Effects of Drilling Fluid Soaking on Surface Morphology of Rocks at Different Temperatures
-
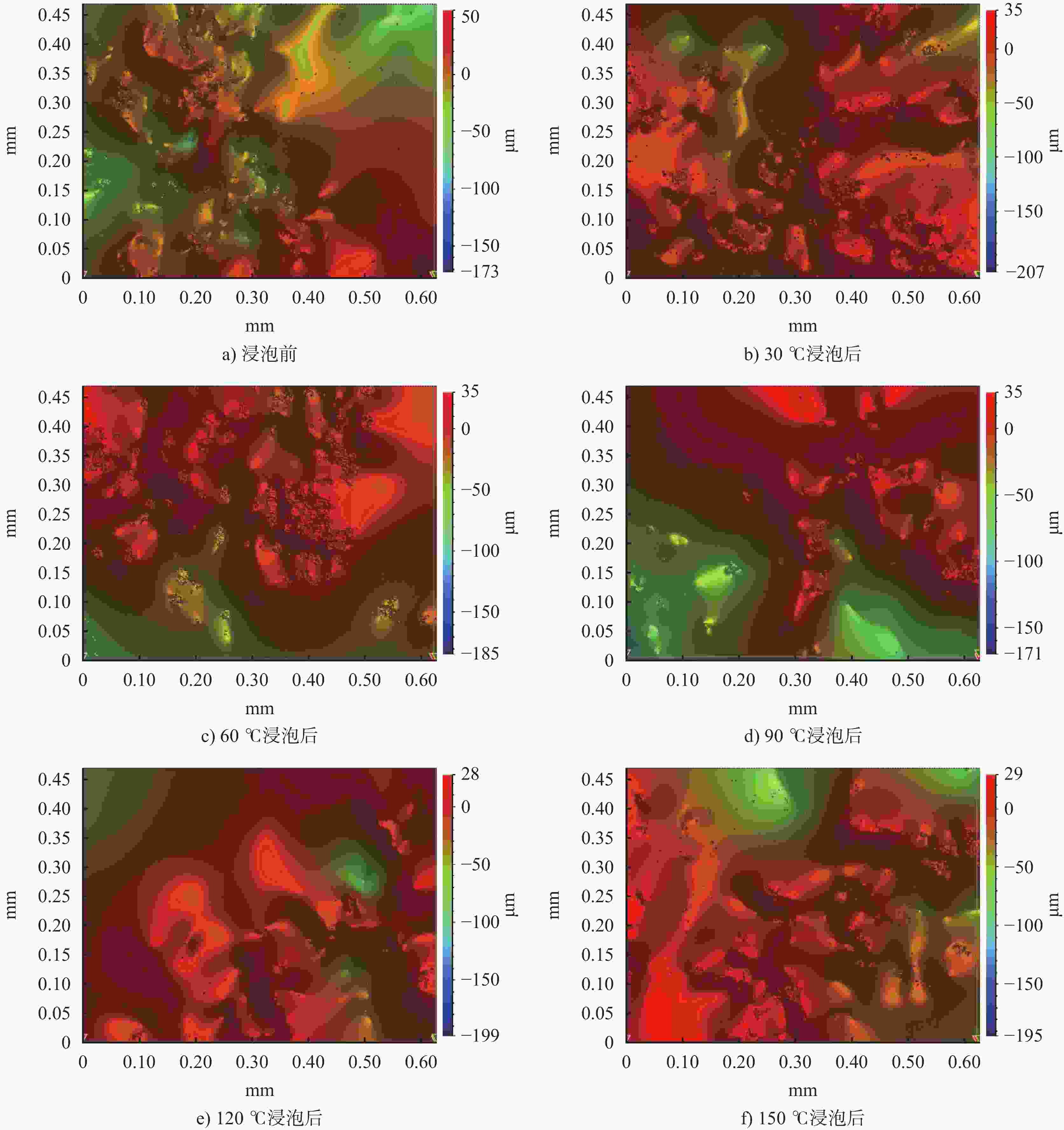
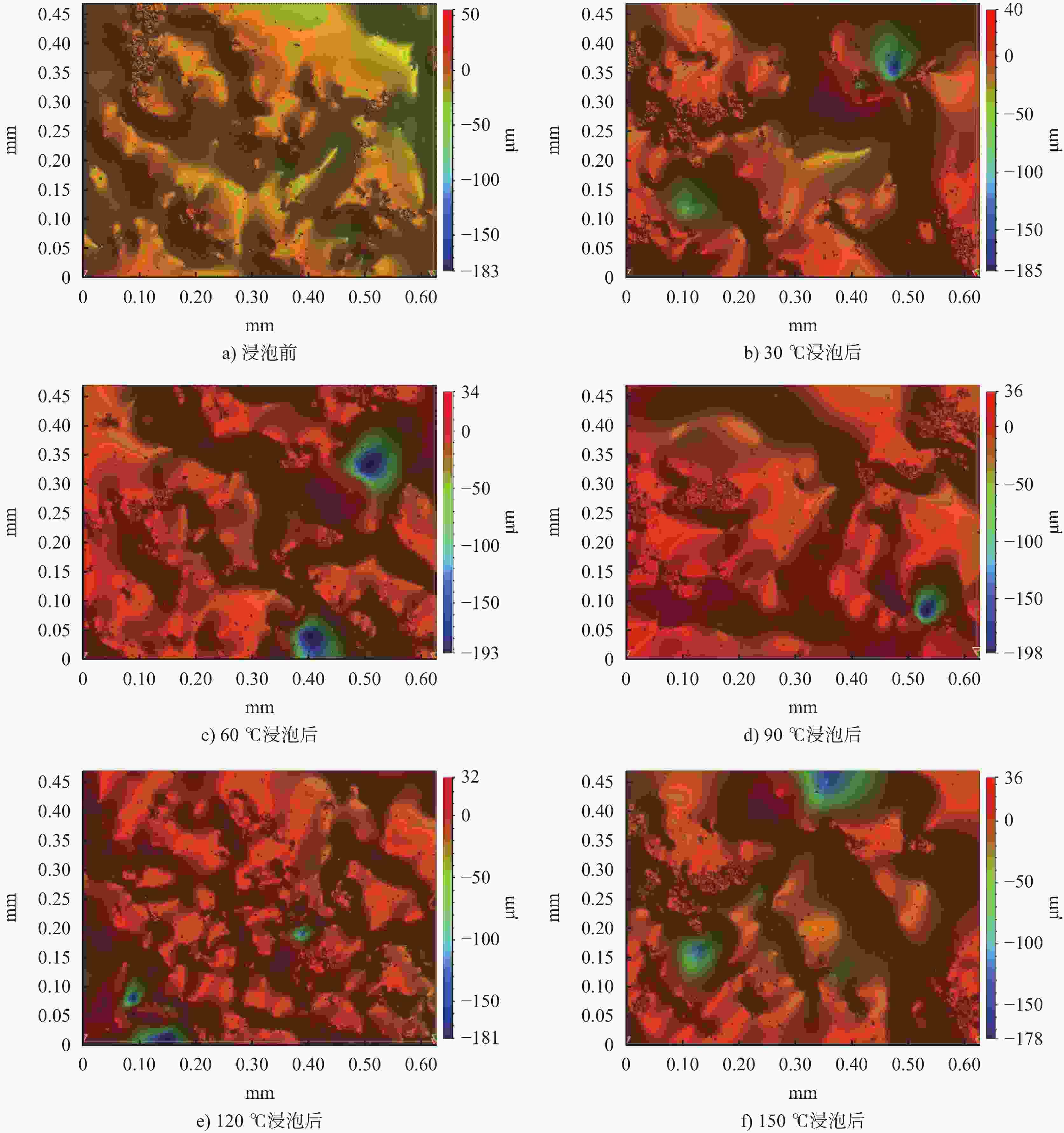
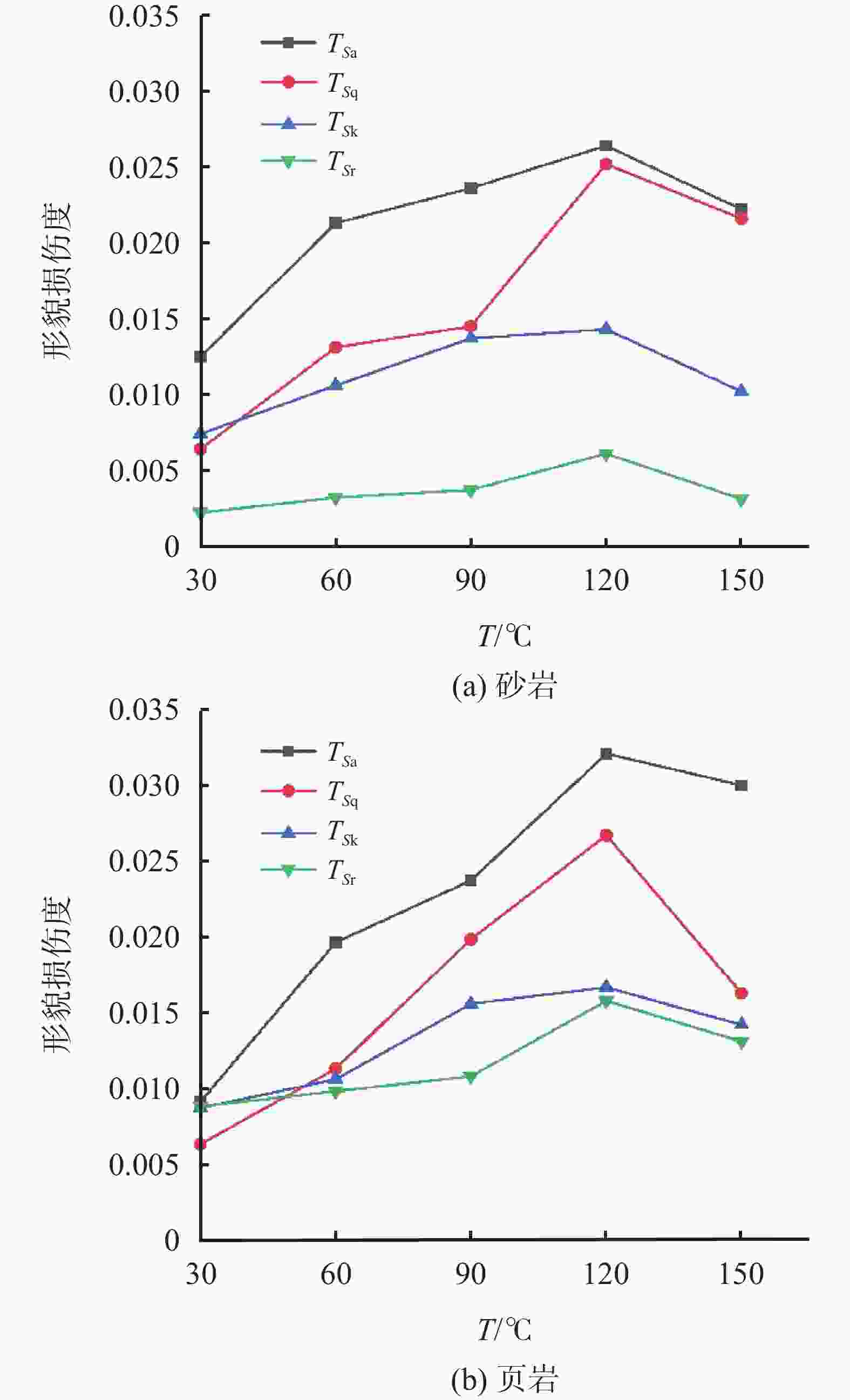
摘要: 为揭示钻井液浸泡岩石产生表面形貌损伤引起井壁失稳,选取砂岩、页岩岩样,利用三维光学显微镜,对不同温度钻井液浸泡作用前后的岩石表面形貌进行测试,定量分析其特征参数,探讨温度对岩石表面形貌的影响机制及损伤度。结果表明:随温度的升高,特征参数Sa、Sq、Sk整体上呈增大趋势,特征参数Sr整体上呈减小趋势,导致其形貌轮廓的粗糙度、离散性、波动性增加,轮廓起伏度降低,对称性优于浸泡前;在30~120 ℃时,形貌损伤度逐渐增加,在120~150 ℃时,形貌损伤度降低,形貌损伤度极值点TS在120~150 ℃之间。砂岩和页岩的高度特征参数的损伤度大于纹理特征参数的损伤度。Abstract: Soaking of rocks in drilling fluids often causes the surface morphology of the rocks to be damaged, which is probably related to the collapse of borehole walls. To reveal the relationship between the two phenomena, sandstone and shale samples were selected to test using 3D optical microscope for their surface morphology prior to and after soaking in drilling fluids at different temperatures. The characteristic parameters of the rocks were quantitatively analyzed and the effects on and damage to the surface morphology of the rocks by temperature investigated. It was found that as temperature increases, the characteristic parameters Sa, Sq and Sk also increase, while the characteristic parameter Sr decreases, resulting in increases in the roughness, discreteness and volatility of the morphologic contour of the rocks, reduction in the relief of the rocks and better symmetry of the rocks after soaking than before. In the temperature range of 30-120 ℃, the degree of morphology damage is gradually increasing with temperature, in the temperature range of 120-150 ℃, the degree of morphology damage is gradually decreasing with temperature. The Ts, which is the extreme value of the degree of morphology damage, lies between 120 ℃ and 150 ℃. Compared with sandstones, shale has a bigger relative degree of damage. Compared with the degree of damage of the rocks measured with texture characteristic parameters, degree of damage of the rocks measured with height characteristic parameters is bigger.
-
表 1 岩样关键参数
岩样 孔隙率/
%ρ/
kg·m−3软化系数 抗压强度/
MPa抗拉强度/
MPa砂岩 1.6~28.0 26.0~27.5 0.6~0.97 20~170 4~25 页岩 0.4~10 25.7~27.7 0.55~0.7 10~100 2~10 表 2 不同温度钻井液浸泡前后岩样的表面形貌特征参数
岩样 T/
℃实验
条件Sa/
μmSq/
μmSk Sr/
%岩样 T/
℃实验
条件Sa/
μmSq/
μmSk Sr/
%砂岩 30 浸泡前 9.3 14.0 −2.43 13.4 页岩 30 浸泡前 2.43 5.34 −17.4 12.1 浸泡后 12.8 16.7 −1.87 12.5 浸泡后 3.10 6.38 −12.8 8.9 60 浸泡前 9.2 13.4 −2.25 14.0 60 浸泡前 2.48 5.55 −18.2 13.2 浸泡后 15.1 18.7 −1.53 12.6 浸泡后 3.97 7.44 −12.4 9.3 90 浸泡前 9.0 13.7 −2.32 13.3 90 浸泡前 2.39 5.57 −19.5 12.3 浸泡后 15.4 19.7 −1.35 11.8 浸泡后 4.12 8.92 −10.3 8.3 120 浸泡前 10.7 13.2 −2.51 13.7 120 浸泡前 2.39 5.92 −19.7 13.7 浸泡后 19.2 23.2 −1.43 11.2 浸泡后 4.70 10.71 −9.8 7.2 150 浸泡前 10.9 13.7 −2.34 13.5 150 浸泡前 2.19 5.80 −19.8 12.6 浸泡后 18.2 22.6 −1.62 12.2 浸泡后 4.17 8.66 −11.3 7.67 -
[1] NTAWANGA ATHANAS CHRISTOPHER. 水基钻井液和油基钻井液对地层损害的评价[D]. 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.NTAWANGA ATHANAS CHRISTOPHER. Evaluation of formation damage caused by water based and oil based drilling fluids[D]. China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017 [2] 康毅力,陈强,游利军,等. 钻井液作用下页岩破裂失稳行为试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2016(4):81-89.KANG Yili, CHEN Qiang, YOU Lijun, et al. Laboratory studies of shale fracturing behaviors with rock-drilling fluid interactions[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) , 2016(4):81-89. [3] 薛玉志,李公让,蓝强,等. 超低渗透钻井液稳定井壁的作用机理研究[J]. 石油学报,2009(3):434-439. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.022XUE Yuzhi, LI Gongrang, LAN Qiang, et al. Interaction mechanisms of ultra-low permeable drilling fluid for stability of borehole wall[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009(3):434-439. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.03.022 [4] 张毅,陈东,张慧,等. 钻井液滤失对煤岩井壁稳定性的影响[J]. 煤矿安全,2021(4):78-84.ZHANG Yi, CHEN Dong, ZHANG Hui, et al. Study on the influence of drilling fluid filtration on stability of coalbed wellbore[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021(4):78-84. [5] BARTON N B S. Review of predictive capabilities of JRC-JCS model in engineering practice[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences and Geomechanics Abstracts, 1991(4):A209. [6] 夏才初, 孙宗颀. 工程岩体节理力学[M]. 上海: 同济大学出版社, 2002: 161.XIA Caichu, SUN Zongqi. Joint mechanics of engineering rock mass[M]. Shanghai: Tongji University Press, 2002: 161. [7] BELEM T, SOULEY M, HOMAND F. Method for quantification of wear of sheared joint walls based on surface morphology.[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2009(6):883-910. [8] GRASSELLI G G G I, WIRTH J, EGGER P. Quantitative three-dimensional description of a rough surface and parameter evolution with shearing[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002(6):789-800. [9] 曹平,范祥,蒲成志,等. 节理剪切试验及其表面形貌特征变化分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011(3):480-485.CAO Ping, FAN Xiang, PU Chengzhi, et al. Shear test of joint and analysis of morphology characteristics evolution of joint surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011(3):480-485. [10] CHEN Y C Y, CAO P C P, CHEN R C R, et al. Effect of water-rock interaction on the morphology of a rock surface[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2010(5):816-822. [11] 韩文梅,康天合,李建军. 表面形貌对岩石摩擦滑动本构参数影响研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013(8):1632-1639.HAN Wenmei, KANG Tianhe, LI Jianjun. Influence of surface topography on constitutive parameters of rock frictional sliding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013(8):1632-1639. [12] 韩文梅,杨文博,李建军,等. 煤系地层砂岩抛光面粗糙度和粒度分析[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2019(3):286-290.HAN Wenmei, YANG Wenbo, LI Jianjun, et al. Analysis of roughness and granularity of sandstone polished surface in coal measure strata[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2019(3):286-290. [13] 杨文博. 酸性环境下岩石表面形貌及强度变化研究[D]. 中北大学, 2020.YANG Wenbo. Study on changes of rock surface morphology and strength under acidic environment[D]. North University of China, 2020. [14] 黄曼,洪陈杰,杜时贵,等. 岩石结构面形貌分级方法及两级粗糙特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020(6):1153-1164.HUANG Man, HONG Chenjie, DU Shigui, et al. Study on morphological classification method and two-order roughness of rock joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020(6):1153-1164. [15] 卢运虎,陈勉,金衍,等. 钻井液浸泡下深部泥岩强度特征试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012(7):1399-1405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.07.012LU Yunhu, CHEN Mian, JIN Yan, et al. Experimental study of strength properties of deep mudstone under drilling fluid soaking[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012(7):1399-1405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.07.012 [16] 向朝纲,陈俊斌,杨刚. 钻井液浸泡作用下脆性页岩强度特征实验[J]. 断块油气田,2018(6):803-806.XIANG Chaogang, CHEN Junbin, YANG Gang. Experiment of brittle shale strength characteristics under drilling fluids soaking[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2018(6):803-806. [17] 方朝合,黄志龙,葛稚新,等. 工作液浸泡对页岩裂缝扩展及力学性质影响[J]. 太原理工大学学报,2015(4):414-418.FANG Chaohe, HUANG Zhilong, GE Zhixin, et al. The influence of working fluid on fracture propagation and mechanical properties of shale[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2015(4):414-418. [18] 邓金根, 程远方, 陈勉, 等. 井壁稳定预测技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 158.DENG Jingen, CHENG Yuanfang, CHEN Mian, et al. Wellbore stability prediction technology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 158. [19] 汤连生, 王思敬. 岩石化学损伤的机理及量化方法探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002(3): 314-319.TANG Liansheng, WANG Sijing, Analysis on mechanism and quantitative method of chemical damage in water rock interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002(3): 314-319. [20] 荣传新, 王晓健. 岩石力学[M]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学出版社, 2020: 158.RONG Chuanxin, WANG Xiaojian. Rock mechanics[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2020: 158. -




 下载:
下载: