磷脂润滑剂具有优异的润滑性能、高温稳定性能、抗盐抗钙性能以及钻井液配伍性能,具有潜在钻井液润滑应用前景。Abstract: Soybean lecithin is a derivative of difatty acid glycerophospholipid, whose molecular structure is rich in lubricant adsorption groups, such as phosphate group, hydroxyl and amino group. The difatty acid glyceride in the molecule of the difatty acid glycerophospholipid has very strong hydrophobicity and very low dispersity, makes it difficult to act as a drilling fluid lubricant. By heating the mixture of soybean lecithin, alcohol amine, catalyst and mineral oil dispersant, these chemicals react to produce a modified phospholipid lubricant. The working mechanisms of the ammonolysis (by alcohol amine) modified soybean lecithin was studied with IR and PNMR. The ammonolysis modified soybean lecithin lubricant was tested to determine their performance as a drilling fluid. In the test, the lubricity, high temperature stability, salt and calcium resistance of the new lubricant were compared with those of the other commercially available lubricants. The new lubricant was also tested for its compatibility with the polymer sulfonate drilling fluid and its ability to improve the lubricity of the drilling fluid. The optimum amount of alcohol amine used in the ammonolysis process was determined to be 10%-25%. The alcohol amine can be used to ammonolyze the fatty acid ester in the soybean lecithin to form fatty amide, thereby reducing the content of hydrophobic fatty chain in the soybean lecithin and enhancing its water dispersity. The hydroxyl formed during the ammonolysis can react with the ionic phosphate to form pentacyclic phosphate through lactonization reaction, and the ionic phosphate is thus masked. The modified soybean lecithin lubricant developed has excellent lubricating capacity, good high-temperature resistance, good salt- and calcium-resistance, as well as good compatibility with many water based drilling fluids, making it a potential high performance drilling fluid lubricant.
-
Key words:
- Soybean lecithin /
- Ammonolysis modification /
- Phosphate /
- Lubricant /
- Drilling fluid
-
表 1 不同醇胺加量形成的氨解改性卵磷脂的润滑性能与乳化分散性能
醇胺/% 润滑系数 润滑系数
降低率/%乳化分散性 5 0.328 47.8 棕色油滴漂浮 10 0.185 70.5 均匀分散 15 0.082 86.9 均匀分散 25 0.073 89.3 均匀分散,部分泡沫 30 0.214 68.6 大量细泡,体积膨胀 表 2 不同处理剂在淡水基浆中的润滑与热稳定性能对比
处理
剂实验
条件极压润
滑系数润滑系数
降低率/%黏附
系数黏附系数
降低率/%空白 老化前 0.682 0.14 120 ℃、16 h 0.674 0.15 160 ℃、16 h 0.652 0.15 改性磷脂
润滑剂老化前 0.073 89.3 0.03 78.6 120 ℃、16 h 0.085 87.4 0.02 86.7 160 ℃、16 h 0.094 85.6 0.03 80.0 市售
润滑剂A老化前 0.054 92.1 0.04 71.4 120 ℃、16 h 0.051 92.4 0.02 86.7 160 ℃、16 h 0.072 89.0 0.02 86.7 市售
润滑剂B老化前 0.126 81.5 0.03 78.6 120 ℃、16 h 0.113 83.2 0.03 80.0 160 ℃、16 h 0.149 77.1 0.04 73.3 表 3 不同处理剂在不同基浆中的润滑性能对比
处理剂 测试浆 润滑系数 润滑系数降低率/% 空白 4%盐水基浆 0.694 2%氯化钙基浆 0.701 改性磷脂
润滑剂4%盐水基浆 0.092 86.7 2%氯化钙基浆 0.092 86.9 市售
润滑剂A4%盐水基浆 0.156 77.5 2%氯化钙基浆 0.327 53.4 市售
润滑剂B4%盐水基浆 0.136 80.4 2%氯化钙基浆 0.143 79.6 表 4 不同改性磷脂润滑剂加量对聚磺钻井液性能的影响
润滑剂/
%AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/PaFLAPI/
mLFLHTHP/
mL润滑
系数0 13.0 10 3.0 0.5/3.5 8.8 24 0.174 1 13.5 10 3.5 0.5/3.5 9.0 24 0.152 2 14.0 11 3.0 0.5/4.0 9.0 25 0.112 注:聚磺钻井液的配方为3%膨润土浆+0.2%干粉+1%磺化
褐煤+1.5%磺化酚醛树脂+1%磺化沥青 -
[1] 高小芃,王伟亮,司西强,等. 长南气田水平井定向井段钻井液技术[J]. 山东化工,2016,45(8):79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.08.030GAO Xiaopeng, WANG Weiliang, SI Xiqiang, et al. Drilling fluid technology of directional well section in Changnan gas field horizontal well[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(8):79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.08.030 [2] 徐德行. 长水平段水平井钻井难点与技术对策探讨[J]. 西部探矿工程,2017,29(7):54-55.XU Dexing. Discussion on drilling difficulties and technical countermeasures of long horizontal wells[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2017, 29(7):54-55. [3] 樊好福,司西强,王中华. 水基钻井液用绿色润滑剂研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 应用化工,2019,19(2):1192-1196.FAN Haofu, SI Xiqiang, WANG Zhonghua. Research progress and development trend of green lubricants for water based drilling fluids[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2019, 19(2):1192-1196. [4] 宣扬,钱晓琳,林永学,等. 水基钻井液润滑剂研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 油田化学,2017,34(4):721-726.XUAN Yang, QIAN Xiaolin, LIN Yongxue, et al. Research progress and development trend of lubricants for water based drilling fluids[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2017, 34(4):721-726. [5] 金军斌. 钻井液用润滑剂研究进展[J]. 应用化工,2017,46(4):770-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.04.039JIN Junbin. Research advances of the lubricants for drilling fluid[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2017, 46(4):770-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2017.04.039 [6] 王琳,董晓强,杨小华,等. 高密度钻井液用润滑剂SMJH-1的研制及性能评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2016,33(1):28-32.WANG Lin, DONG Xiaoqiang, YANG Xiaohua, et al. Development and evaluation of a high density drilling fluid lubricant[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2016, 33(1):28-32. [7] LAN P X, LACCINO L L, BAO X Y, et al. The effect of lubricant additives on the tribological performance of oil and gas drilling applications up to 200 ℃[J]. Tribology International, 2020, 141:1-11. [8] 李公让,王承俊. 极性吸附钻井液润滑剂的研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):541-549.LI Gongrang, WANG Chengjun. Research progress made and development trend of drilling fluid lubricants with polaradsorption ability[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5):541-549. [9] 王兰,吴琦,蒋官澄. 改性大豆卵磷脂在水基钻井液中的润滑性能[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(1):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.01.002WANG Lan, WU Qi, JIANG Guancheng. Modified soybean lecithin used as water base drilling fluid lubricant[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(1):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.01.002 [10] 蒋笃孝,彭一鸣,宋龄瑛. 改性卵磷脂的微乳化性研究[J]. 食品科学,2004,25(4):28-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2004.04.002JIANG Duxiao, PENG Yiming, SONG Lingying. Investigation of microemulsions of modified lecithin[J]. Food science, 2004, 25(4):28-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2004.04.002 [11] 霍永琛. 大豆卵磷脂的研究进展[J]. 明胶科学与技术,2007,27(3):113-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9657.2007.03.001HUO Yongchen. Research progress of soy lecithin[J]. The Science and Technology of Gelatin, 2007, 27(3):113-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9657.2007.03.001 [12] QUIN LOUIS D, WILLIAMS ANTONY J. Practical interpretation of P-31 NMR spectra and computer assisted structure verification[M]. Toronto, Canada: Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc. , 2004: 15-26. -





 下载:
下载: