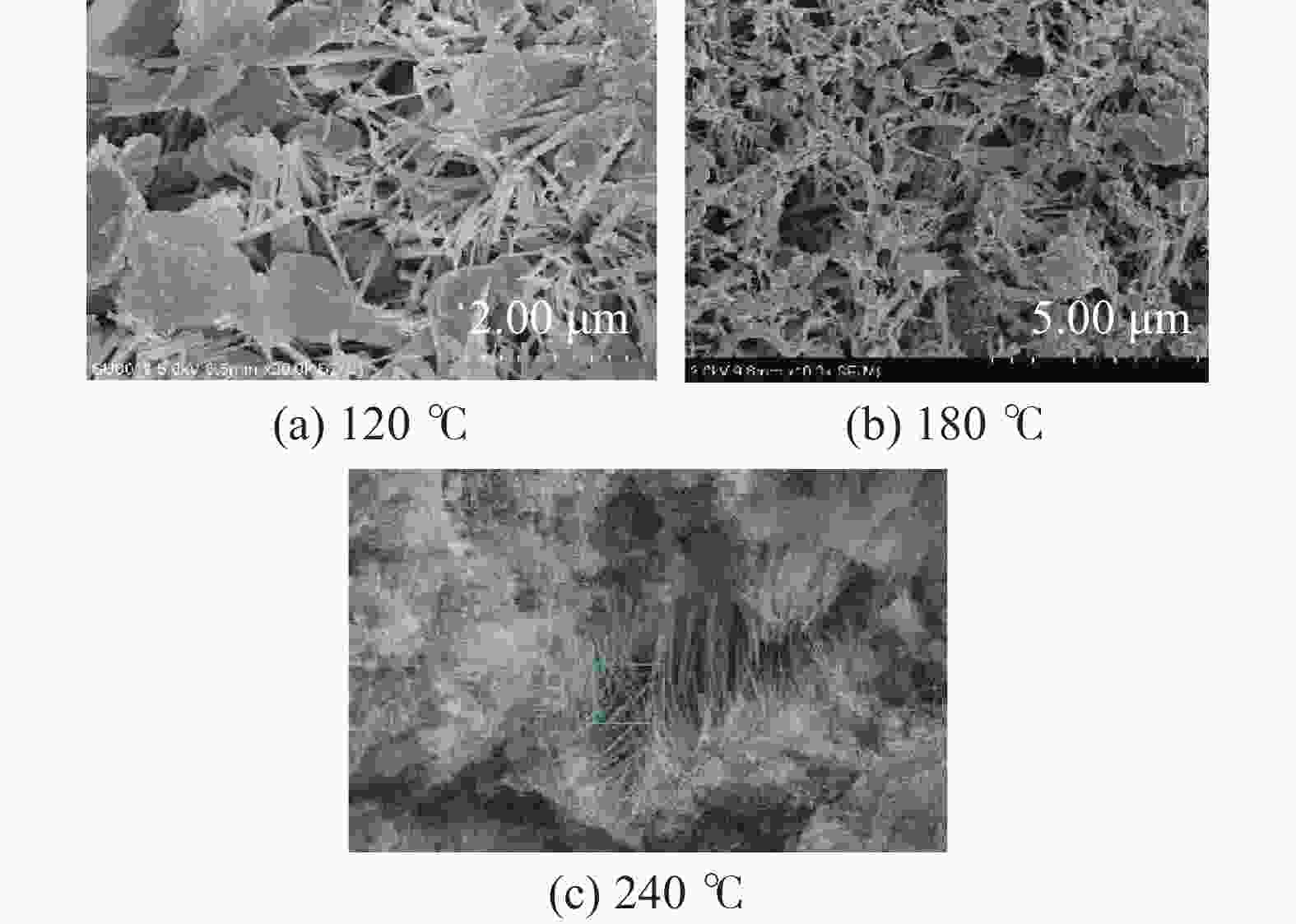
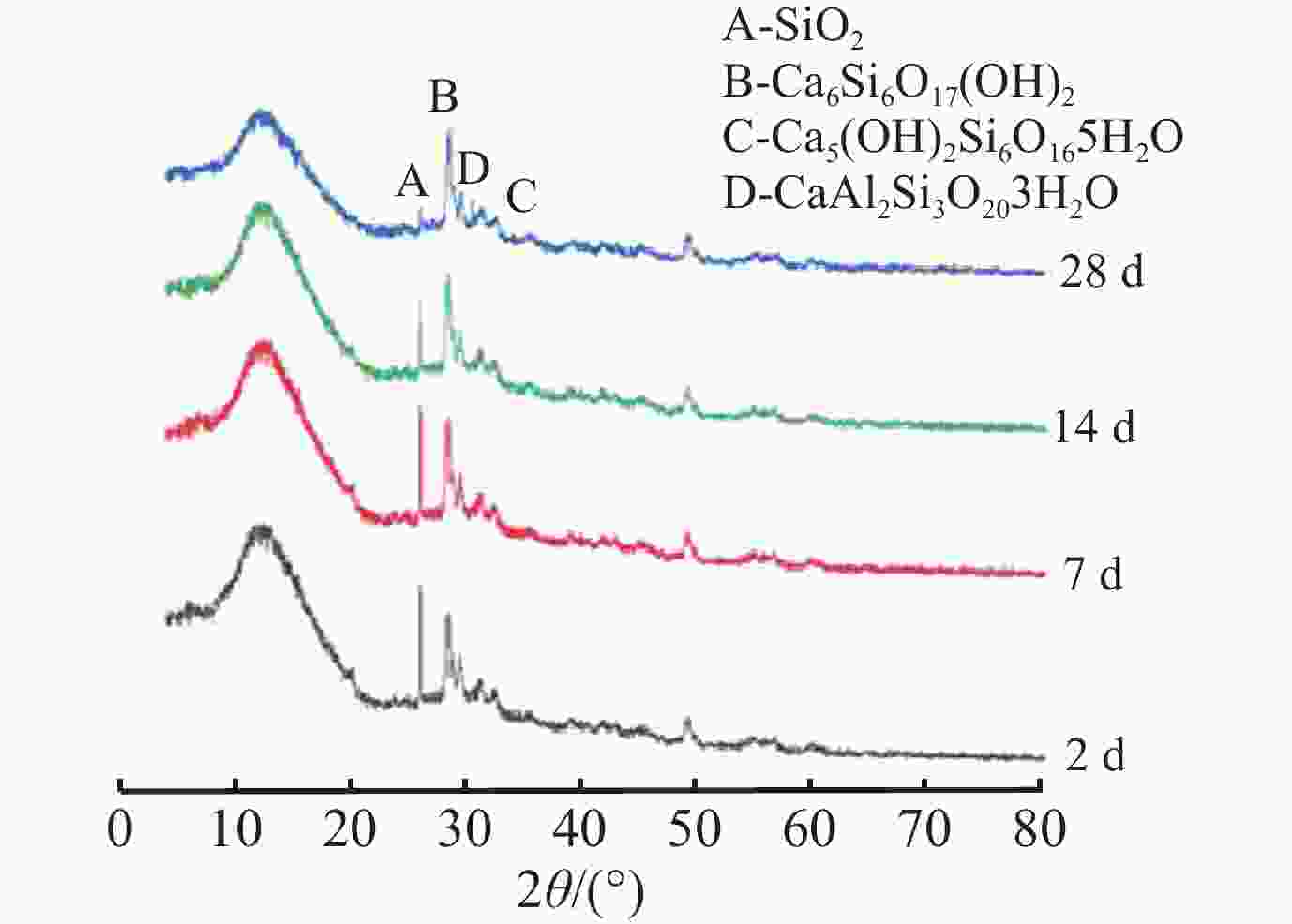
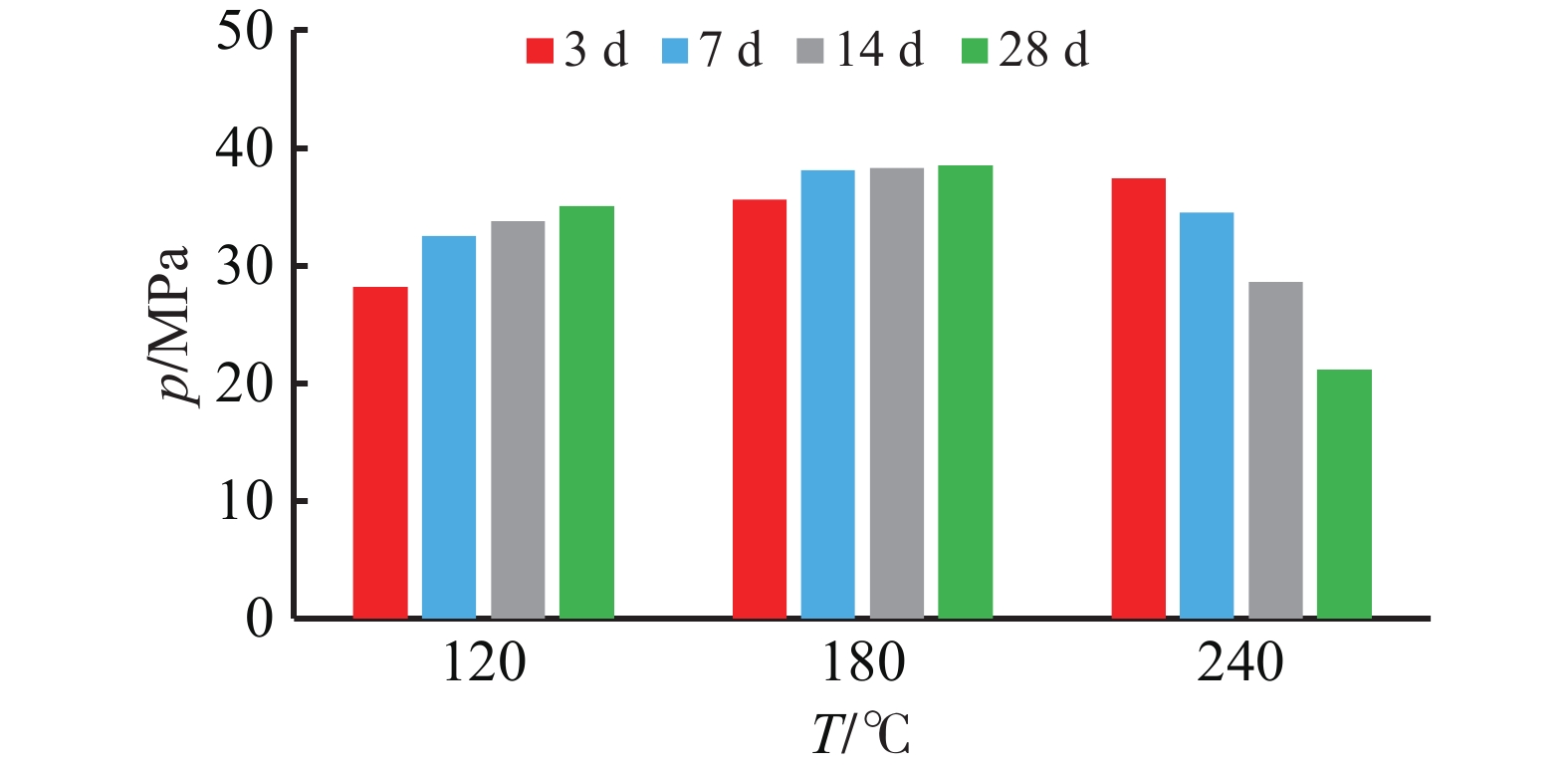
Research on A New Material to Prevent the Strength Decline of Set Cement Under Ultra-High Temperature
-
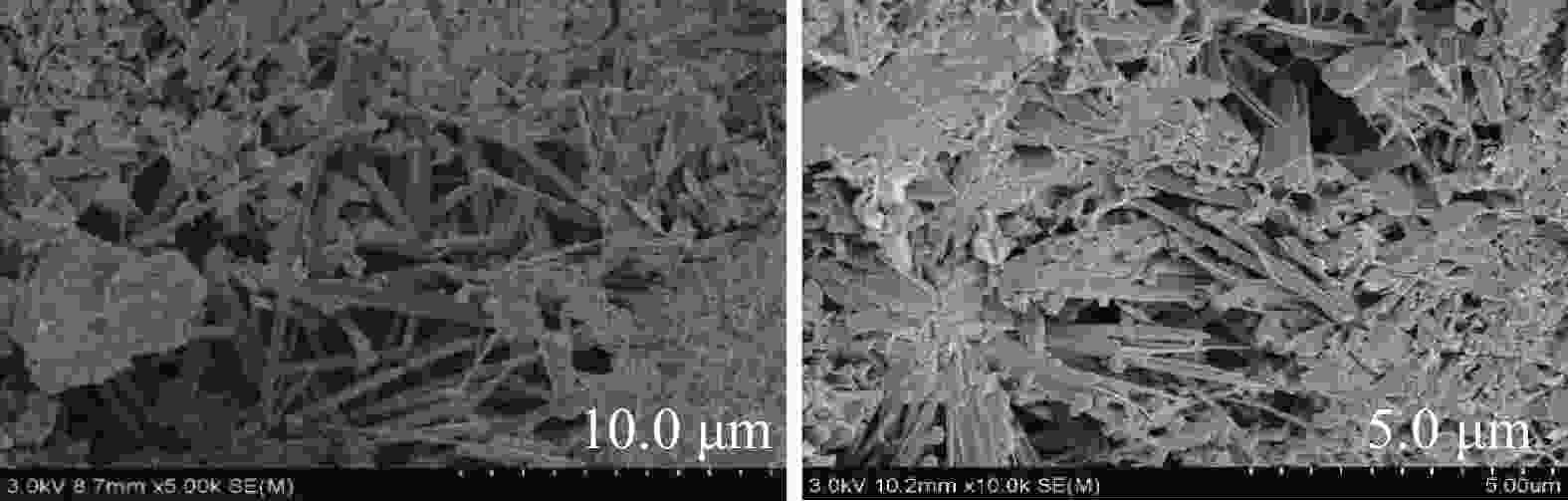
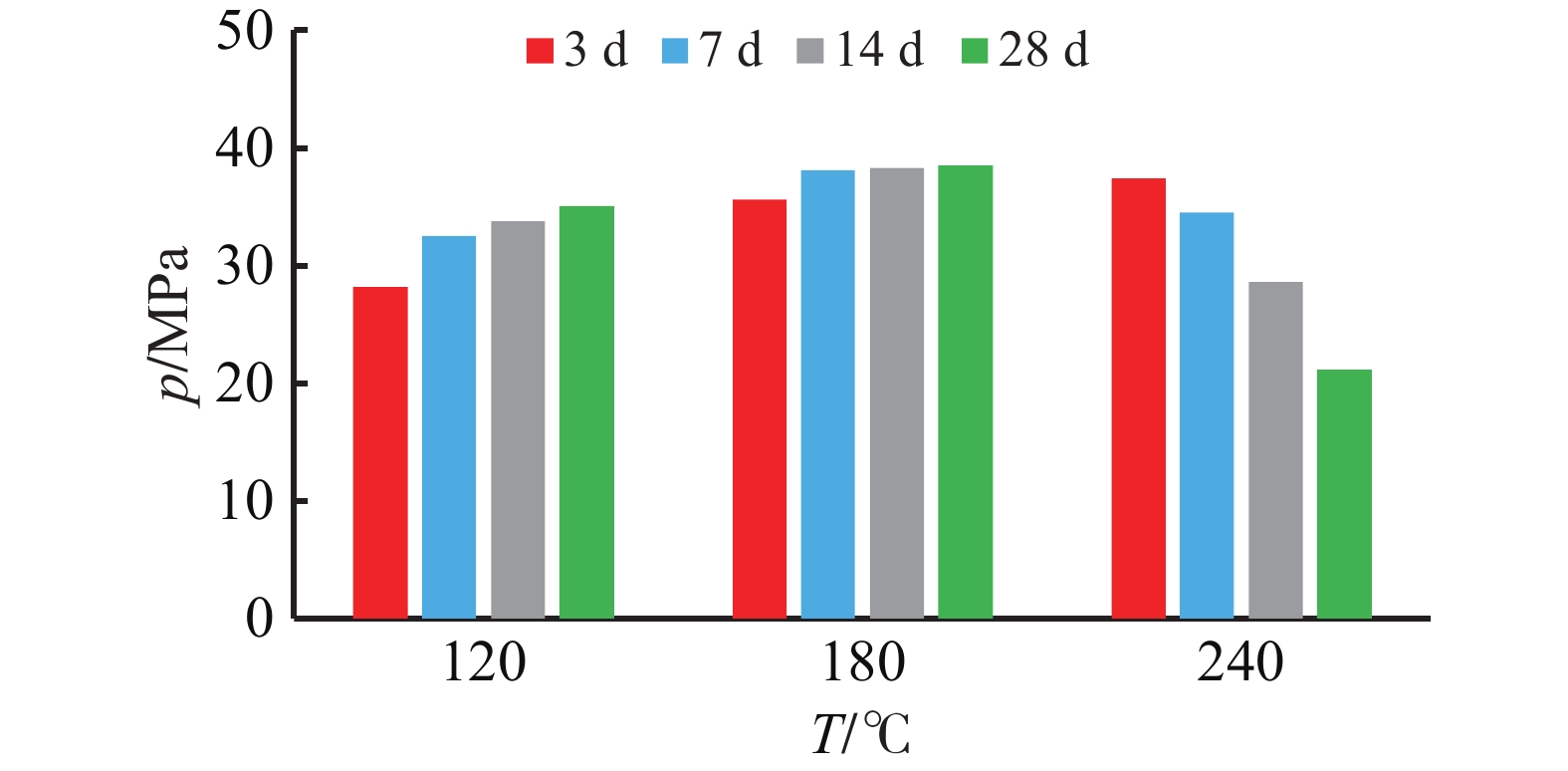
摘要: 在200 ℃以上超高温下,加砂水泥石强度发生衰退,导致超高温深井固井水泥环层间封隔失效,无法满足高温油气井长期开采的需求。对加砂水泥石的强度衰退机理进行探索,研究发现超高温下加砂水泥水化生成平行疏松的硬硅钙石,孔隙率增大,是其力学性能衰退的根本原因。通过高温水化产物优化设计,优选晶体层间距为纳米尺寸的含铝矿物和纳米管材料,开发了一种新型超高温水泥石抗强度衰退材料DRB-4S。在240 ℃下,DRB-4S加量为10%~20%时,水泥石28 d强度不衰退且大于50 MPa。通过X射线衍射分析、扫描电镜测试、孔结构测试等方法进一步对DRB-4S抗强度衰退机理进行了分析,晶体层间距为纳米尺寸的含铝矿物促进了高温稳定水化产物铝硅钙石的生成,纳米管的加入抑制了雪硅钙石向硬硅钙石转化,并且在水泥石中起到桥联填充作用,降低了水泥石的孔隙率。掺有DRB-4S的固井水泥浆失水量小于50 mL,稠化时间易调,稳定性良好,总体施工性能良好,为高温油气井长期开采提供了有力的技术支持。Abstract: In wells with bottomhole temperatures of 200 ℃ or higher, the strength of the set cement with sand will inevitably decrease with time, causing the zonal isolation by the cement sheaths to fail. Wells with this kind of problem will not be able to produce for the designed long time. Researches have been done to investigate the mechanisms of strength retrogression of sanded set cement, showing that the root cause of strength retrogression is the increase in the porosity of the set cement resulted from the generation of parallel loose xonotlite from the hydration of that cement at ultra-high temperatures. To deal with this problem, a new material against strength retrogression of set cement at ultra-high temperatures, DRB-4S, has been developed with optimized aluminum mineral having nanometer crystal layer spacing and nanotube materials. At 240 ℃, a set cement containing 10%–20% DRB-4S has a strength of 50 MPa and does not decrease. Studies on the mechanisms of DRB-4S against strength retrogression of set cement with SEM, XRD and pore structure analysis showed that the use of the nanometer crystal layer spacing aluminum mineral in DRB-4S helps the production of chalcomorphite, a hydration product that is stable at elevated temperatures, in the set cement. The nanotube used in DRB-4S inhibits the conversion of tobermorite to xonotlite and reduces the porosity of the set cement through bridging and filling. Cement slurries treated with DRB-4S have filter loss of less than 50 mL, easy-to-adjust thickening time, good stability and operational performance, all these are of great technical support to the long-term production of high-temperature oil and gas wells.
-
Key words:
- Ultra-high temperature /
- Set cement /
- Strength retrogression /
- Hydration product /
- Porosity
-
表 1 添加不同材料的超高温(220 ℃)水泥石抗压强度
水泥石 抗强度衰退
材料p2 d/
MPap7 d/
MPap14 d/
MPap28 d/
MPa1# 空白 33.2 37.8 32.9 22.3 2# 铝矾土 36.7 35.2 17.2 15.7 3# 无定形硅铝 35.2 33.8 37.1 31.5 4# 埃洛石 34.2 31.4 31.2 29.5 5# 煤矸石 33.5 34.2 20.4 19.8 6# DRB-4S 38.2 44.0 50.1 51.5 注:水泥浆配方为G级水泥+50%混掺石英砂+10%抗强度衰退材料+1.5%悬浮剂DRY-S2+3%增韧材料DRE-3S+
0.9%分散剂DRS-1S+1.5%降失水剂DRF-12S+4%缓凝剂DRH-22L+0.5%消泡剂DRX-1L+56%自来水表 2 掺有DRB-4S的超高温水泥石抗压强度(220 ℃、21 MPa)
DRB-4S/% p2 d/MPa p7 d/MPa p14 d/MPa p28 d/MPa 10 38.2 44.0 50.1 51.5 15 38.7 45.6 53.2 55.4 20 40.1 43.5 49.6 52.7 注:水泥浆配方:G级水泥+50%混掺石英砂+DRB-4S+
3%矿物纤维+分散剂+降失水剂+缓凝剂+水表 3 掺有DRB-4S的超高温水泥石抗压强度(240 ℃、21 MPa)
DRB-4S/% p2 d/MPa p7 d/MPa p14 d/MPa p28 d/MPa 10 44.6 50.7 51.2 52.2 15 45.4 55.3 56.1 58.2 20 44.1 45.6 53.2 57.3 注:水泥浆配方:G级水泥+50%混掺石英砂+DRB-4S+
3%矿物纤维+分散剂+降失水剂+缓凝剂+水表 4 DRB-4S对水泥石孔隙率及渗透率的影响
DRB-4S/
%孔隙率/% 渗透率/mD 2 d 7 d 28 d 2 d 7 d 28 d 0 35.2 36.9 40.2 0.020 0.032 0.043 10 28.9 30.1 30.6 0.005 0.006 0.006 注:水泥浆配方:G级水泥+50%混掺石英砂+DRB-4S+
3%矿物纤维+分散剂+降失水剂+缓凝剂+水 -
[1] 肖夏. 高温固井水泥石力学变形及材料改性效果研究[D]. 西南石油大学, 2018.XIAO Xia. Research on the mechanical deformation and material modification effect of cement paste in high temperature cementing[D]. Southwest Petroleum University, 2018. [2] 王磊,曾义金,张青庆,等. 高温环境下油井水泥石力学性能试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报 (自然科学版 ),2018,42(6):88-95.WANG Lei, ZENG Yijin, ZHANG Qingqing, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of oil well cement under high temperature[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) , 2018, 42(6):88-95. [3] RODERICK B, PERNITES, ASHOK K SANTRA. Portland cement solutions for ultra-high temperature wellbore applications[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2016:72. [4] ZHANG Jingfu,LIU Kai, HOU Ruixue, et al. Development and change of compressive strength for class G oil well cement under high temperature[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2014(1885): 1441-1444. [5] 张景富,徐明,高莉莉,等. 温度及外加剂对G级油井水泥强度的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺,2003,25(3):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2003.03.005ZHANG Jingfu, XU Ming, GAO Lili, et al. Effect of temperature and additives on strength of class G oilwell cement[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2003, 25(3):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2003.03.005 [6] 姚晓, 葛荘, 汪晓静, 等. 加砂油井水泥石高温力学性能衰退机制研究进展[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2018, 46(1): 17-23.YAO Xiao, GE Zhuang, WANG Xiaojing, et al. Research progress of dagradation of mechanical properties of sand-containing cement in high temperature regimes [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2018, 46(1): 17-23. -




 下载:
下载: