Study on Effects of Temperature and Pressure on Density of Oil Based Drilling Fluids and the Mathematical Model Thereof
-
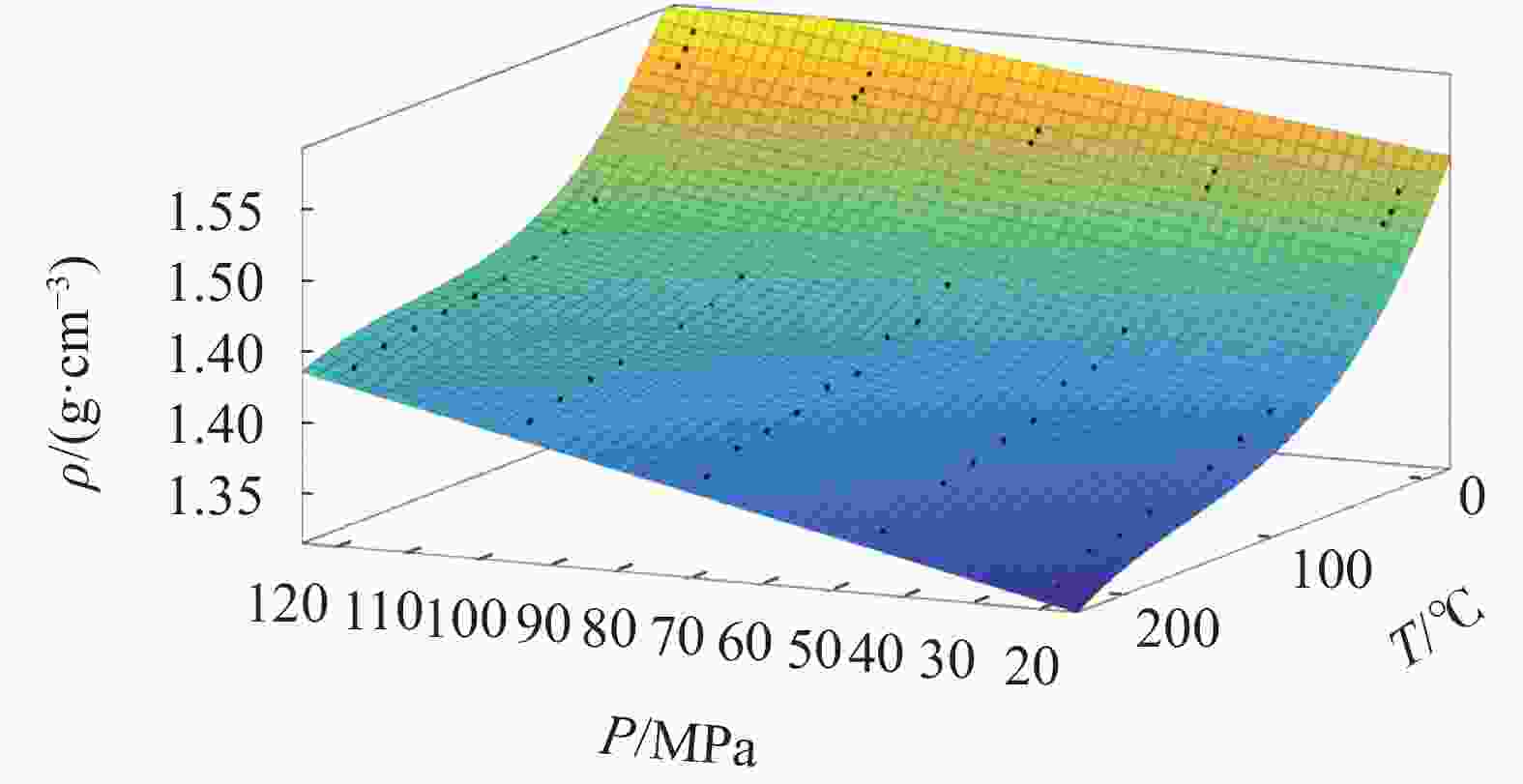
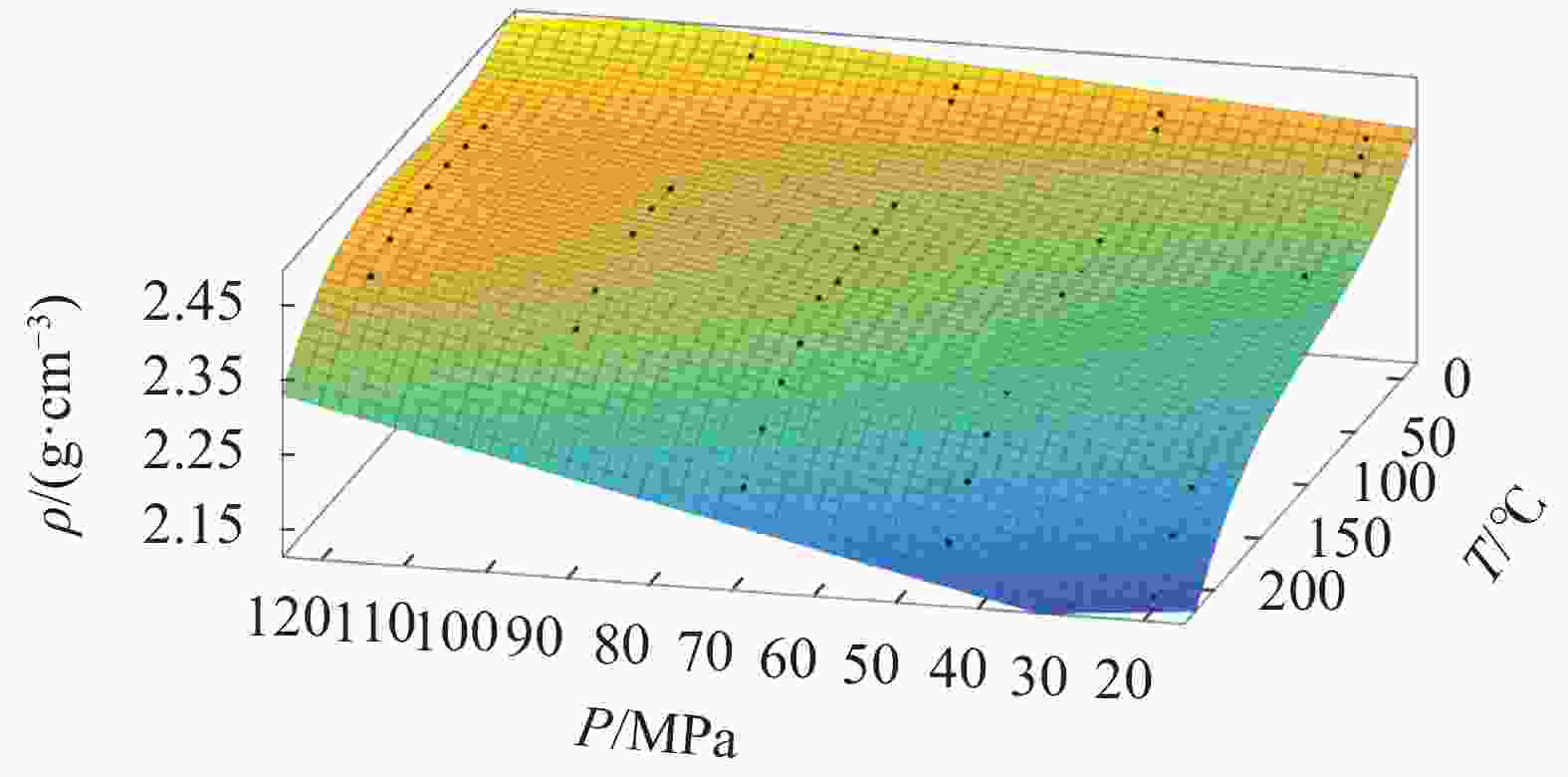
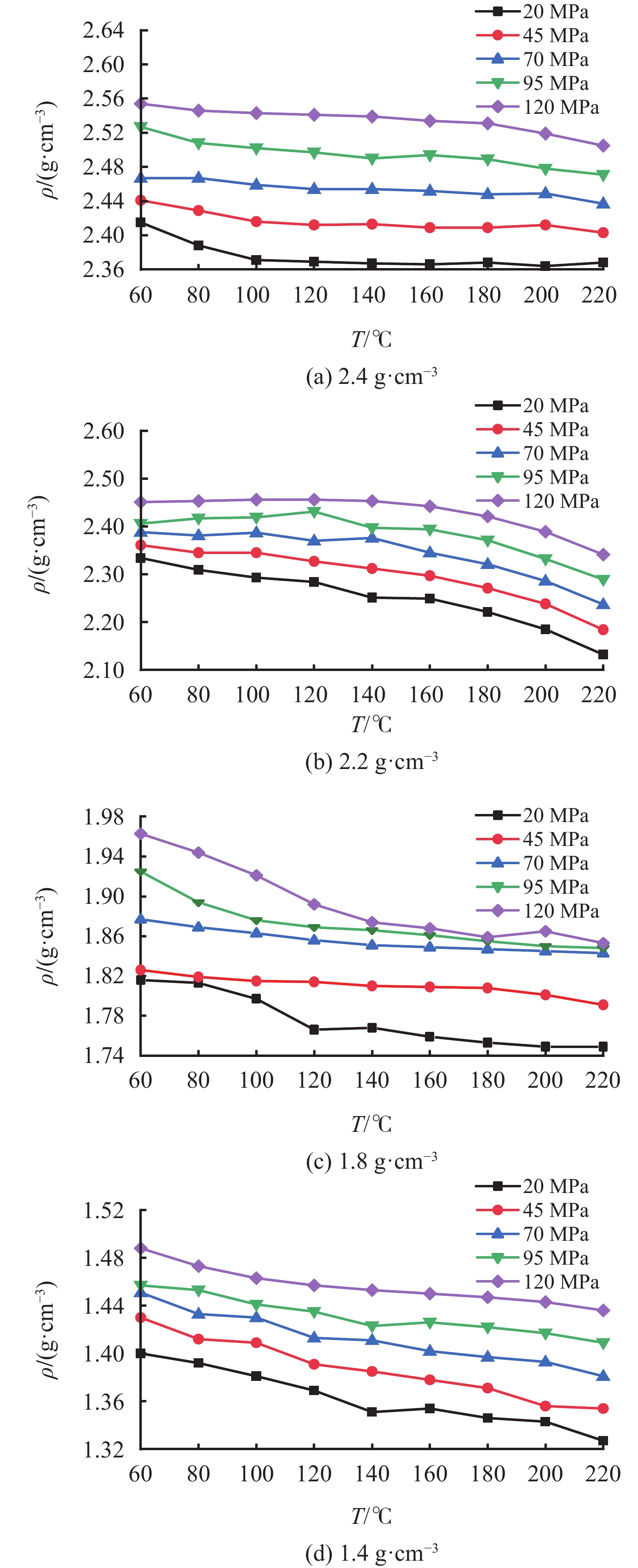
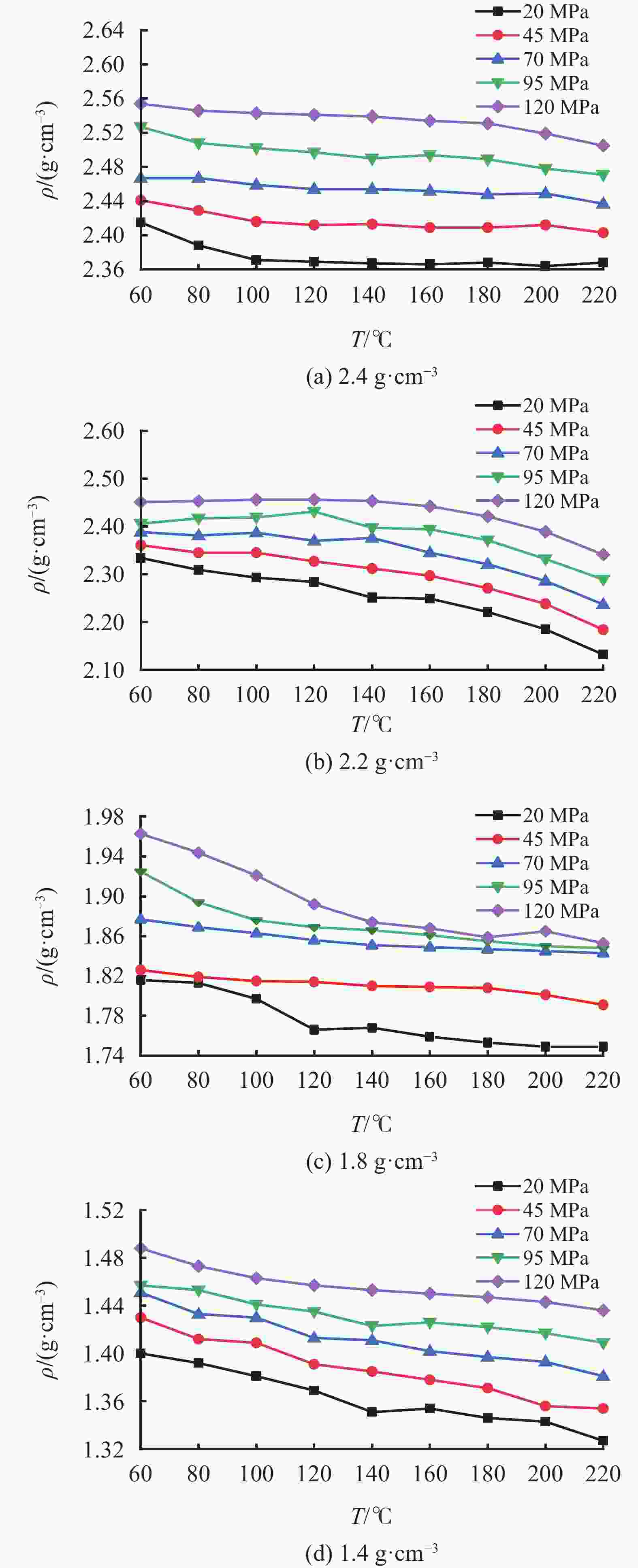
摘要: 油基钻井液的密度受温度和压力影响显著,掌握油基钻井液在不同温度和压力条件下密度的变化规律是钻井安全的重要保障。基于现场配方在室内配制了相同组分、不同密度的4种油基钻井液,使用Anton Paar公司的流体高温高压密度测试仪测定了4种油基钻井液的密度在温度范围60~220 ℃、压力范围20~120 MPa内的变化,探究了温度和压力对油基钻井液密度的影响规律,并建立了油基钻井液密度的温压二元数学模型。使用现场不同密度的油基钻井液对模型的准确性进行了验证,结果表明预测值与实测值之间具有较高的一致性,平均预测准确度达97.93%,能够满足现场使用的需要。另外对2种类似配方的油基钻井液进行了密度准确性验证,结果显示平均误差为9.24%,精度较高。Abstract: The density of oil based drilling fluids is significantly affected by temperature and pressure. Understanding the change of the density of oil based drilling fluids is of importance to the safety of the drilling operation. Oil based drilling fluids of 4 different densities with the same composition copied from the composition of a field drilling fluid were formulated in laboratory and were tested for the change of density with an HTHP density balance made by Anton Paar Company in temperature range of 60 – 220 ℃ and pressure range of 20 – 120 MPa. Using the teste results, the effects of temperature and pressure on the density of the oil based drilling fluids were investigated, and a temperature-pressure binary mathematical model about the density of oil based drilling fluid was established. The accuracy of the model was verified with field oil based drilling fluids of different densities, and it was found that the values predicted with the model and the values measured agreed closely with each other, the average prediction accuracy of the model is up to 97.93%, meaning that the model is able to satisfy the needs of field application. Verification of the model on another two oil based drilling fluids with similar composition showed an average error of 9.24%, indicating a high prediction accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Oil based drilling fluid /
- Temperature /
- Pressure /
- Density /
- Prediction
-
表 1 不同密度油基钻井液老化前后的基本性能
ρ /
g·cm−3老化
条件PV/
mPa·sYP/
Paφ6/φ3 Gel/
Pa/PaES/
V2.4 老化前 40.0 11.24 10/9 4/8.0 1561 220 ℃、16 h 59.0 6.64 5/3 3/7.0 1012 2.2 老化前 43.0 10.22 9/6 4/8.0 1443 220 ℃、16 h 58.5 5.11 4/3 3/7.0 992 1.8 老化前 39.0 10.22 6/5 3/4.0 1012 220 ℃、16 h 46.0 5.62 3/2 1/1.5 786 1.4 老化前 19.0 7.66 7/4 3/3.0 825 220 ℃、16 h 21.5 1.79 1.5/1 1/1.0 654 表 2 不同密度油基钻井液的密度数学模型参数及可决系数
ρ0/(g·cm−3) β0 β1 β2 β3 β4 R 2.4 1.078×10−3 −2.488×10−3 3.163×10−6 1.461×10−5 −3.255×10−8 0.99 2.2 8.374×10−4 −1.976×10−3 6.493×10−6 1.418×10−5 −5.198×10−8 0.99 1.8 1.309×10−3 −1.632×10−3 −1.053×10−6 7.169×10−6 1.093×10−8 0.97 1.4 6.870×10−4 −2.149×10−3 1.760×10−6 1.129×10−5 −2.383×10−8 0.99 表 3 蓬深1井油基钻井液密度预测值与实测值的对比
T/℃ P/MPa ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 89 20 1.372 1.308 4.64 89 45 1.388 1.329 4.23 89 65 1.393 1.346 3.36 120 20 1.369 1.291 5.66 120 45 1.382 1.314 4.93 120 65 1.391 1.332 4.25 表 4 高石130井油基钻井液密度预测值与实测值的对比
T/℃ P/MPa ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 75 20 1.792 1.777 0.83 75 70 1.875 1.839 1.94 75 92 1.888 1.866 1.18 141 20 1.777 1.796 −1.08 141 70 1.859 1.854 0.25 141 92 1.870 1.880 −0.52 表 5 天府1井油基钻井液密度预测值与实测值的对比
T/℃ P/MPa ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 119 20 2.222 2.140 3.68 119 70 2.269 2.221 2.12 119 100 2.290 2.269 0.91 150 20 2.183 2.113 3.19 150 70 2.265 2.204 2.69 150 100 2.297 2.258 1.68 表 6 得胜1井油基钻井液密度预测值与实测值的对比
T/℃ P/MPa ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 142 20 2.289 2.259 1.33 142 89 2.391 2.364 1.13 142 115 2.425 2.404 0.88 180 20 2.275 2.249 1.16 180 89 2.381 2.362 0.79 180 115 2.419 2.405 0.57 表 7 不同温度压力下5#配方油基钻井液密度预测值与实际值的对比
P/
MPa140 ℃ 160 ℃ ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 10 1.5485 1.7324 11.87 1.5336 1.7178 12.01 30 1.5991 1.7555 9.78 1.5899 1.7407 9.48 50 1.6384 1.7789 8.57 1.6207 1.7639 8.84 70 1.6594 1.8026 8.63 1.6516 1.7875 8.23 90 1.7122 1.8267 6.69 1.7099 1.8113 5.93 表 8 不同温度压力下6#配方油基钻井液密度预测值与实际值的对比
P/
MPa200 ℃ 220 ℃ ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% ρ实测/(g·cm−3) ρ预测/(g·cm−3) 误差/% 10 1.9135 2.1497 12.34 1.8943 2.1323 10.03 30 1.9723 2.1796 10.51 1.9648 2.1619 8.24 50 2.0332 2.2099 8.69 2.0251 2.1920 6.66 70 2.0961 2.2407 6.90 2.0860 2.2250 9.41 90 2.1765 2.2719 4.38 2.1596 2.2534 4.34 -
[1] 罗绪武,赵雄虎,余加水,等. 生物柴油包水钻井液体系[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(6):721-725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.06.007LUO Xuwu, ZHAO Xionghu, YU Jiashui, et al. Laboratory study on water in oil drilling fluid formulated with biodiesel oil[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(6):721-725. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.06.007 [2] 潘谊党,于培志. 密度对油基钻井液性能的影响[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(3):273-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.03.002PAN Yidang, YU Peizhi. Effect of density on the performance of oil base drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(3):273-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.03.002 [3] 邱正松,赵冲,张现斌,等. 超高温高密度油基钻井液研究与性能评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(6):663-670.QIU Zhengsong, ZHAO Chong, ZHANG Xianbin, et al. Study and performance evaluation of ultra-high temperature high density oil based drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(6):663-670. [4] 王骁男. 塔河油田二叠系井壁失稳机理及防塌强抑制钻井液体系研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.WANG Xiaonan. Study on the instability mechanism of permian borehole in Tahe oilfield and drilling fluid system with strong suppression for collapse[D]. China University of Geosciences (Beijing) , 2019. [5] 谢春林,杨丽丽,蒋官澄,等. 高温高压耦合条件下油基钻井液的流变特性规律及其数学模型[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2021,38(5):568-575.XIE Chunlin, YANG Lili, JIANG Guancheng, et al. Rheological characteristics of oil base drilling fluids and its mathematical model under coupled hthp conditions[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2021, 38(5):568-575. [6] 王敏生,易灿,徐加放. 高温高压对超深井钻井液密度的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2007,29(5):85-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2007.05.024WANG Minsheng, YI Can, XU Jiafang. Effects on high temperature and pressure density[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2007, 29(5):85-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2007.05.024 [7] 李旭,任胜利,刘文成,等. 钻井流体液相组分密度的温度压力修正模型[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(2):168-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.02.006LI Xu, REN Shengli, LIU Wencheng, et al. Study on temperature and pressure correction model for predicting liquid phase density of drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(2):168-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.02.006 [8] 汪海阁,刘岩生,杨立平. 高温高压井中温度和压力对钻井液密度的影响[J]. 钻采工艺,2000,23(1):56-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2000.01.016WANG Haige, LIU Yansheng, YANG Liping. Effect of temperature and pressure on drilling fluid density in HTHP wells[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2000, 23(1):56-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2000.01.016 [9] BARKLM, CUNHA J C. Olefin-based synthetic-drilling-fluid volumetric behavior under downhole condition[R]. SPE 108159, 2009. [10] 宋晓雪. 密度等因素对油基钻井液性能的影响情况研究[J]. 西部探矿工程,2021,33(4):59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.04.019SONG Xiaoxue. Study on influence of density and other factors on the performance of oil-based drilling fluids[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2021, 33(4):59-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2021.04.019 [11] MCMORDIE Jr W C, BLAND R G, HAUDER J M. Effort of temperature and pressure on the density of drilling fluid[R]. SPE 11114, 1982. [12] 赵胜英,鄢捷年,舒勇,等. 油基钻井液高温高压流变参数预测模型[J]. 石油学报,2009,30(4):603-606. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.04.023ZHAO Shengying, YAN Jienian, SHU Yong, et al. Prediction model for rheological parameters of oil-based drilling fluids at high temperature and high pressure[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(4):603-606. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.04.023 [13] 管志川. 温度和压力对深水钻井油基钻井液液柱压力的影响[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版),2003,27(4):48-52,57.GUAN Zhichuan. Effect of temperature and pressure on fluid column pressure of wellbore drilling fluid in deep-water drilling with oil-based drilling fluid[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science) , 2003, 27(4):48-52,57. [14] 唐明月. 油基钻井液在高温高压下的密度预测——基于自适应极限学习机模型[J]. 新疆石油天然气,2019,15(2):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2019.02.009TANG Mingyue. Prediction of oil-based drilling fluid density under high temperature and pressure——based on adaptive limit learning machine model[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2019, 15(2):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2019.02.009 [15] 王富华, 王瑞和, 王力, 等. 深井水基钻井液流变性影响因素的实验研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液, 2010, 27(1): 17-20.WANG Fuhua, WANG Ruihe, WANG Li, et al. Experimental research on the influencing factors of rheology of deep well water-based drilling fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2010, 27(1):17-20. [16] 鄢捷年, 李志勇, 张金波. 深井油基钻井液在高温高压下表观粘度和密度的快速预测方法[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2005, 33(5): 38-42.YAN Jienian, LI Zhiyong, ZHANG Jinbo. Methods for quickly predicting apparent viscosity and density of oilbased drilling fluids under HTHP conditions[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2005, 33(5): 38-42. [17] 罗宇维, 朱江林, 李东, 等. 温度和压力对井内流体密度的影响[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2012, 40(2): 30-34.LUO Yuwei, ZHU Jianglin, LI Dong, et al. The impact of temperature and pressure on borehole fluids density[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2012, 40(2): 30-34. -




 下载:
下载: