A Modified Hectorite Viscosifier and Gelling Agent for Oil Based Drilling Fluids
-
摘要:
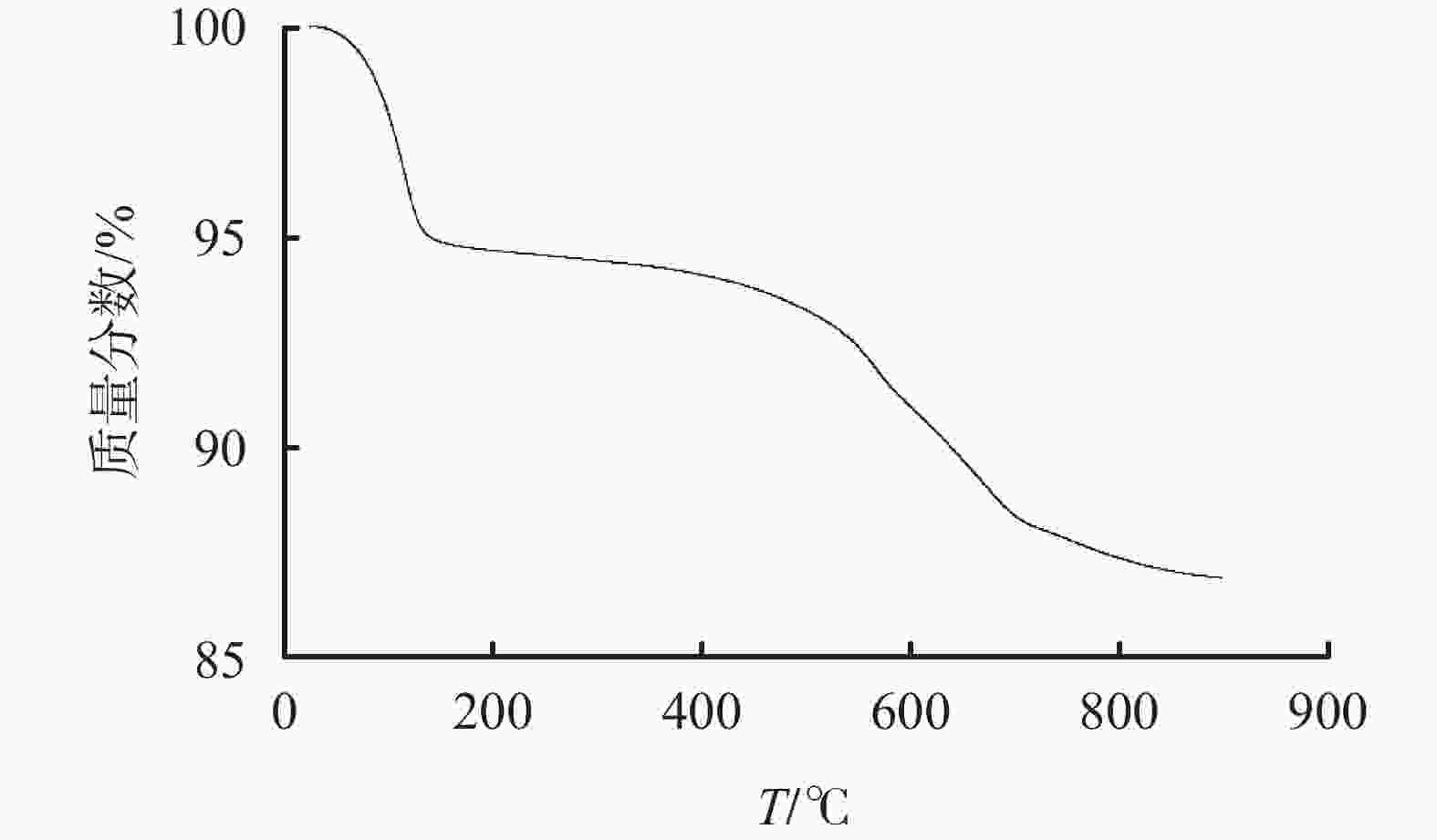
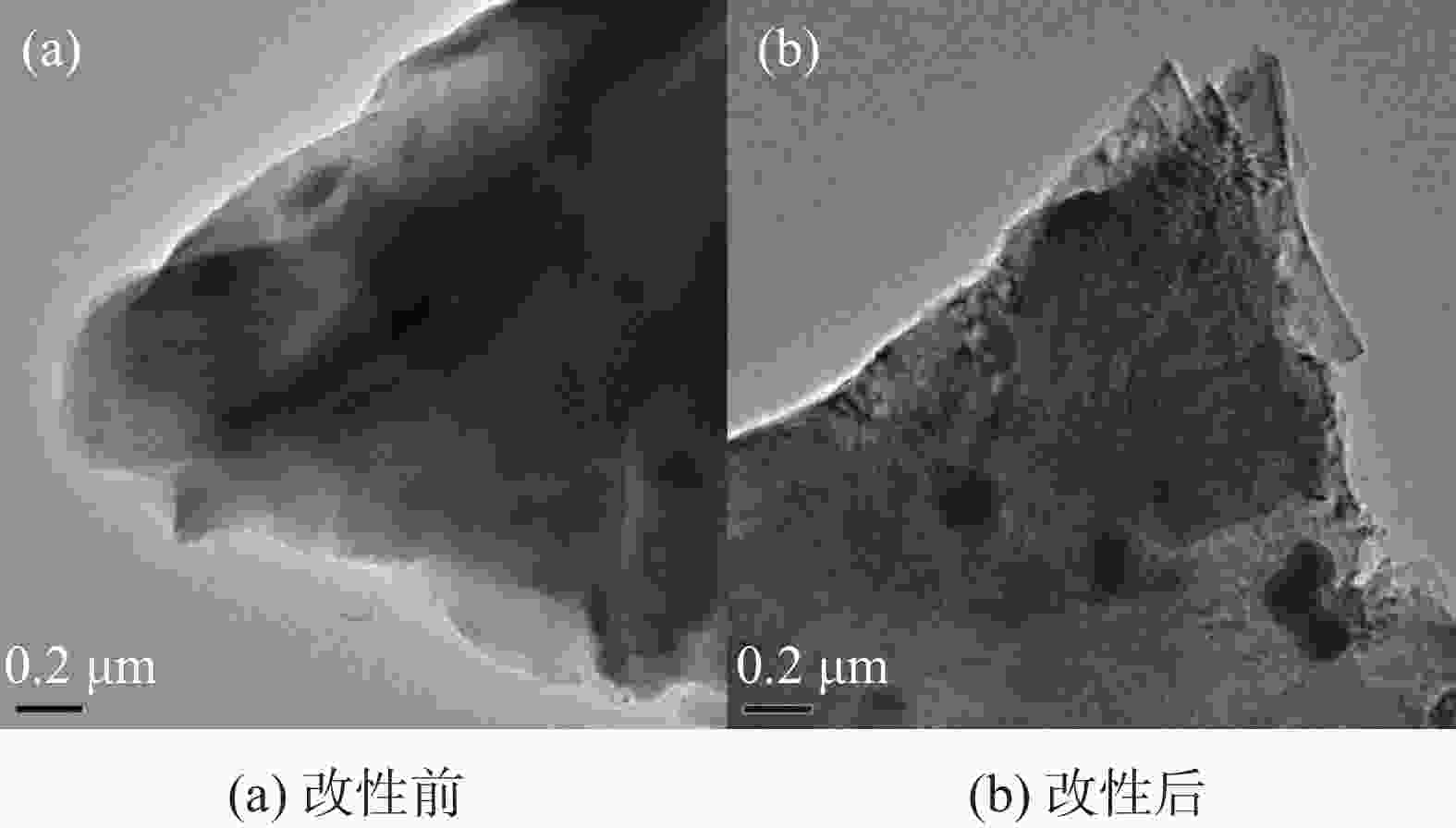
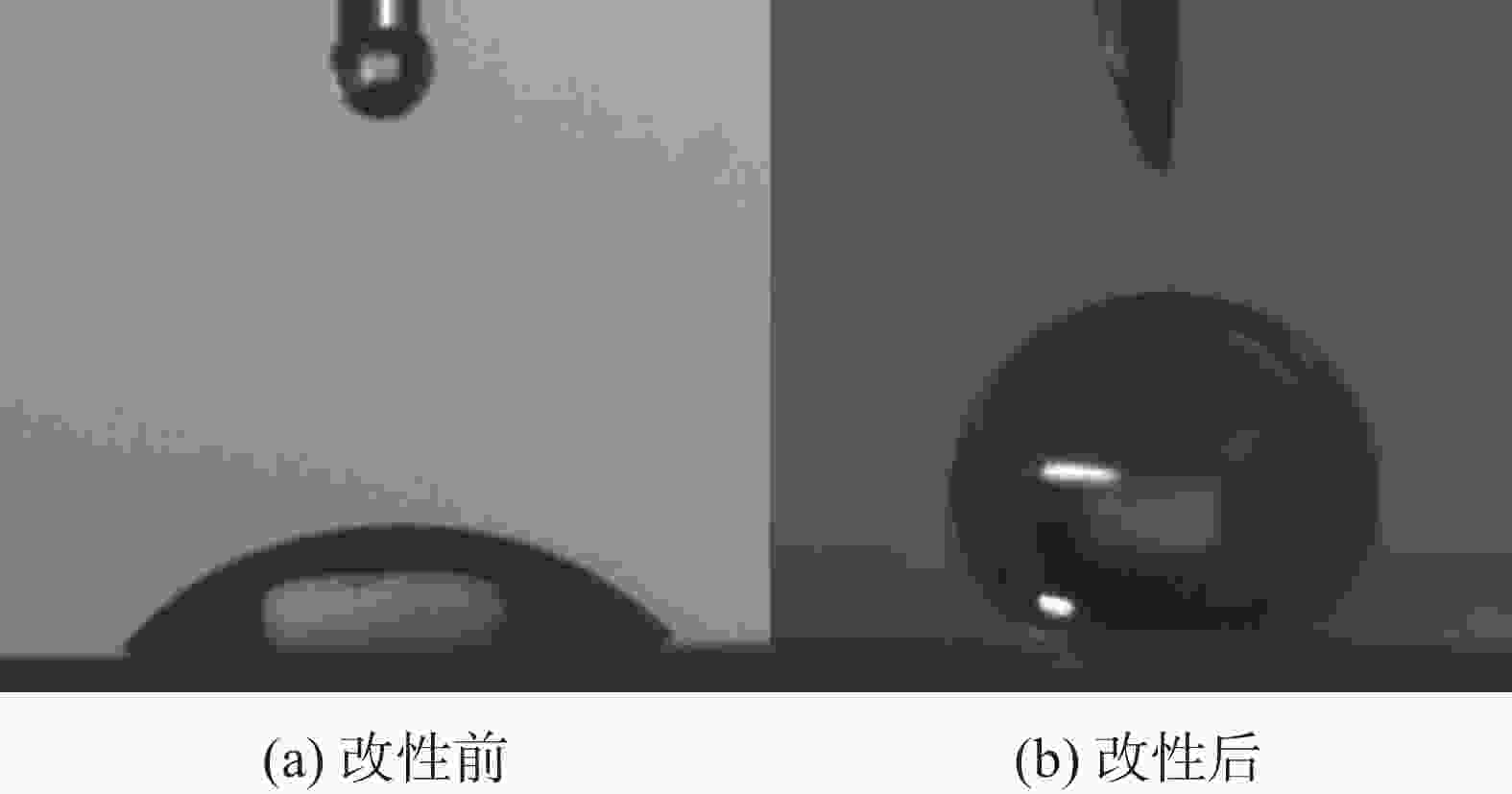
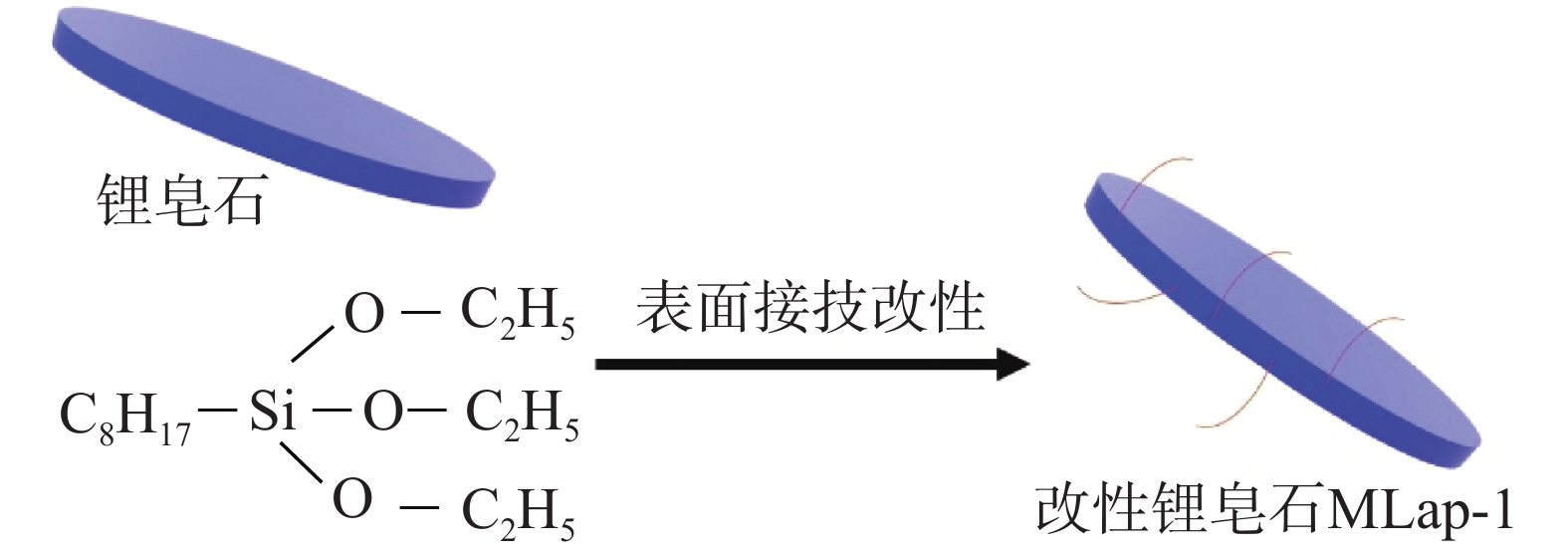
以正辛基三乙氧基硅烷和锂皂石为原料,利用溶胶-凝胶法一步合成了油基钻井液用增黏提切剂改性锂皂石MLap-1,分别利用红外光谱、热重分析、透射电镜和表面润湿性对其单体进行表征,证明其合成成功。通过对改性锂皂石MLap-1单剂评价发现,该剂能够提高油水比为80∶20乳液的乳化效率和破乳电压,在0.3%加量下,乳液破乳电压值达到1200 V以上,使得乳液的表观黏度和动切力由12 mPa·s和0 Pa增大至23 mPa·s和10 Pa,同时能够抗200 ℃高温。以改性锂皂石MLap-1为基础构建的高密度油基钻井液在200 ℃老化后,其动切力维持在4 Pa以上,低剪切速率切力维持在3 Pa以上,破乳电压高于1000 V,滤失量低于5.0 mL,很好地维护了钻井液的悬浮稳定性,保持了良好的乳化稳定性和降滤失效果。为油基钻井液进一步钻探深井、超深井提供了技术支持。
Abstract:A modified hectorite viscosifier and gelling agent, MLap-1, for oil based drilling fluids, has been developed through one-step sol-gel method using triethoxyoctylsilane and hectorite. Characterization of the product with IR spectroscopy, TGA, TEM and surface wettability has proved the success of the synthesis. Evaluation of MLap-1 showed that it can improve the emulsion efficiency and electric stability of 80∶20 (O/W) emulsion; at 0.3% concentration of MLap-1 the electric stability of the emulsion was at least 1,200 V, and the apparent viscosity and yield point of the emulsion were increased from 12 mPa·s and 0 Pa to 23 mPa·s and 10 Pa, respectively. A high density oil based drilling fluid treated with MLap-1, after aging at 200 ℃, had its yield point maintained at above 4 Pa, low-shear-rate yield point above 3 Pa, electric stability above 1,000 V, and filtration rate less than 5.0 mL. These data indicate that MLap-1 is able to maintain the oil based drilling fluid in good suspension stability, good emulsion stability and good filtration control. The development of MLap-1 can be used to technically support the deep and ultra-deep drilling with oil based drilling fluids.
-
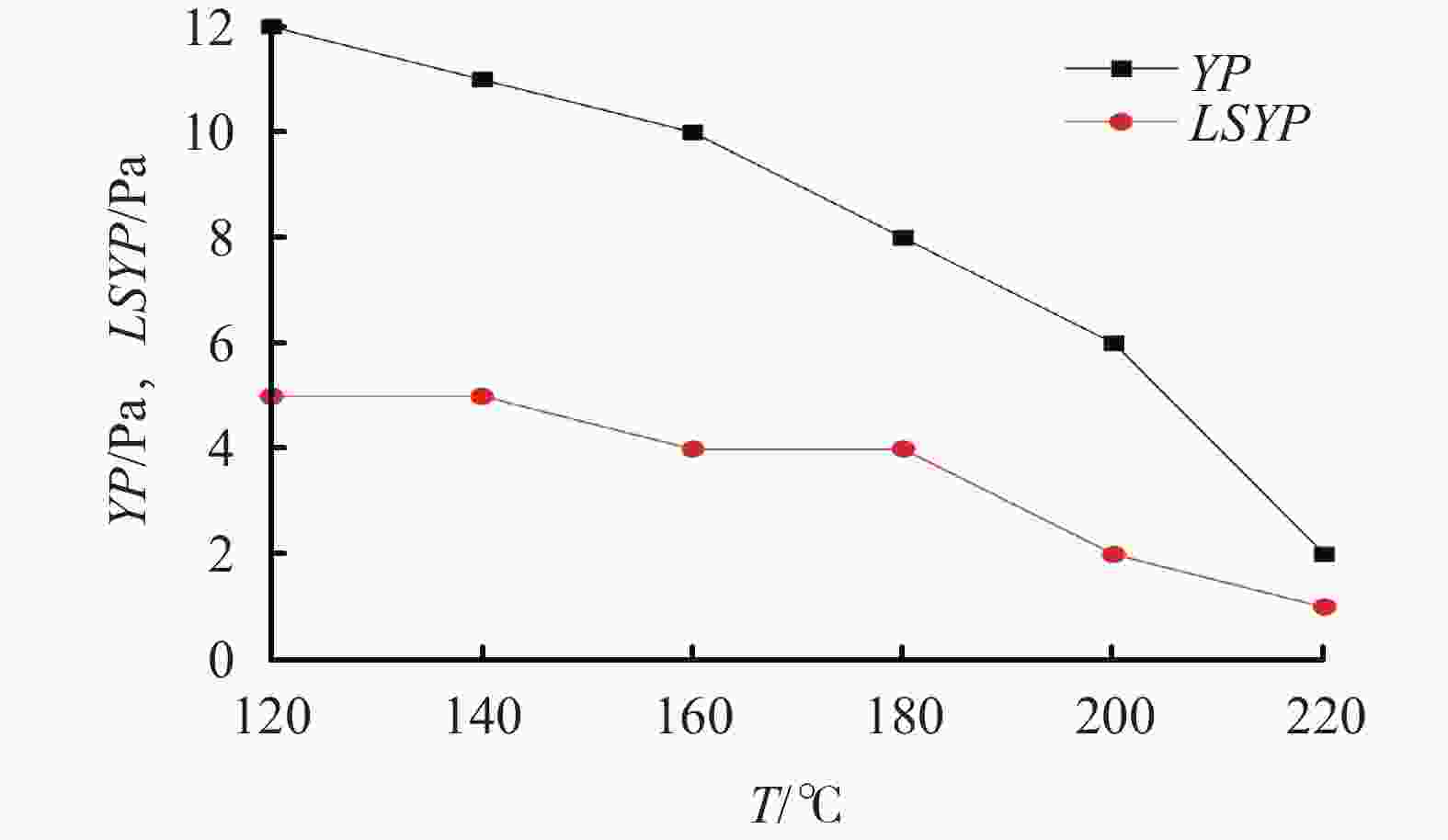
表 1 改性锂皂石MLap-1的增黏提切 性能评价及与同类产品对比
样品 AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/Pa3# 12 12 0 0.5/0.5 3#+0.3%MLap-1 23 13 10 3.0/4.5 3#+0.3%VERSAMOD 16 13 3 0.5/1.0 3#+0.3%RHEMODTML 18 14 4 1.0/1.5 表 2 MLap-1对油基钻井液性能的影响
T/
℃ρ/
g·cm−3PV/
mPa·sYP/
PaLSYP/
PaFLHTHP/
mLES/
V常温 2.0 50 7 5 986 2.2 65 6 4 919 2.4 82 6 4 844 180 2.0 49 6 5 3.0 1021 2.2 63 5 4 3.2 1245 2.4 81 4 4 3.6 1336 200 2.0 47 5 4 3.4 1074 2.2 59 5 3 4.0 1308 2.4 74 4 3 4.8 1389 注:高温老化时间为16 h,高温高压滤失量测量温度为180 ℃ -
[1] 王中华. 国内钻井液技术进展评述[J]. 石油钻探技术,2019,47(3):95-102. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019054WANG Zhonghua. Review of progress on drilling fluid technology in China[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2019, 47(3):95-102. doi: 10.11911/syztjs.2019054 [2] JIANG G, NI X, YANG L, et al. Synthesis of superamphiphobic nanofluid as a multi-functional additive in oil-based drilling fluid, especially the stabilization performance on the water/oil interface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020(588):124385. [3] 黄贤斌. 抗高温高性能无土相油基钻井液技术研究[D]. 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.HUANG Xianbin. High-temperature high-performance organoclay-free oil-based drilling fluid technology research[D]. China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2017. [4] 王星媛,陆灯云,吴正良. 抗220 ℃高密度油基钻井液的研究与应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(5):550-554,560.WANG Xingyuan, LU Dengyun, WU Zhengliang. Study and application of a high density oil base drilling fluid with high temperature resistance of 220 ℃[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(5):550-554,560. [5] 赵素丽. 以季戊四醇为支化剂合成低黏度高切力钻井液提切剂[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(3):282-287. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.03.003ZHAO Suli. A drilling fluid gelling agent synthesized with pentaerythritol as branching agent[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(3):282-287. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2020.03.003 [6] 褚奇,石秉忠,李涛,等. 水基钻井液用低增黏提切剂的合成与性能评价[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(6):689-693. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.06.005CHU Qi, SHI Bingzhong, LI Tao, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a low viscosity gelling agent for water base drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(6):689-693. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.06.005 [7] 孙金声,黄贤斌,蒋官澄,等. 无土相油基钻井液关键处理剂研制及体系性能评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2018,45(4):713-718.SUN Jinsheng, HUANG Xianbin, JIANG Guancheng, et al. Development of key additives for organoclay-free oil-based drilling mud and system performance evaluation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4):713-718. [8] 蒋官澄,贺垠博,黄贤斌,等. 基于超分子技术的高密度无黏土油基钻井液体系[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2016,43(1):131-135. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30015-5JIANG Guancheng, HE Yinbo, HUANG Xianbin, et al. A high-density organoclay-free oil base drilling fluid based on supramolecular chemistry[J]. P etroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(1):131-135. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30015-5 [9] 薛文佳. 抗高温环保型增黏剂的合成与性能评价[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2016, 44(6): 67-73.XUE Wenjia. Synthesis and properties of high temperature resistance and environmental-friendly viscosifier[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2016, 44(6): 67-73. [10] HEINZ M, DIANA M, NADJA H. Thickeners for oil-based drilling fluids: US, 2010/0256021A1[P]. 2010. [11] CARL J T. Suspending agent: US, 6908887B2 [P]. 2002. [12] 米远祝,罗跃,李建成,等. 油基钻井液聚合物增黏剂的合成及性能研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2013,30(2):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.02.002MI Yuanzhu, LUO Yue, LI Jiancheng, et al. Synthesis and performance evaluation of polymer viscosifier for oil-based drilling fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2013, 30(2):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.02.002 [13] 樊雪敏,方善宝,陈志兴,等. 纳米黏土锂皂石的研究现状与应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1622-1627. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3053FAN Xuemin, FANG Shanbao, CHEN Zhixing, et al. Status and application prospects of nano-clay Laponite[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10):1622-1627. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3053 [14] 熊正强,李晓东,付帆,等. 合成锂皂石用作超高温水基钻井液增黏剂实验研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2018,35(5):19-25. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.05.004XIONG Zhengqiang, LI Xiaodong, FU Fan, et al. Mechanisms of synthetic hectorite to viscosify ultra-high temperature water base muds[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2018, 35(5):19-25. doi: doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2018.05.004 [15] HENCH L L, WEST J K. The sol-gel process[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1990, 90(1):33-72. doi: 10.1021/cr00099a003 [16] HUANG Xianbin, SHEN Haokun, SUN Jinsheng, et al. Nanoscale laponite as a potential shale inhibitor in water-based drilling fluid for stabilization of wellbore stability and mechanism study[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10:33252-33259. -




 下载:
下载: