Study on High Temperature Stability of Invert Emulsion
-
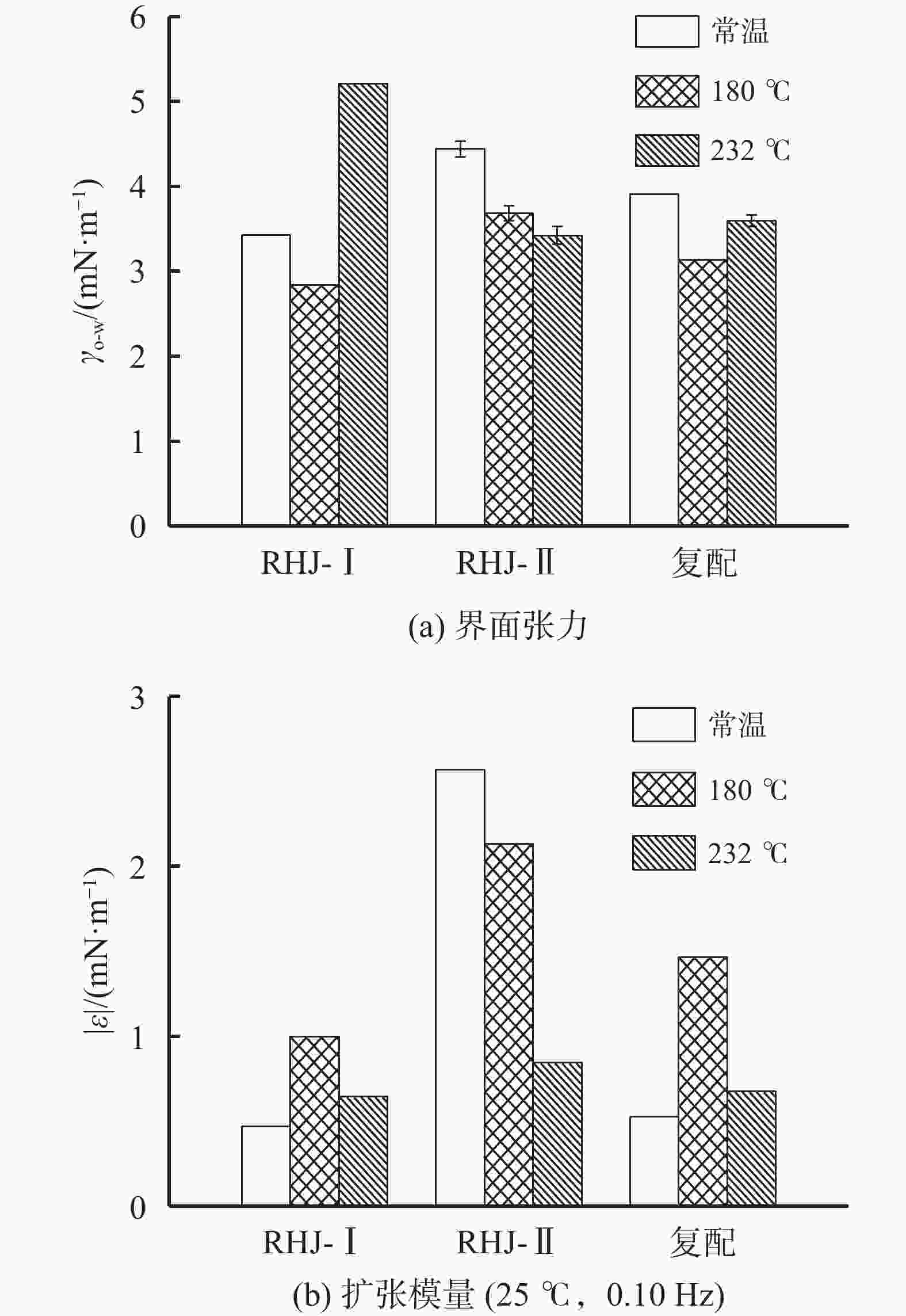
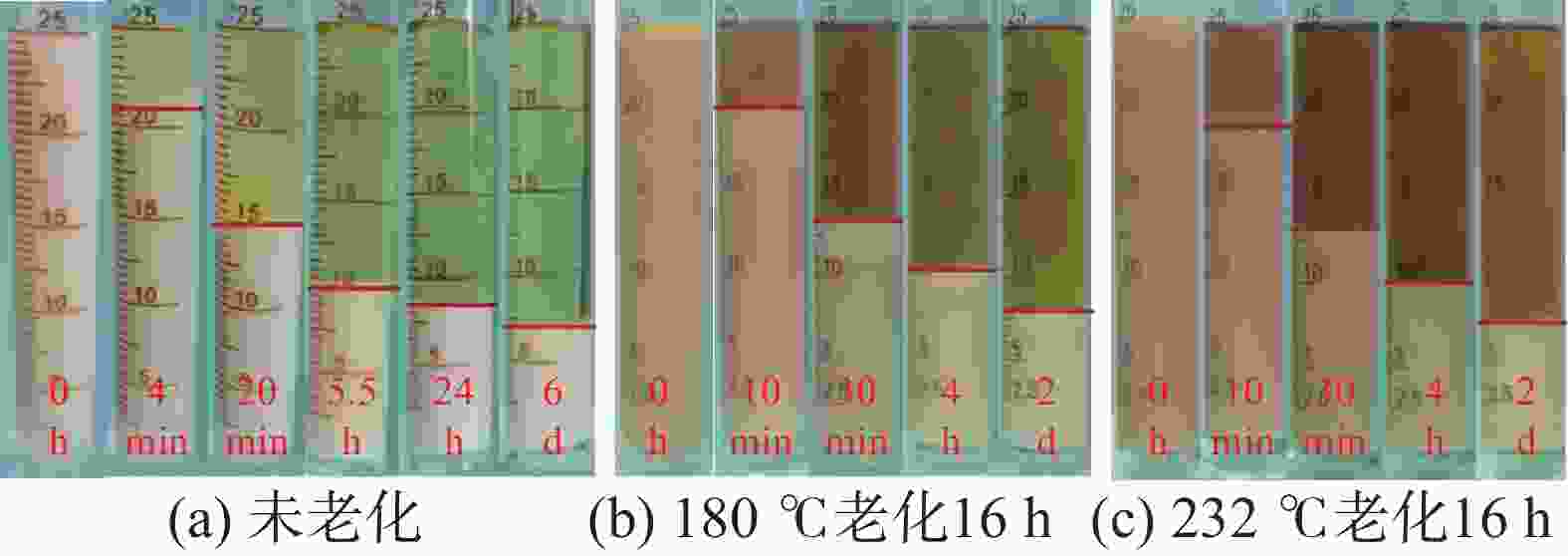
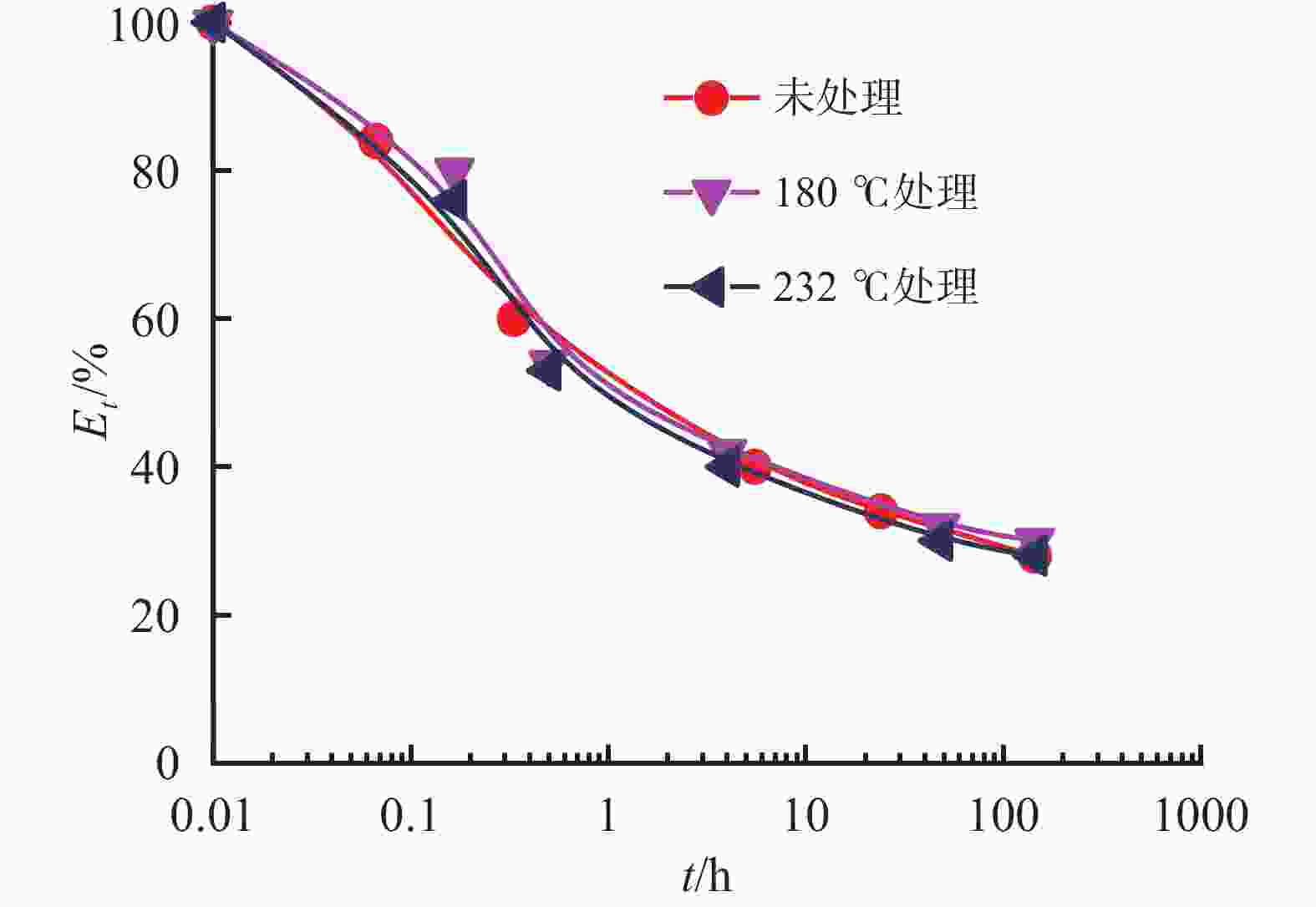
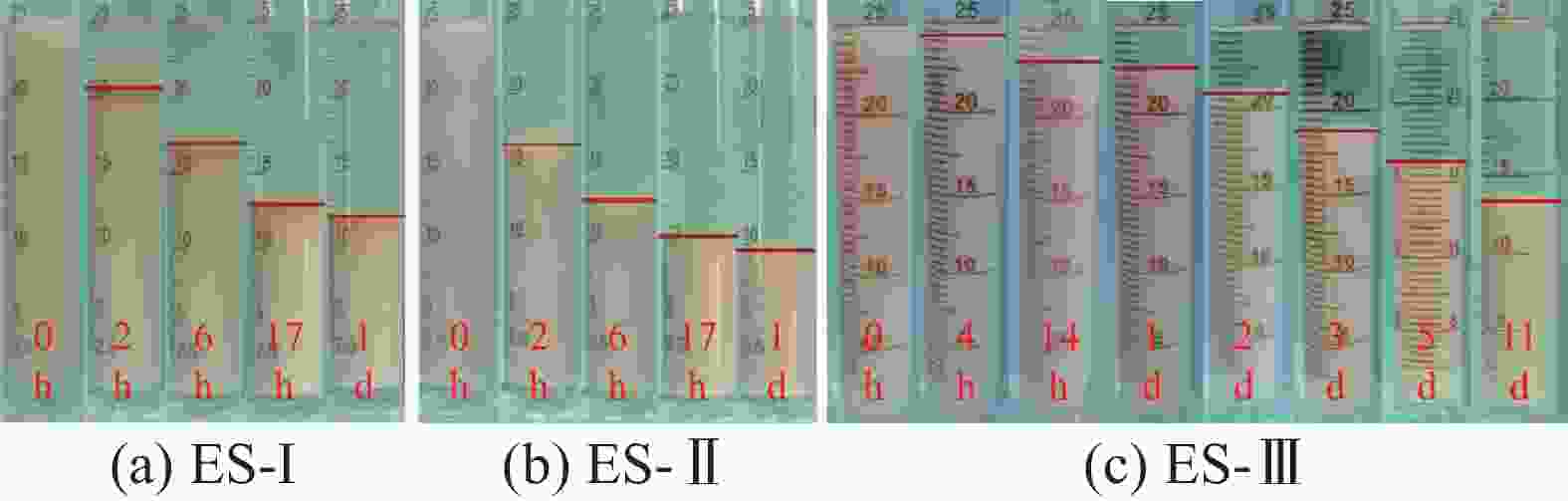
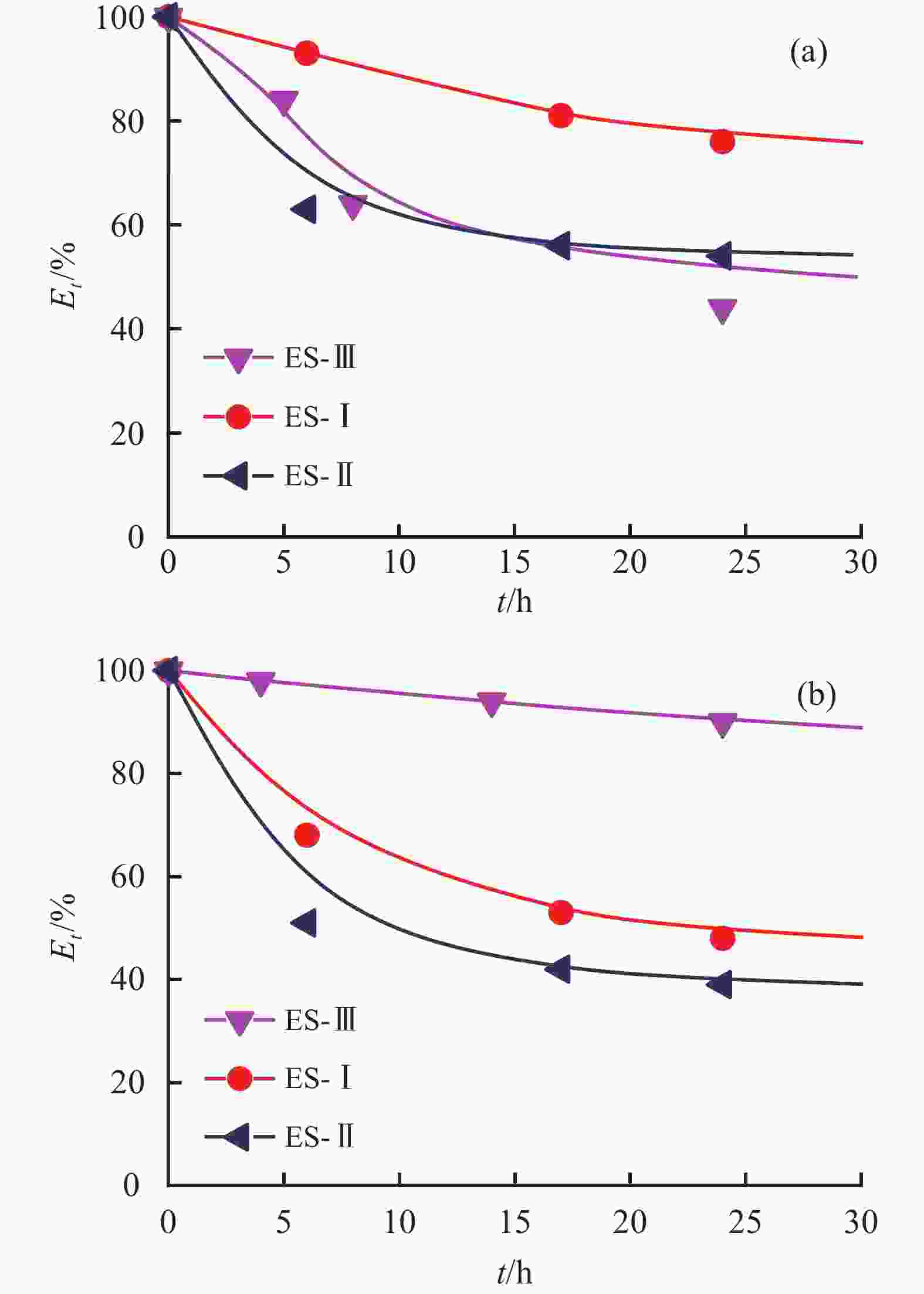
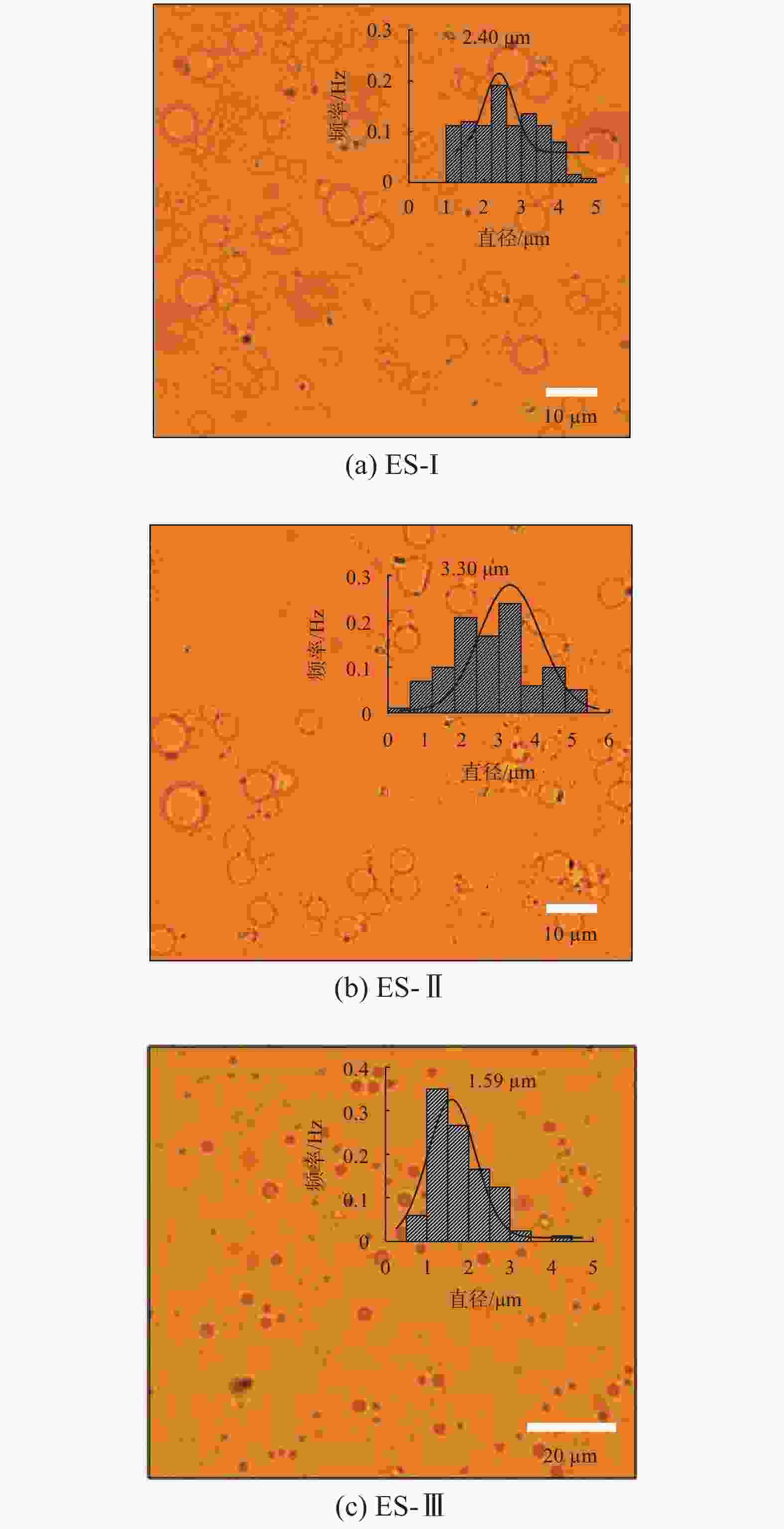
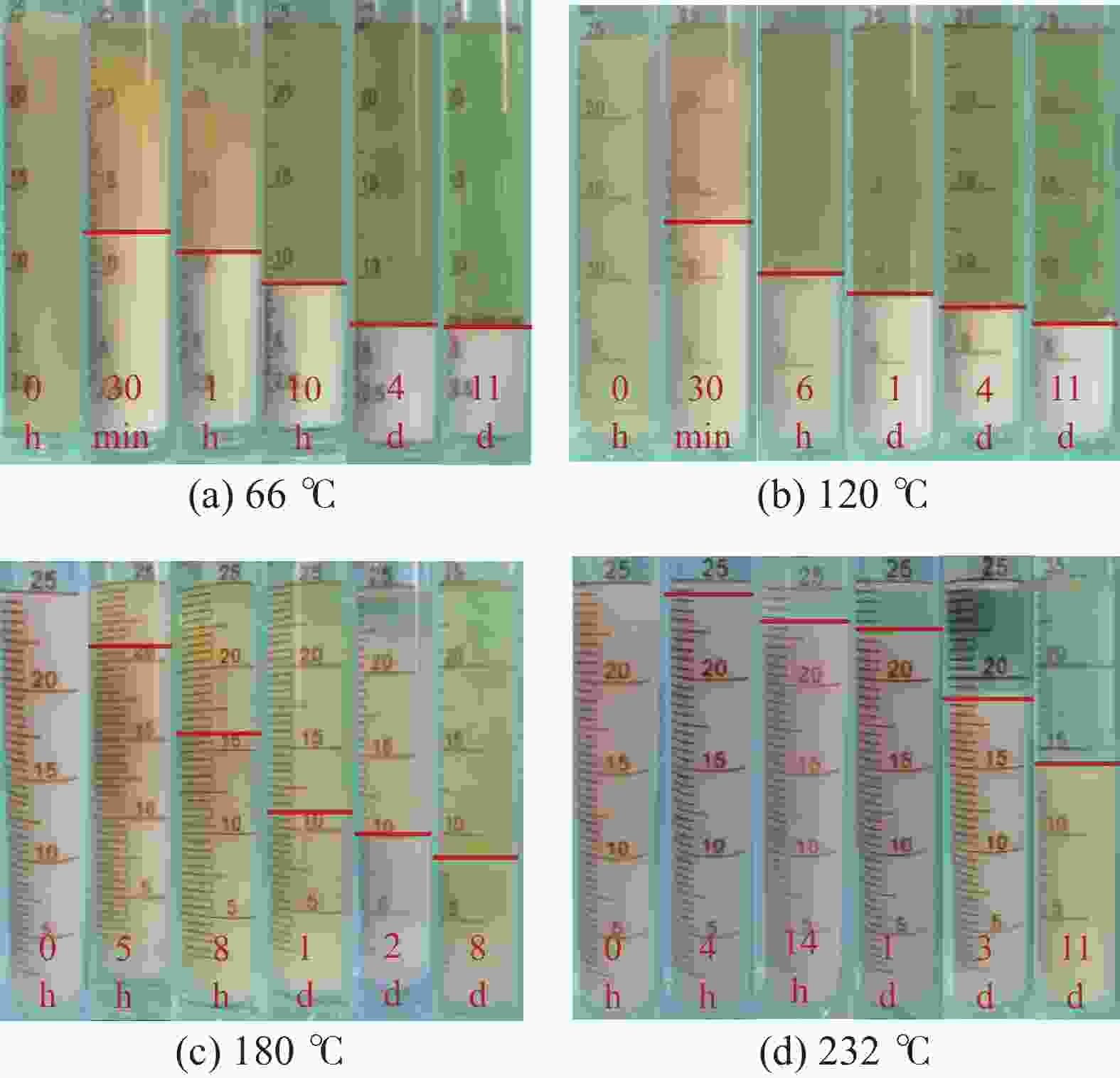
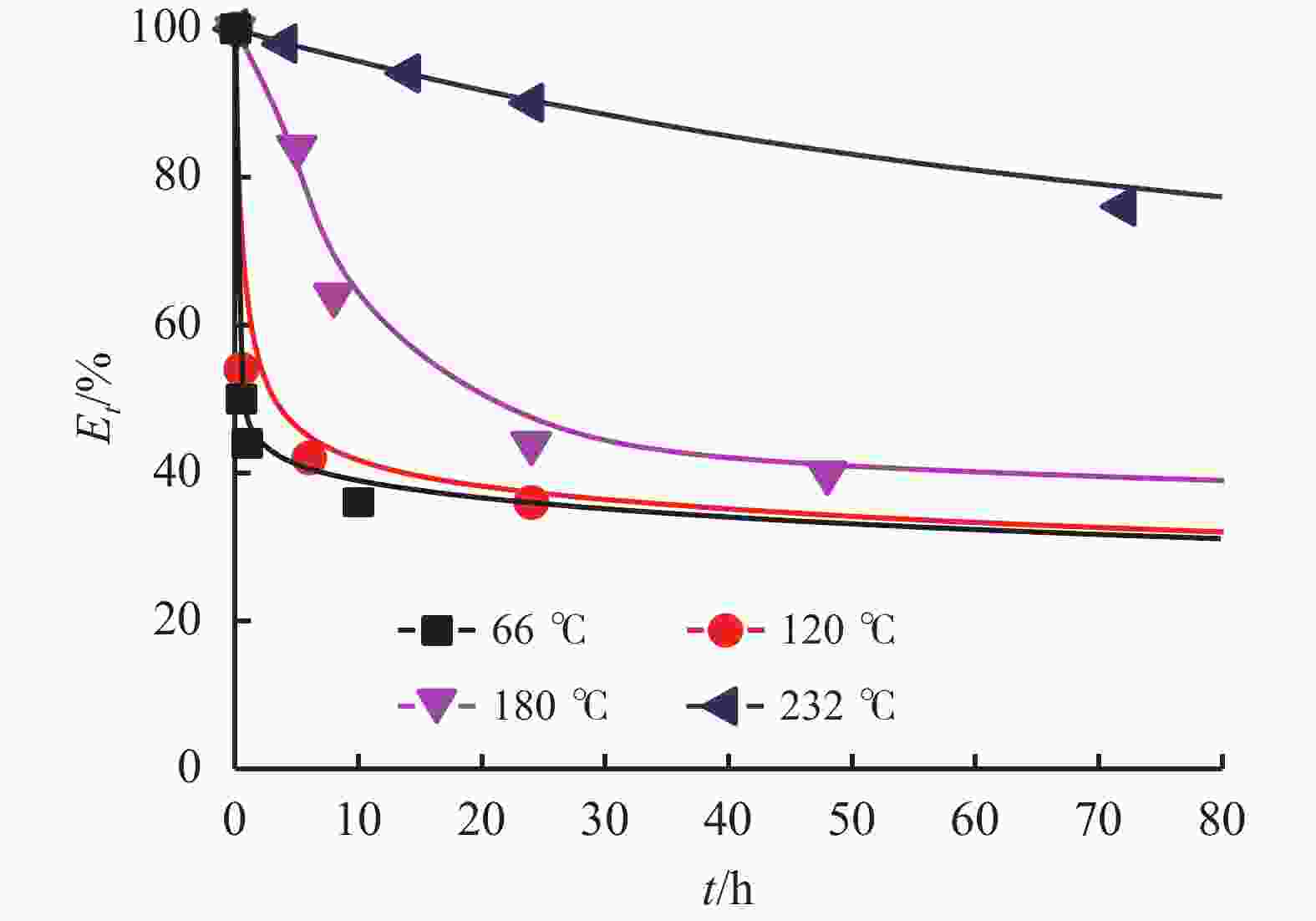
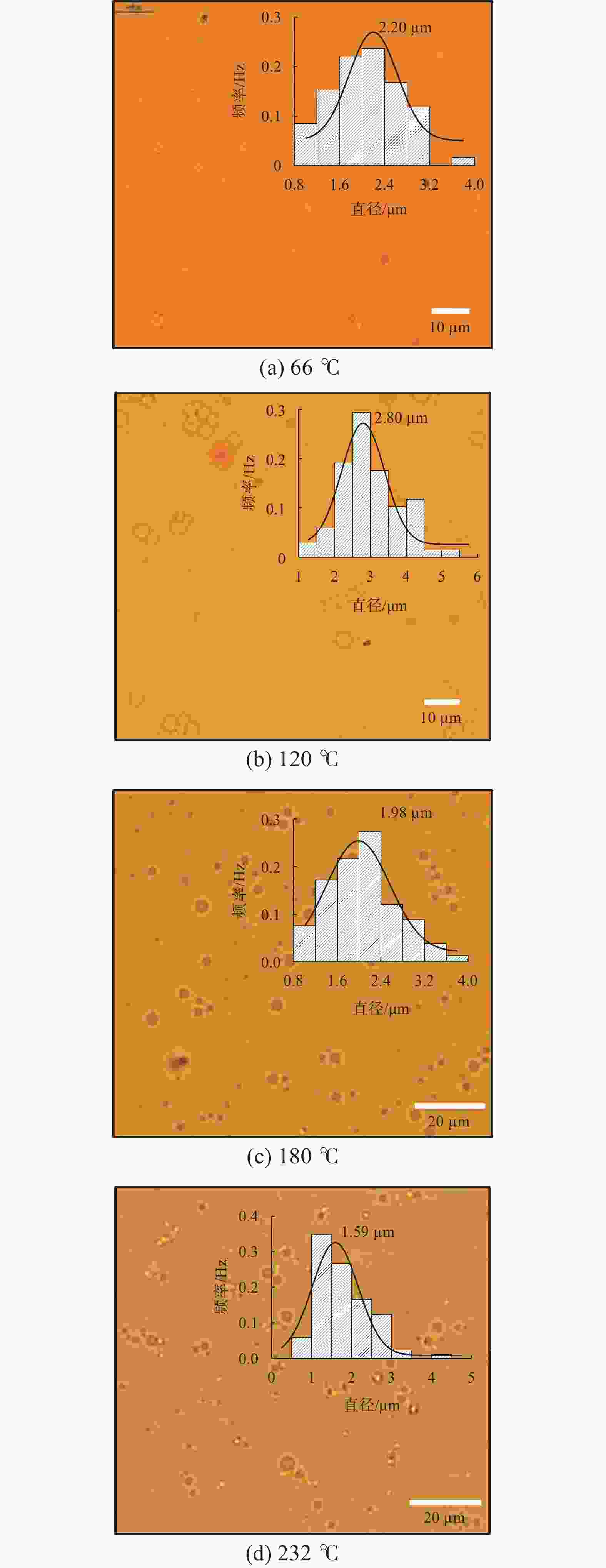
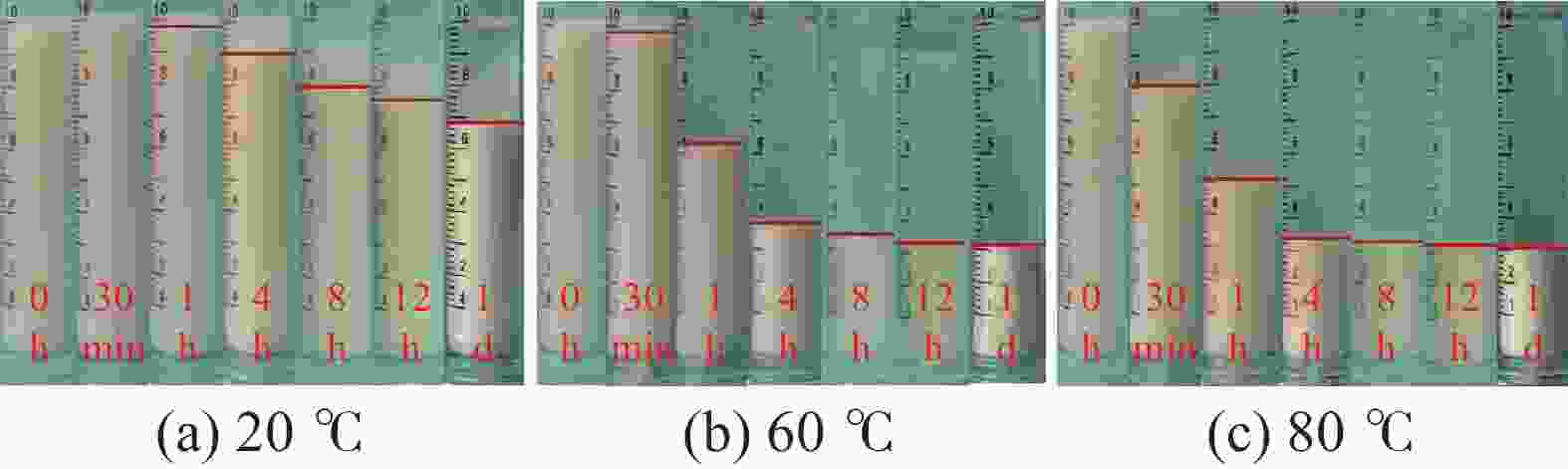
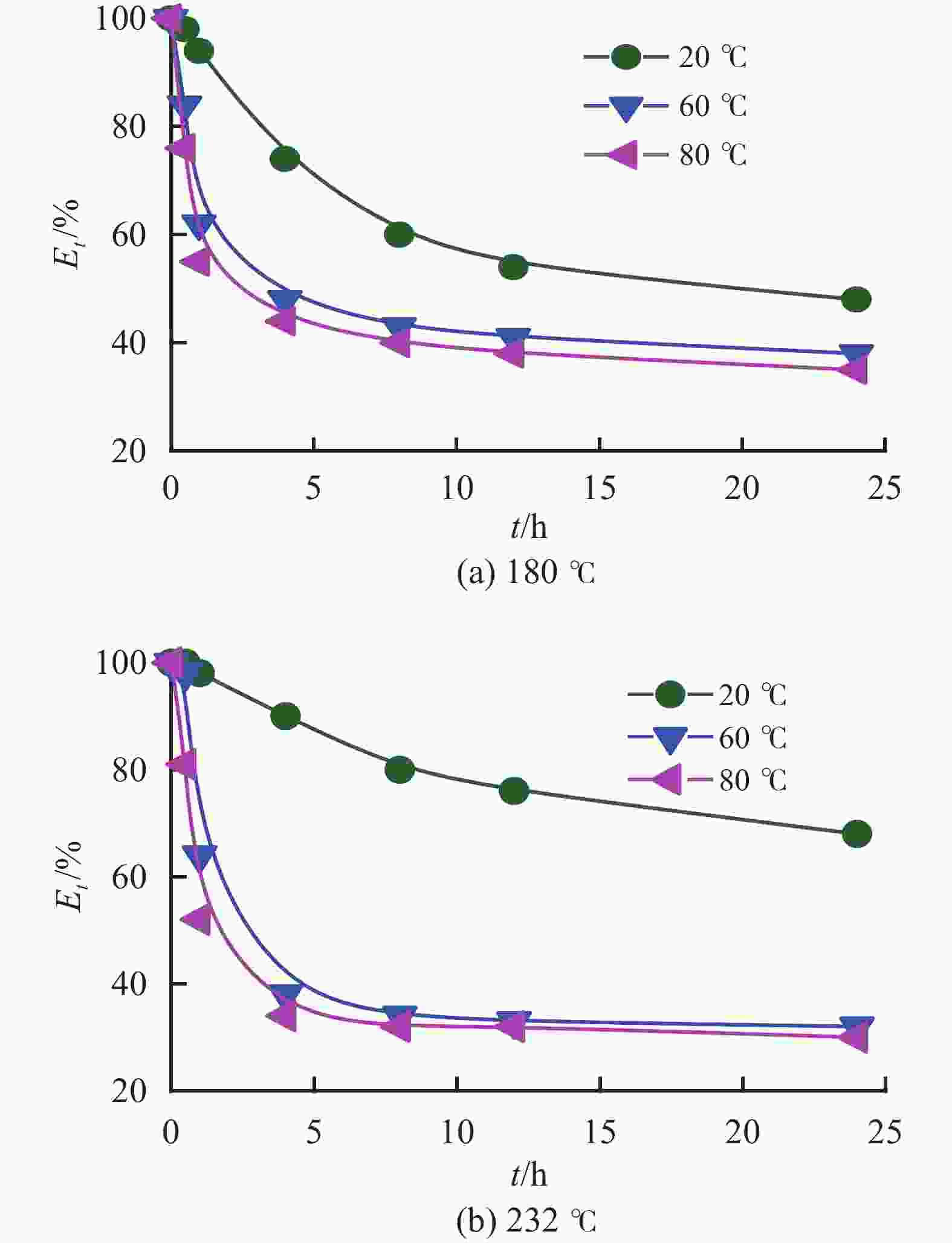
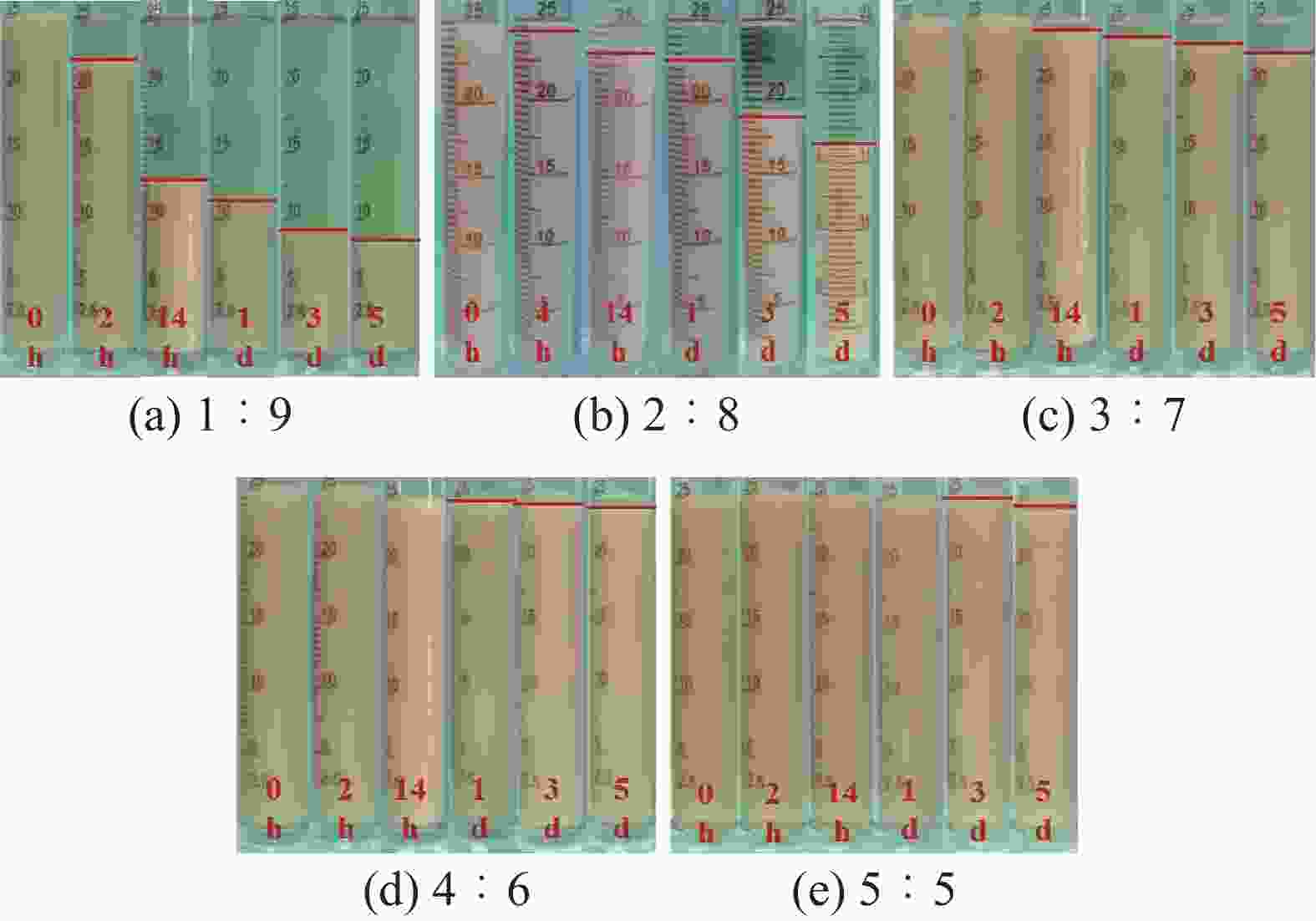
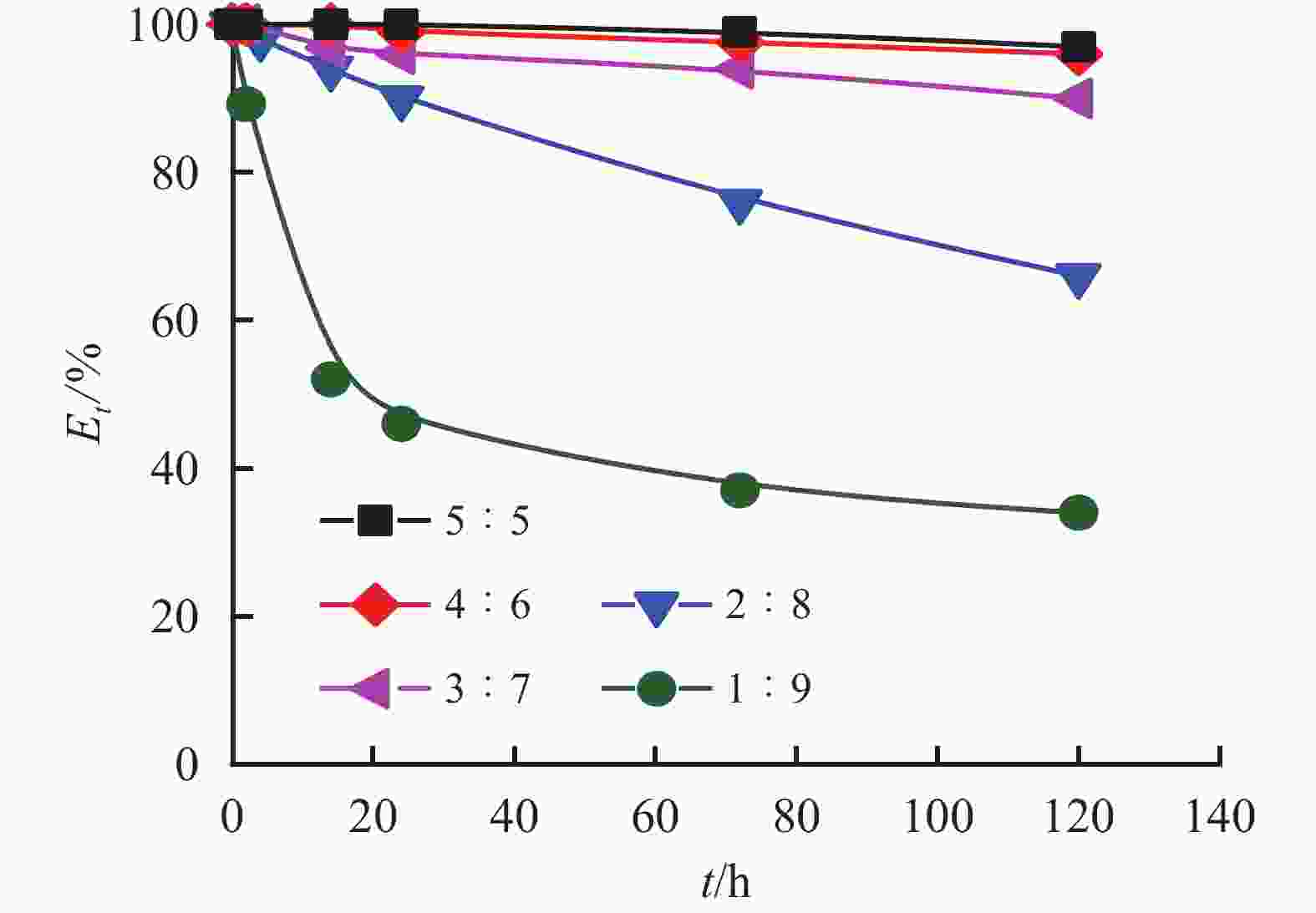
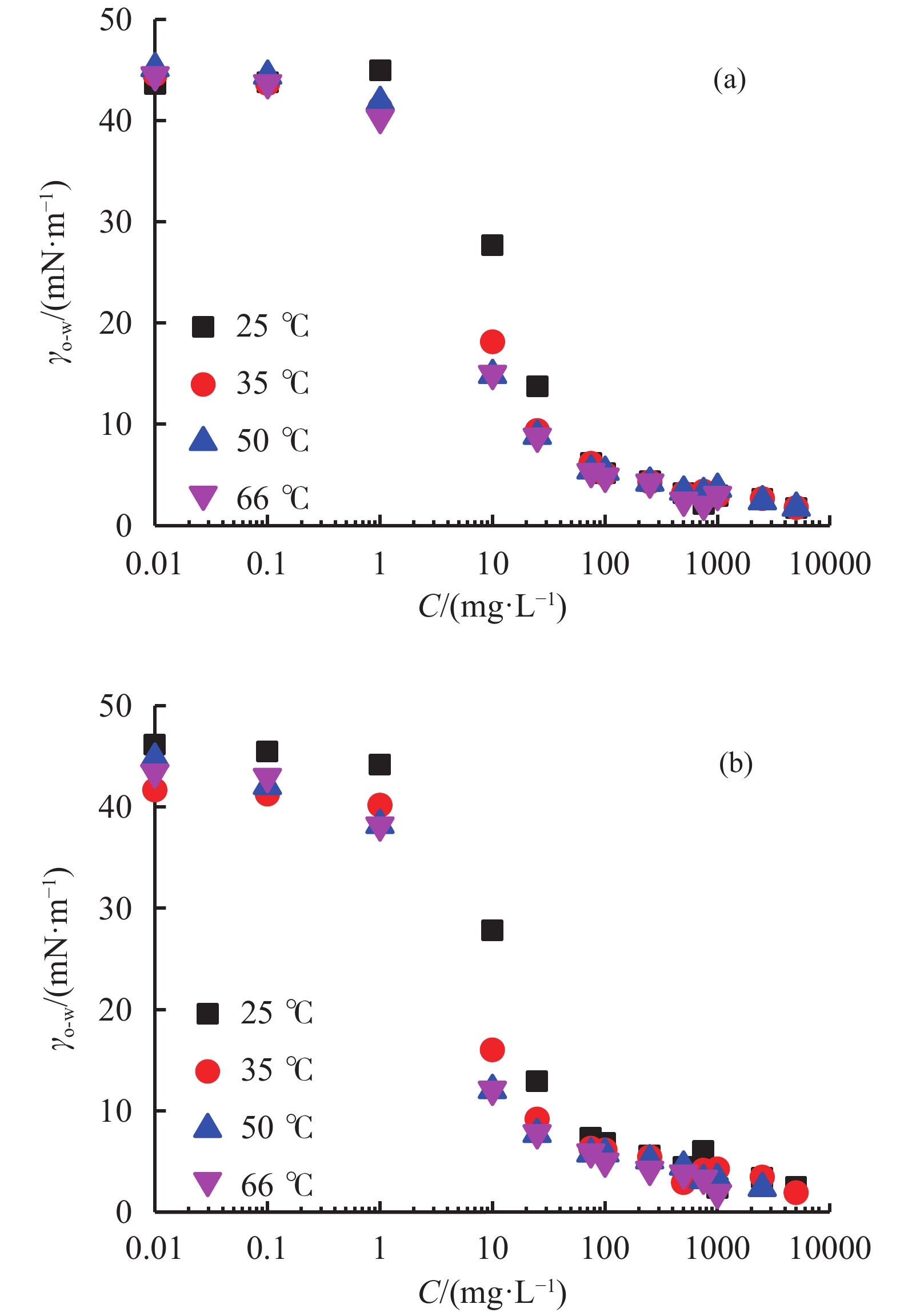
摘要: 研究了2种乳化剂RHJ-Ⅰ和RHJ-Ⅱ的油/水界面活性及温度的影响。以国产合成油为基础油,25% CaCl2水溶液为水相,并添加Ca(OH)2制备了油包水(W/O)型乳状液,考察了体系组成、老化处理温度和静置温度等对其稳定性的影响,探讨了稳定机理。结果表明,所研究的乳化剂可显著降低合成油/水界面张力,在油/水界面形成黏弹性界面膜。所制备的W/O型乳状液具良好的分散稳定性,RHJ-Ⅰ和RHJ-Ⅱ复配具协同增稳效应。乳状液经高温(180和232 ℃)老化处理后,其稳定性明显增强,缘于乳化剂与Ca(OH)2作用形成“有机Ca(OH)2”,从而增强乳状液的高温稳定性。水/油比在1∶9~5∶5范围内增大,稳定性明显增强。Abstract: The effects of the oil/water interface activity and temperature on two emulsifiers RHJ-I and RHJ-II were studied. An invert emulsion (W/O) was formulated with a synthetic oil (made in China) as the base oil, 25% CaCl2 solution as the water phase and a certain amount of Ca(OH)2. The composition of the emulsion and the effects of aging temperature and the temperature at which the emulsion stand still were investigated, and the stability mechanisms of the emulsion were studied. The results of the investigation and study show that RHJ-I and RHJ-II are able to reduce the interfacial tension between the synthetic oil and water, forming a viscoelastic interfacial film at the interface between the oil and water. The invert emulsion has good dispersion stability, and a synergistic action which improvs the stability can be found between RHJ-I and RHJ-II. After being aged at 180 °C and 232 °C, the stability of the emulsion was found enhanced, probably because of the production of an “organic Ca(OH)2” by the reaction between the emulsifiers and Ca(OH)2 which helps improve the high temperature stability of the emulsion. The stability of the emulsion is significantly enhanced when the oil/water ratio is between 1∶9 and 5∶5.
-
Key words:
- Emulsion /
- Oil based drilling fluid /
- High temperature stability /
- Emulsifier /
- Synthetic oil
-
表 1 乳化剂在不同pH值下的水溶解度(25.0 ℃ ± 0.5 ℃)
乳化剂 不同pH值下的水溶解度/(mg/L) pH=6.0 pH=8.0 pH=10.0 pH=12.0 RHJ-Ⅰ 11.4 23.8 29.6 71.8 RHJ-Ⅱ 8.1 28.6 52.5 57.4 -
[1] 徐同台,彭芳芳,潘小镛,等. 气制油的性质与气制油钻井液[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2010,27(5):75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2010.05.023XU Tongtai, PENG Fangfang, PAN Xiaoyong, et al. Performance of GTL and GTL based drilling fluid[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2010, 27(5):75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5620.2010.05.023 [2] ZHUANG G, ZHANG Z, YANG H, et al. Structures and rheological properties of organo-sepiolite in oil-based drilling fluids[J]. Appl Clay Sci, 2018, 154:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.048 [3] ZHUANG G, ZHANG Z, PENG S, et al. Enhancing the rheological properties and thermal stability of oil-based drilling fluids by synergetic use of organo-montmorillonite and organosepiolite[J]. Appl Clay Sci, 2018, 161:505-512. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.05.018 [4] 史赫,蒋官澄,王国帅,等. 恒流变合成基钻井液关键机理研究[J]. 钻井液与完井液,2020,37(1):31-37.SHI He, JIANG Guancheng, WANG Guoshuai, et al. Study on key mechanisms of constant rheology synthetic based drilling fluids[J]. Drilling Fluid & Completion Fluid, 2020, 37(1):31-37. [5] 康万利,张红艳,李道山,等. 破乳剂对油水界面膜作用机理研究[J]. 物理化学学报,2004,20(2):194-198. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20040218KANG Wanli, ZHANG Hongyan, LI Daoshan, et al. The action mechanism of demulsifiers at model O/W interfacial film[J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin, 2004, 20(2):194-198. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20040218 [6] MCCLEMENTS D J, JAFARI S M. Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers: A review[J]. Adv Colloid Interface Sci, 2018, 251:55-79. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.12.001 [7] 曹亚峰,杨锦宗,刘兆丽,等. 脂肪酸盐用于反相乳液中淀粉接枝反应乳化剂的研究[J]. 精细化工,2003,20(6):326-328, 336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5214.2003.06.003CAO Yafeng, YANG Jinzong, LIU Zhaoli, et al. Study of salts of fatty acid as emulsifiers for starch-grafting copolymerization in inverse emulsion[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2003, 20(6):326-328, 336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5214.2003.06.003 [8] SONG N, WANG A, LI J, et al. Study on influencing factors of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with nonionic surfactants[J]. Soft Matter, 2018, 14:3889-3901. doi: 10.1039/C8SM00241J -




 下载:
下载: