Study and Application of a High Efficiency Liquid Pipe Freeing Agent in Pakistan
-
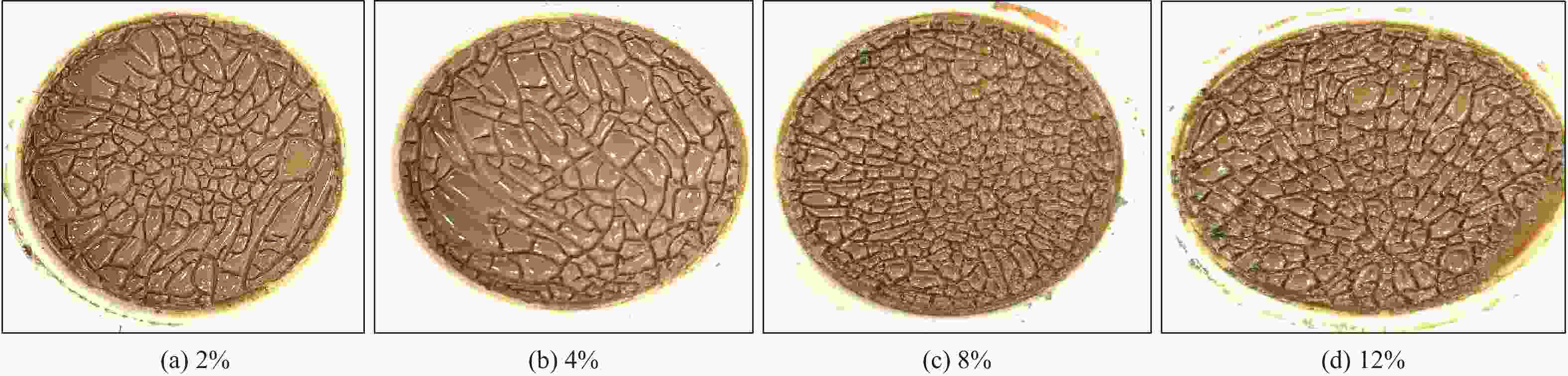
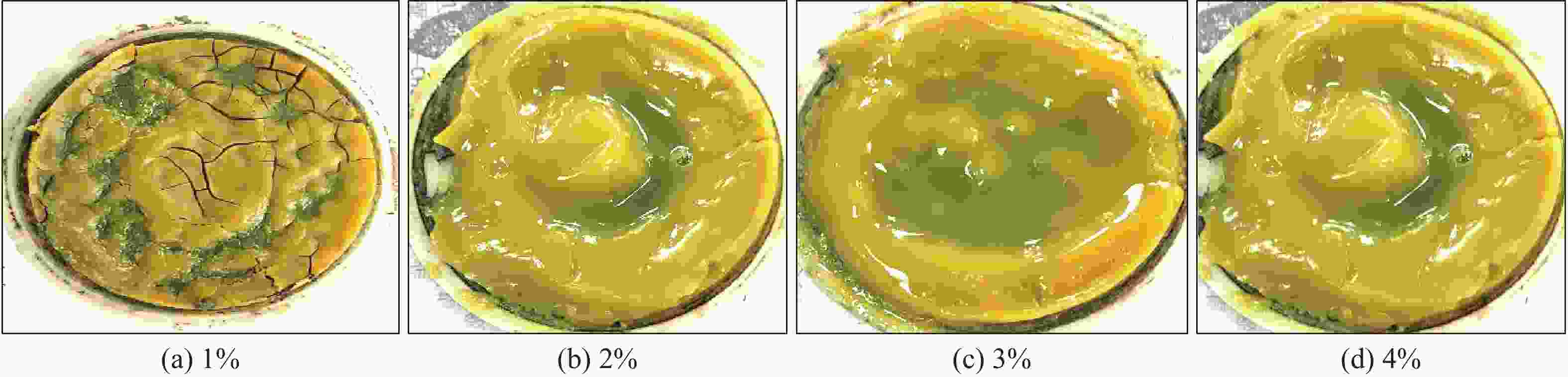
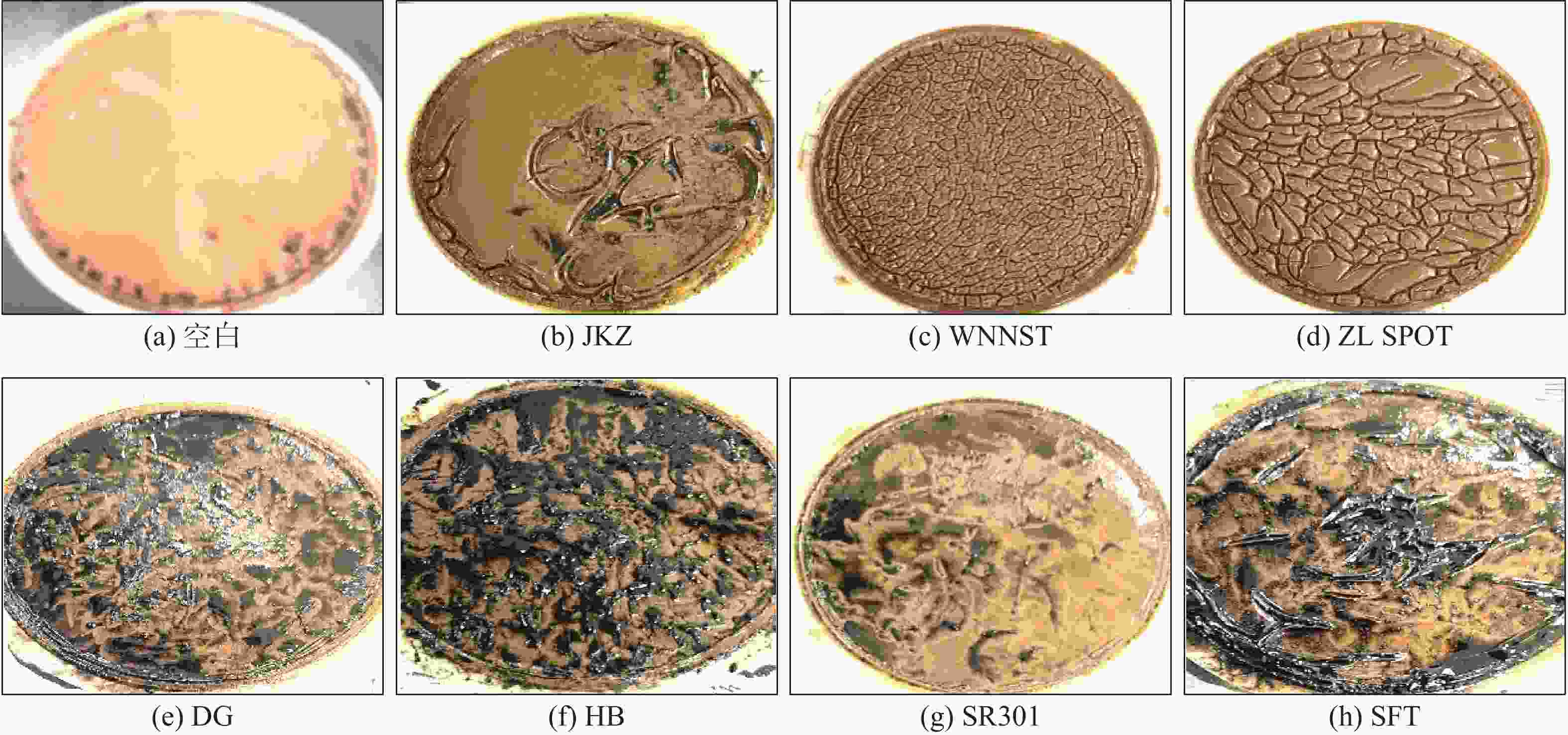
摘要: 针对目前巴基斯坦常用粉末解卡剂Black Magic存在配制时间长,加重易沉淀,与钻井液兼容性差,解卡成功率低等问题,以解卡剂对泥饼的破坏泥饼效果、穿透泥饼时间和极压润滑系数为评价指标,实验优选得到了一种高效液体解卡剂ZL SPOT。在此基础上,通过考察油水比、解卡剂和增黏剂对泥饼破坏和穿透的影响,得到了以0#柴油、解卡剂、清水和有机土组成的加重解卡液配方。实验结果发现:对于非加重解卡液,液体解卡剂在1.0%~2.5%浓度下,其极压润滑系数为0.069,100 mL解卡液穿透泥饼时间仅15 min,泥饼浸泡2 h后能见明显的网状裂纹,优于粉末解卡剂;对于加重解卡液,固相的加入会严重影响解卡效果,但提高解卡剂浓度至8%后,解卡液浸泡后的泥饼能出现网状裂纹;密度1.32~1.80 g/cm3的解卡液在120 ℃静置16 h后,无重晶石沉淀;解卡液与水基钻井液按1∶1比例混合,钻井液流变性和滤失基本不受影响。该液体解卡剂在巴基斯坦成功应用两口井,验证了解卡效果,且施工简单,具有推广应用前景。Abstract: Black Magic is a widely used pipe freeing agent in Pakistan. Problems existed with the use of this pipe freeing agent include long time of preparation, weighting agents in the pipe freeing slurry which are easy to settle, poor compatibility of the Black Magic with drilling fluids used and low success rate of pipe freeing operations. A new high efficiency pipe freeing agent, ZL SPOT, was selected to solve these problems based on three evaluation parameters, say, degree of mud cakes broken down by the pipe freeing agent, time spent penetrating the mud cakes and extreme pressure friction coefficient. By studying the effects of oil/water ratio, pipe freeing agent and viscosifier on the break-down and penetration of the mud cakes, a weighted pipe freeing slurry was formulated with 0# diesel oil, ZL SPOT, water and organophilic clay. Laboratory experimental results showed that for unweighted pipe freeing slurry, at a concentration of the pipe freeing agent between 1% and 2.5%, the extreme pressure friction coefficient was 0.069, time for 100 mL pipe freeing slurry to penetrate the mud cakes was only 15 min, and after soaking in the pipe freeing slurry, mud cakes were obviously developed with fracture network on the surfaces, indicating the ZL SPOT is superior to the dry pipe freeing agent Black Magic. For weighted pipe freeing slurry, addition of solids into the slurry greatly affects the efficiency of freeing a stuck pipe. However, when the concentration of the ZL SPOT was increased to 8%, the mud cakes were developed with fracture network after being soaked in the pipe freeing slurry. When stood still for 16 h at 120 ℃, the pipe freeing slurry with its density between 1.32 g/cm3 and 1.80 g/cm3 showed no signs of barite settling. When mixed with water based drilling fluid at a ratio of 1∶1, the pipe freeing slurry basically did not affect the rheology and filtration rate of the drilling fluid. This liquid pipe freeing agent has been successfully used on two wells drilled in Pakistan, proving its pipe freeing ability. Field operation with this pipe freeing agent is easy, and the application of this pipe freeing agent will popularize in the future.
-
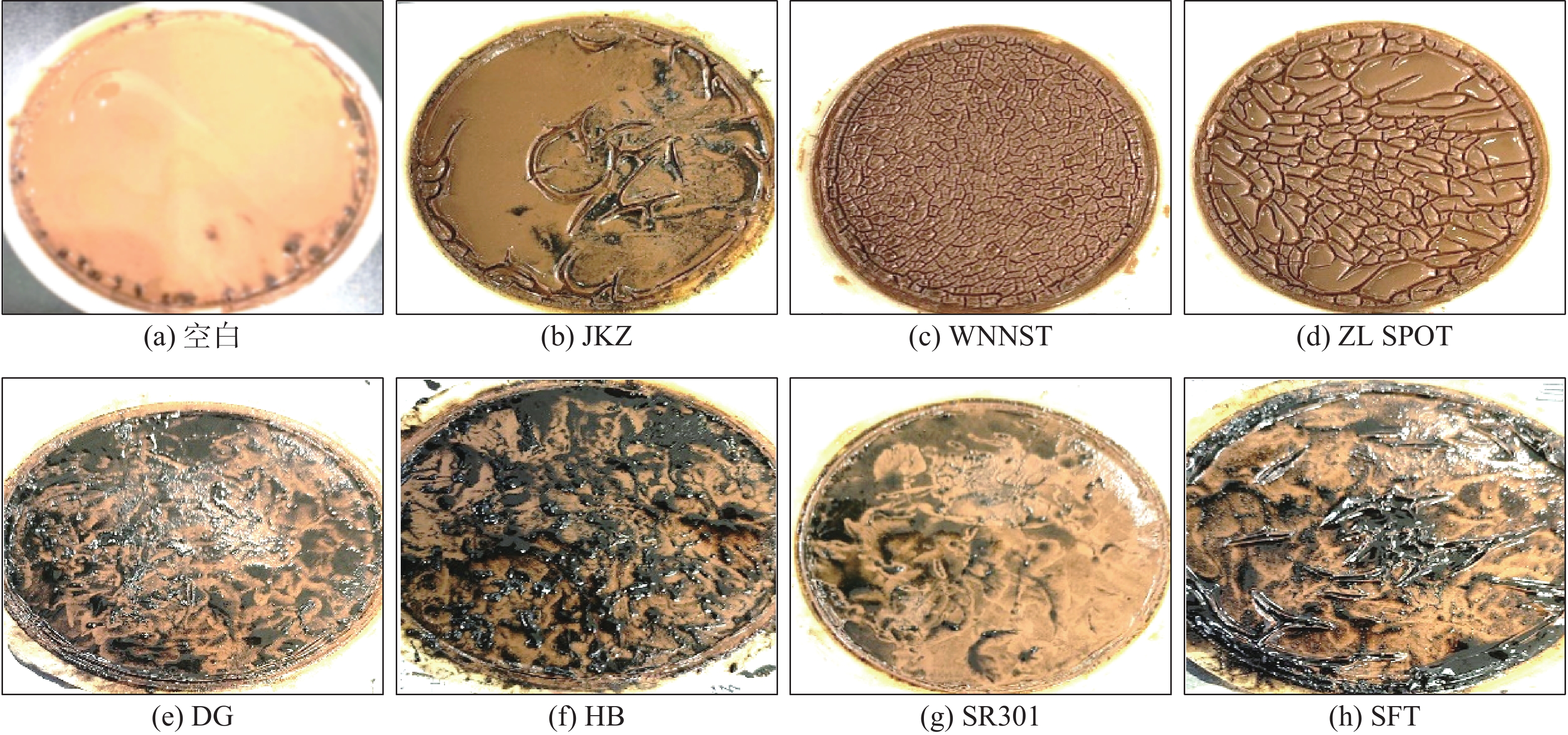
表 1 不同液体和粉末解卡剂的极压润滑系数
解卡剂 类型 极压润滑系数 空白 空白 0.401 JKZ 液体 0.082 WNNST 液体 0.094 ZL SPOT 液体 0.069 DG
HB粉末
粉末0.157
0.150SR301 粉末 0.135 Black Magic SFT 粉末 0.080 表 2 不同液体和粉末解卡剂的穿透泥饼能力
解卡剂 类型 100 mL滤液时间/min JKZ 液体 150 WNNST 液体 76 ZL SPOT 液体 15 DG
HB粉末
粉末67
155SR301 粉末 144 Black Magic SFT 粉末 155 表 3 不同密度解卡液破坏泥饼效果
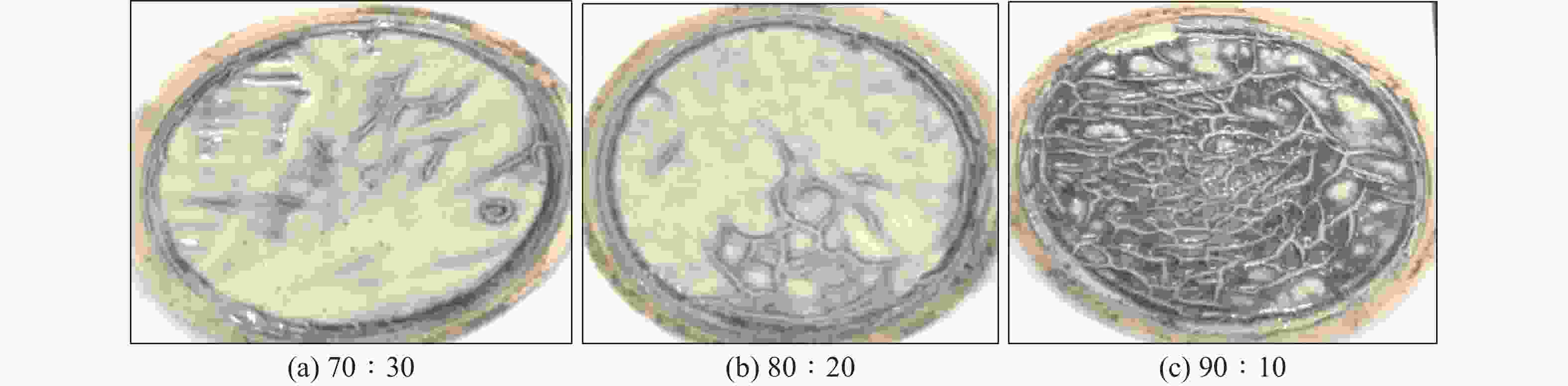
ρ/
g·cm−3油水比 解卡剂/
%有机土/
%浸泡后泥饼变化情况 1.32 80∶20 8.0 1.0 变硬,有明显的网状裂纹 1.32 90∶10 4.0 0.5 变软,无明显裂纹 1.56 80∶20 8.0 1.0 变硬,有少量裂纹 1.56 90∶10 4.0 0.5 变软,无明显裂纹 1.80 80∶20 8.0 1.0 变软,有少量裂纹 1.80 90∶10 4.0 0.5 变软,无明显裂纹 表 4 不同密度的解卡液性能
ρ /
g·cm−3实验条件 AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/PaES/
V1.32 老化前 19.0 15.0 4.0 1.5/3.0 520 老化后 18.0 14.0 4.0 1.5/2.5 510 1.56 老化前 24.5 20.0 4.5 2.5/5.0 537 老化后 22.0 18.0 3.0 2.0/4.5 528 1.80 老化前 31.0 27.0 4.0 2.5/6.0 540 老化后 30.0 26.0 4.0 2.5/5.5 536 注:老化条件为120 ℃静置16 h;均老化静置后无沉淀 表 5 解卡液对钻井液的污染实验结果
ρ /
g·cm−3钻井液 解卡液/
%PV/
mPa·sYP/
PaGel/
Pa/PaFLAPI/
mL1.44 Siab-01井
钾聚合物0.0 33.0 5.0 1.5/2.5 4.2 100 38.0 7.0 2.0/4.0 5.0 1.64 Siab-01井
柴油基0.0 48.0 18.0 4.5/9.0 1.0 100 37.0 7.0 2.5/4.0 1.0 1.87 Nashpa-10井
KL-KLS水基0.0 56.0 17.0 2.5/8.0 2.0 10 57.0 18.0 3.0/9.5 2.6 100 65.0 23.0 4.5/12.5 4.6 表 6 巴基斯坦2口井应用液体解卡剂ZL SPOT情况统计
井号 钻井液 ρ / (g·cm−3) 解卡剂类型 卡点/m 井眼/套管尺寸 /mm 解卡时间及效果 QP DEEP
X-1AKCl
聚合物1.30 SFT粉剂 974 558.8/473.1 应用2次,均未解卡 ZL SPOT液体 应用1次,8.0 h后解卡 SENI GUMBAT-1 柴油基 1.47 ZL SPOT液体 5744 149.2 应用1次,9.5 h后解卡 -
[1] 丁振龙,黄晓川,土林,等. 巴基斯坦NASHPA-2井钻井复杂事故处理技术[J]. 钻采工艺,2013,36(2):112-113. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2013.02.32DING Zhenlong, HUANG Xiaochuan, TU Lin, et al. Pakistan NASHPA-2 well drilling complex incident treatment technology[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2013, 36(2):112-113. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2013.02.32 [2] 杨远程,潘登. 巴基斯坦Mela-1井钻井施工中的问题与建议[J]. 钻采工艺,2008,31(4):141-142,145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2008.04.047YANG Yuancheng, PAN Deng. Pakistan Mela-1 well drilling operation problems and suggestion[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2008, 31(4):141-142,145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-768X.2008.04.047 [3] 丁振龙, 胡军, 张远彬, 等. 巴基斯坦DAKHNI-11井钻井复杂事故处理技术[J]. 天然气技术, 2013, 4(5): 33-34.DING Zhenlong, HU Jun, ZHANG Yuanbin, et al. Treatment technology for complex accidents during drilling DAKHNI-11 well, Pakistan[J]. Natural Gas Technology, 2013, 4(5): 33-34. [4] 滕华信,蒲明江,刘常旭,等. SUI-93井卡钻事故处理[J]. 西部探矿工程,2013,25(9):63-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2013.09.022TENG Huaxin, PU Mingjiang, LIU Changxu, et al. Treatment of drilling string sticking accident in SUI-93 well[J]. West China Exploration Engineering, 2013, 25(9):63-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2013.09.022 [5] 张健. 水包生物柴油解卡液体系研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.ZHANG Jian. A study of biodiesel-in-water spotting fluid[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. [6] CLARK R K, ALMQUIST S G. Evaluation of spotting fluids in a full-scale differential pressure sticking apparatus[C]. SPE 22550, 1992. [7] AA ALSHAIKH, M AMANULLAH. A comprehensive review of differential sticking, spotting fluids, and the current testing and evaluation methods [C]. SPE 192169, 2018. [8] 乔东宇,陈若铭,郑义平,等. 高效解卡剂的研究与应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2013,30(6):24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.06.007QIAO Dongyu, CHEN Ruoming, ZHENG Yiping, et al. The studies and application of high-performance pipe-freeing agents[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2013, 30(6):24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2013.06.007 [9] 张坤,李明华,万永生,等. 有效解除水平井段压差卡钻技术—在磨溪地区钻井中的应用[J]. 天然气工业,2007,27(7):56-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.07.016ZHANG Kun, LI Minghua, WAN Yongsheng, et al. Techniques used to remove pressure sticking in horizontal wells and its actual application in Moxi gas field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(7):56-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2007.07.016 [10] 刘梅全,张禄远,李德全,等. 无机盐水基解卡液的研究及其在长5井的应用[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2007,24(3):45-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2007.03.014LIU Meiquan, ZHANG Luyuan, LI Dequan, et al. Research on inorganic saltwater spotting fluid and its application in well Chang-5[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2007, 24(3):45-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2007.03.014 [11] 李晓岚. 提高解卡剂解卡效率的途径[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2005.LI Xiaolan. Approaches to improve the efficiency of a stuck releasing agent [D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Shiyou University, 2005. -




 下载:
下载: