Study on Rheological Modifier of High Temperature High Density Clay-free Oil-based Drilling Fluid
-
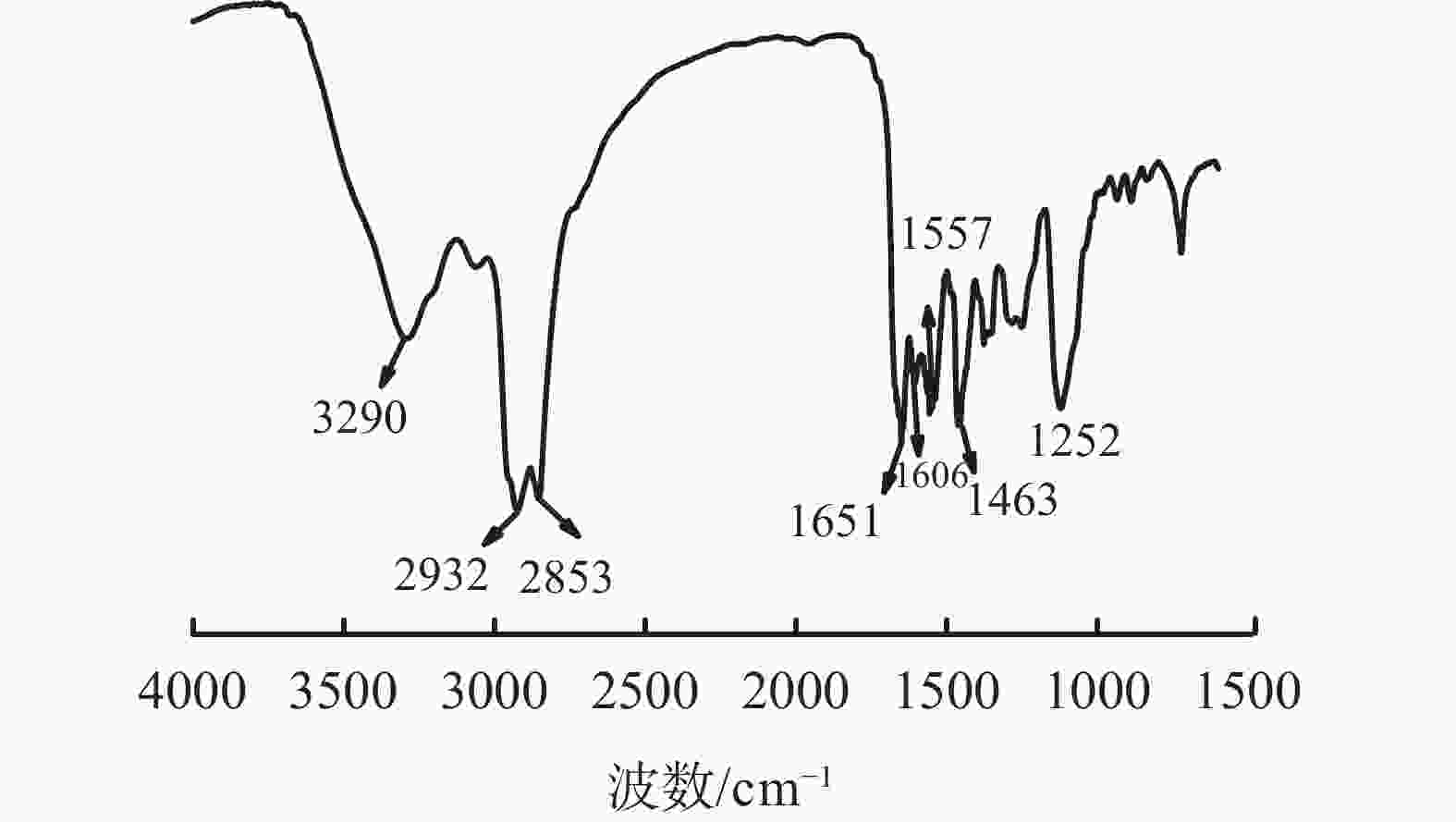
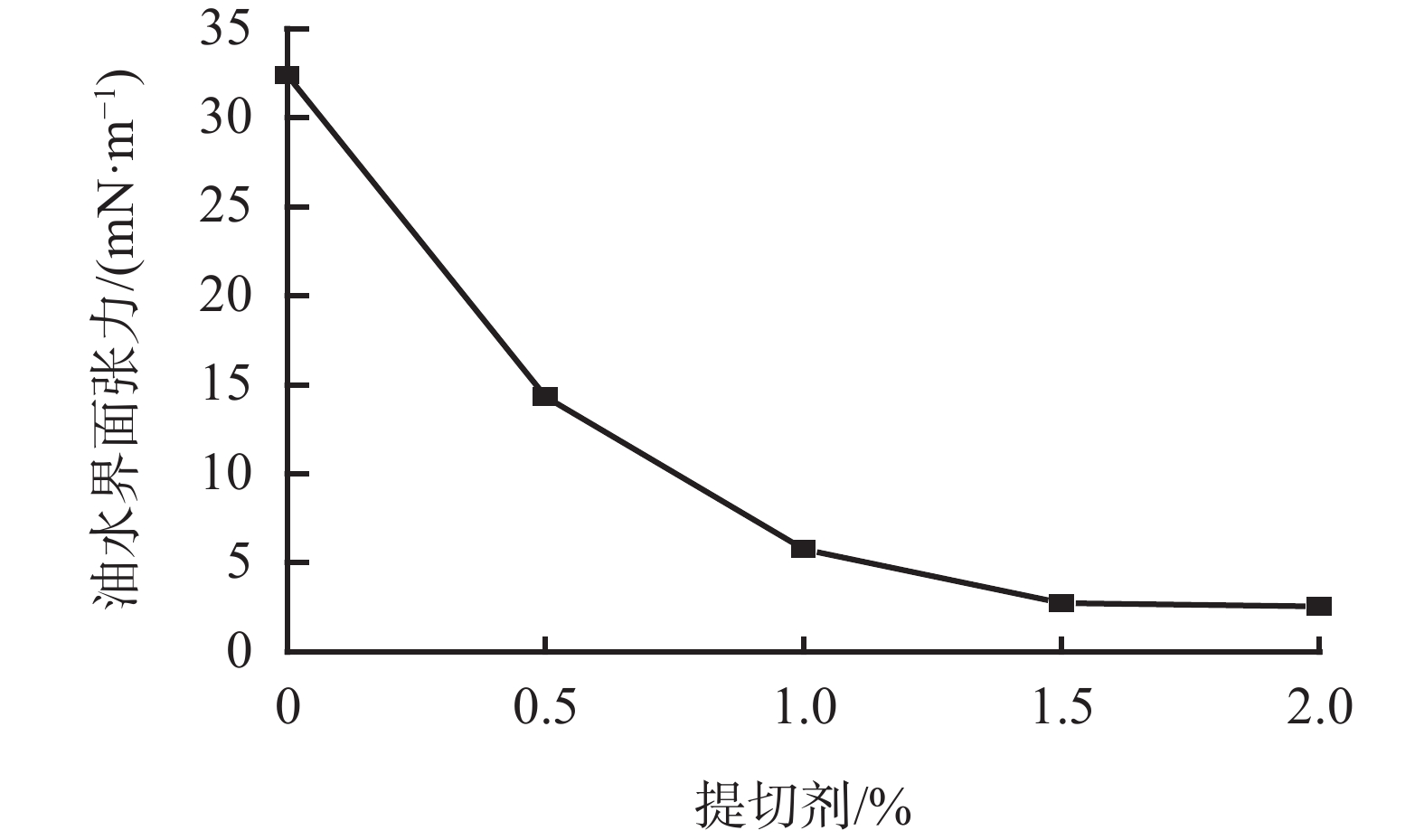
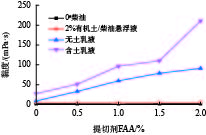
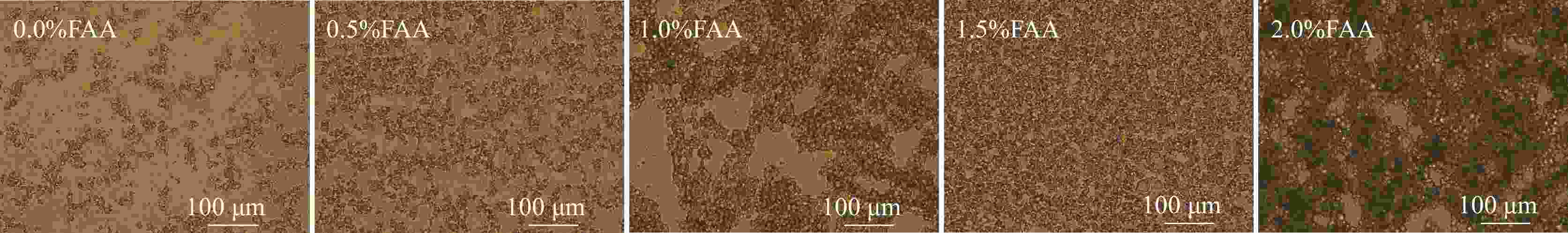
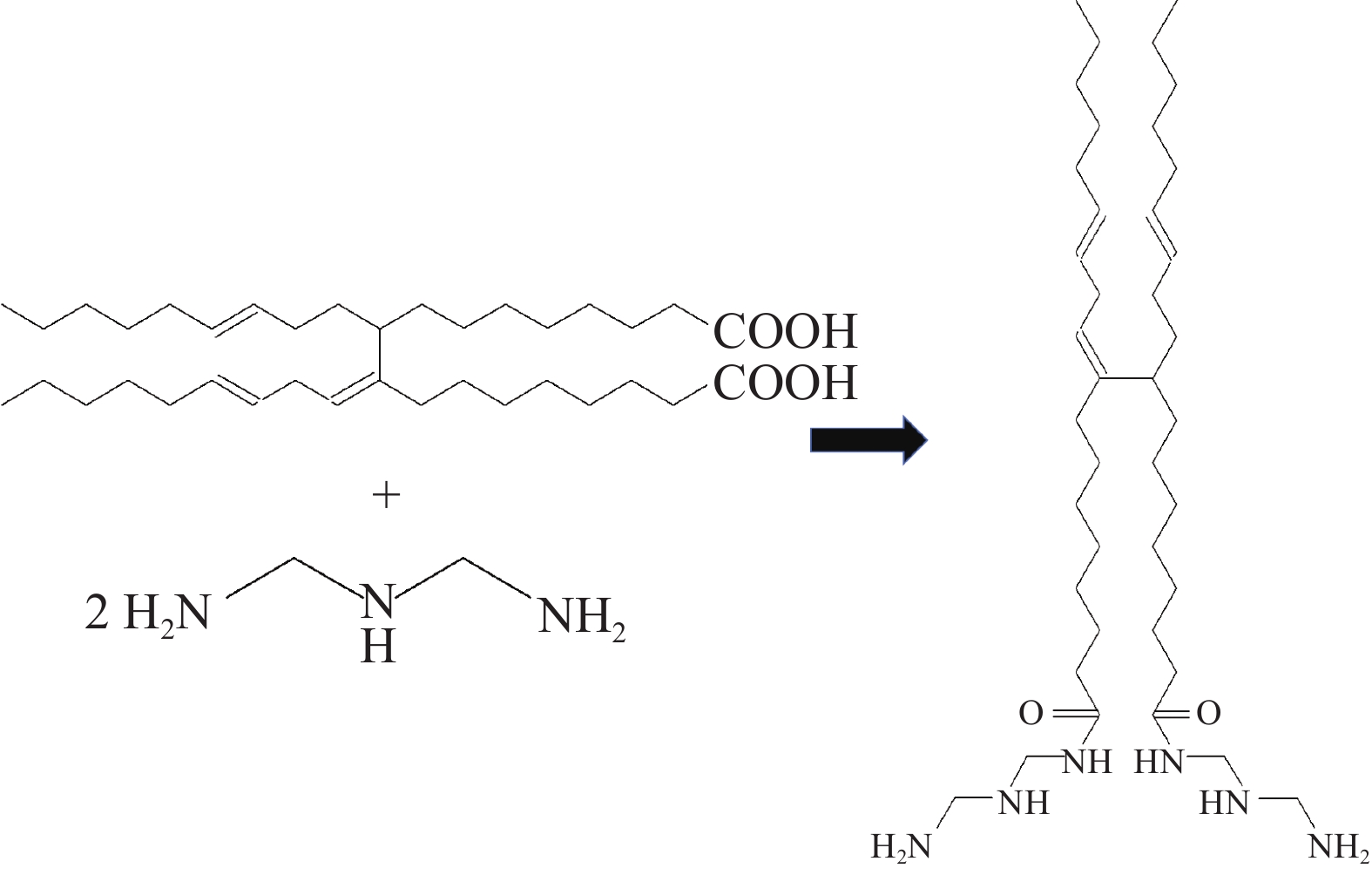
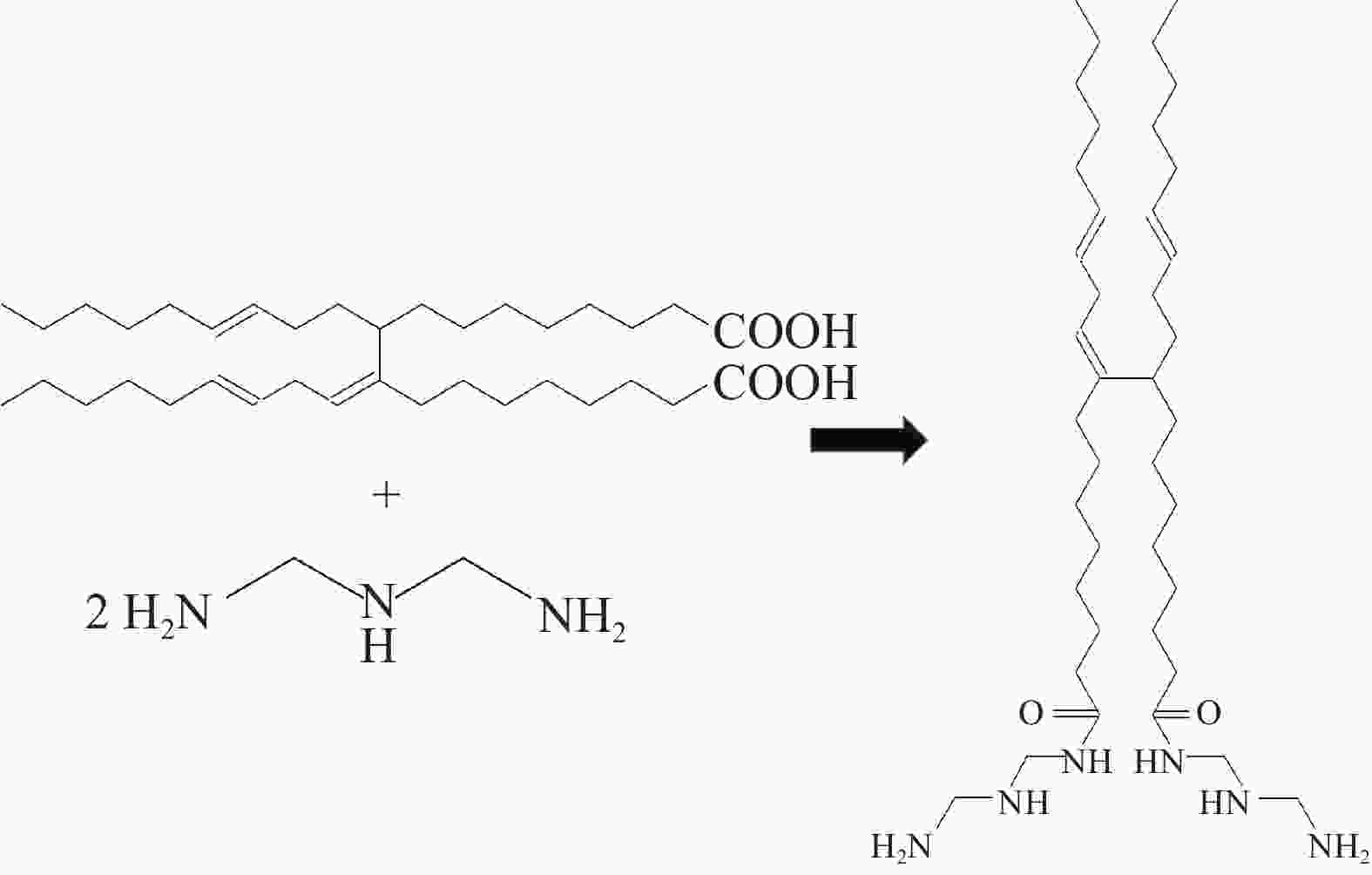
摘要: 针对油基钻井液体系高温环境下沉降稳定性不足的难题,将二聚脂肪酸和二乙烯三胺以物质的量比1∶2反应合成了一种小分子脂肪酸酰胺型抗高温提切剂FAA,并对其进行了结构表征、机理分析和性能评价。流变实验和显微镜观察结果表明,提切剂FAA主要通过在乳液滴之间桥联形成凝胶网络结构来有效提高油基钻井液的结构强度,从而改善其固相悬浮能力及沉降稳定性。在柴油基钻井液体系中的评价结果表明,FAA可有效提高体系的动切力、φ6/φ3读数以及动塑比,并可有效改善体系的高温沉降稳定性,使体系在220 ℃下静置5 d后沉降因子SF小于0.52,无明显沉降现象出现。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of insufficient settlement stability of oil-based drilling fluids in high temperature environments, a small molecule fatty acid amide type rheological modifier FAA which can be used in high temperature environment was synthesized by reacting dimer fatty acids and diethylene triamine at a molar ratio of 1∶2, with the structural characterization, mechanism analysis and performance evaluation were also carried out. The results of rheological experiments and microscopic observations show that the FAA effectively improves the structural strength of the oil-based drilling fluid system by bridging the emulsion droplets to form a gel-like network structure, thereby effectively improving its solid-phase suspension ability and settlement stability. The evaluation results in the diesel-based drilling fluid system show that the FAA can effectively improve the yield point, φ6/φ3 revolution reading and yield point/plastic viscosity ratio of the system, and can effectively improve the high-temperature sedimentation stability of the system, making it standing at 220℃ for 5 days with the sedimentation factor SF less than 0.52 and no obvious sedimentation phenomenon occures.
-
表 1 FAA加量对油包水乳液破乳电压及乳化率的影响
提切剂/% ES /V 乳化率/% 0 674 83 0.5 831 85 1.0 1097 89 1.5 1225 91 2.0 1247 90 表 2 提切剂FAA加量对不同油水比油基钻井液体系常规性能的影响
油水比 FAA/
%测试
条件AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
Paφ6/φ3 Gel/
Pa/PaYP/PV/
Pa/mPa·sFLHTHP/
mLES/
V90∶10 0 老化前 23.5 23 0.5 2/1 1.0/0.5 0.02 8.6 787 老化后 22.0 22 0 0/0 0/0 0 463 1 老化前 36.0 32 4.0 5/4 3.0/4.0 0.13 4.2 989 老化后 37.5 34 3.5 4/3 2.0/3.0 0.10 699 80∶20 0 老化前 34.0 32 2.0 3/2 1.5/1.0 0.06 6.2 933 老化后 31.0 30 1.0 1/1 0.5/0.5 0.03 578 1 老化前 47.0 41 6.0 8/7 4.0/6.0 0.15 5.6 1107 老化后 44.0 40 4.0 5/4 2.0/3.0 0.10 741 70∶30 0 老化前 45.5 43 2.5 3/2 1.5/1.0 0.06 4.4 544 老化后 42.5 41 1.5 2/1 1.0/0 0.04 473 1 老化前 58.0 47 11.0 10/8 6.0/8.0 0.23 3.2 826 老化后 54.0 46 8.0 7/6 4.0/5.0 0.17 735 注:老化条件为180 ℃、16 h;流变性测试温度为65 ℃;高温高压滤失量测试温度为180 ℃ 表 3 不同老化温度下提切剂FAA对油基钻井液常规性能的影响
FAA/
%测试条件 开罐
状态AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
Paφ6/φ3 Gel/
Pa/PaYP/PV/
Pa/mPa·sFLHTHP/
mLES/
V0 老化前 34.0 32 2.0 3/2 1.5/1.0 0.06 933 180 ℃×16 h 软沉 31.0 30 1.0 1/1 0.5/0.5 0.03 6.2 578 200 ℃×16 h 硬沉 27.5 27 0.5 1/0 0/0.5 0.02 9.8 402 220 ℃×16 h 硬沉 28.0 29 −1.0 0/0 0/0 14.2 359 240 ℃*16 h 硬沉 26.5 28 −1.5 0/0 0/0 16.4 316 1 老化前 47.0 41 6.0 8/7 4.0/6.0 0.15 1107 180 ℃×16 h 无沉 44.0 40 4.0 5/4 2.0/3.0 0.10 5.6 741 200 ℃×16 h 无沉 45.0 41 4.0 5/4 2.0/3.0 0.10 6.2 762 220 ℃×16 h 无沉 42.0 39 3.0 4/3 2.0/2.5 0.07 6.8 643 240 ℃×16 h 软沉 36.0 35 1.0 1/0 0/0.5 0.03 9.0 392 220 ℃×32 h 无沉 47.0 42 5.0 5/4 3.0/4.0 0.12 785 220 ℃×48 h 无沉 45.0 42 3.0 4/3 3.0/3.5 0.07 811 220 ℃×72 h 无沉 47.0 43 4.0 4/3 3.0/4.0 0.09 5.8 835 注:流变性测试温度为65 ℃;高温高压滤失量测试温度为180 ℃ 表 4 油基钻井液岩屑污染评价实验
岩屑污染量/
%测试
条件开罐
状态流动
状态AV/
mPa·sPV/
mPa·sYP/
Paφ6/φ3 Gel/
Pa/PaYP/PV/
Pa/mPa·sFLHTHP/
mLES/
V5 老化前 良好 49 43 6 5/4 2/3 0.14 7.0 915 老化后 无沉 43 38 5 4/3 2/3 0.13 606 10 老化前 良好 58 52 6 6/5 3/4 0.12 5.6 1107 老化后 无沉 51 46 5 5/4 2/3 0.11 741 15 老化前 良好 72 64 8 9/8 6/8 0.13 4.2 1296 老化后 无沉 71 62 9 10/9 6/10 0.15 982 20 老化前 稠化严重 96 82 14 13/12 8/13 0.17 5.4 1431 老化后 无沉 119 101 18 16/14 8/15 0.18 943 注:老化温度为220 ℃;流变性测试温度为65 ℃;高温高压滤失量测试温度为180 ℃ 表 5 提切剂FAA对油基钻井液 高温沉降稳定性的影响
FAA/
%t静置/
dρ上部/
g·cm-3ρ下部/
g·cm-3沉降
状态SF 0 0 1.96 2.08 软沉 0.515 1 1.83 2.12 软沉 0.537 3 1.68 2.24 硬沉 0.571 5 1.54 2.32 硬沉 0.601 7 1.52 2.36 硬沉 0.608 1 0 2.03 2.03 无沉 0.500 1 2.03 2.03 无沉 0.500 3 2.01 2.06 无沉 0.506 5 1.99 2.07 无沉 0.509 7 1.94 2.11 软沉 0.521 注:静置温度为220 ℃ -
[1] 刘明华,胡小燕,国安平,等. 油基钻井液用抗高温乳化剂的合成及性能[J]. 精细石油化工进展,2017,18(4):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8348.2017.04.003LIU Minghua, HU Xiaoyan, GUO Anping, et al. Synthesis and performance of anti-high temperature emulsifier for oil-based drilling fluid[J]. Fine Petrochemical Progress, 2017, 18(4):9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8348.2017.04.003 [2] 唐军,吴正良,李杰,等. 超低密度仿油基钻井液工艺技术及应用[J]. 钻采工艺,2013,36(1):94-97. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2013.01.29TANG Jun, WU Zhengliang, LI Jie, et al. Technology and application of ultra-low density oil-like drilling fluid[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2013, 36(1):94-97. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2013.01.29 [3] 张清廉,朱思成,孙惠章,等. 低伤害油基压井液的研制[J]. 山东师大学报(自然科学版),1997,12(2):164-166.ZHANG Qinglian, ZHU Sicheng, SUN Huizhang, et al. Development of low-damage oil-based well killing fluid[J]. Journal of Shandong Normal University(Natural Science) , 1997, 12(2):164-166. [4] 杨双春,韩颖,侯晨虹,等. 环保型白油基钻井液研究和应用进展[J]. 油田化学,2017,34(4):739-744.YANG Shuangchun, HAN Ying, HOU Chenhong, et al. Research and application progress of environmentally friendly white oil-based drilling fluids[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2017, 34(4):739-744. [5] 刘均一,邱正松,黄维安,等. 南海东方气田高密度抗高温钻井液完井液室内研究[J]. 石油钻探技术,2013,41(4):78-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.04.017LIU Junyi, QIU Zhengsong, HUANG Weian, et al. Laboratory study of high-density and high-temperature resistant drilling fluid and completion fluid in Dongfang Gas Field, South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(4):78-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.04.017 [6] 王健,彭芳芳,徐同台,等. 钻井液沉降稳定性测试与预测方法研究进展[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2012,29(5):79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.05.022WANG Jian, PENG Fangfang, XU Tongtai, et al. Research progress of testing and prediction methods of drilling fluid settlement stability[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2012, 29(5):79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2012.05.022 [7] 李家学,蒋绍宾, 晏智航,等. 钻完井液静态沉降稳定性评价方法[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2019,36(5):575-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.05.009LI Jiaxue,JIANG Shaobin,YAN Zhihang,et al. Evaluation method of static settlement stability of drilling and completion fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2019, 36(5):575-580. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2019.05.009 [8] ZHUANG Guanzheng, ZHANG Zepeng, JABER M, et al. Comparative study on the structures and properties of organo-montmorillonite and organo-palygorskite in oil-based drilling fluids[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 56: 248-257. [9] SUN Jinsheng, HUANG Xianbin, JIANG Guancheng, et al. Development of key additives for organoclay-free oil-based drilling mud and system performance evaluation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4):764-769. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(18)30079-X [10] SUN Wujuan, TIAN Guoqing, HUANG Hangjuan, et al. Synthesis and characterisation of a multifunctional oil-based drilling fluid additive[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(24):793. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7982-5 [11] ZHUANG Guanzheng, ZHANG Zepeng, GAO Jiahua, et al. Influences of surfactants on the structures and properties of organo-palygorskite in oil-based drilling fluids[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 244: 37-46. [12] HERMOSO J, MARTINEZ-BOZA F, GALLEGOS C. Influence of viscosity modifier nature and concentration on the viscous flow behaviour of oil-based drilling fluids at high pressure[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2014, 87: 14-21. [13] HILFIGER M G, THAEMLITZ C J, MOELLENDICK E, et al. Investigating the chemical nature of flat rheology [M]. SPE Deepwater Drilling and Completions Conference. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 2016. [14] HUANG Xianbin, JIANG Guancheng, HE Yinbo, et al. Improvement of rheological properties of invert drilling fluids by enhancing interactions of water droplets using hydrogen bonding linker[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 506: 467-475. [15] HE Yinbo, JIANG Guancheng, DENG Zhengqiang, et al. Polyhydroxy gemini surfactant as a mechano-responsive rheology modifier for inverted emulsion drilling fluid[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(1):342-353. doi: 10.1039/C7RA11300E [16] 王星媛, 陆灯云, 袁志平. 川西地区油基钻井液井壁强化技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2021, 49(1): 34-40.WANG Xingyuan, LU Dengyun, YUAN Zhiping. Borehole strengthening technology with oil-based drilling fluid in the western Sichuan basin[J].Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(1): 34-40. [17] 王志远,黄维安,范宇,等. 长宁区块强封堵油基钻井液技术研究及应用[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2021, 49(5): 31-38.WANG Zhiyuan, HUANG Weian, FAN Yu, et al.Technical research and application of oil base drilling fluid with strong plugging property in Changning block[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(5): 31-38. -




 下载:
下载: